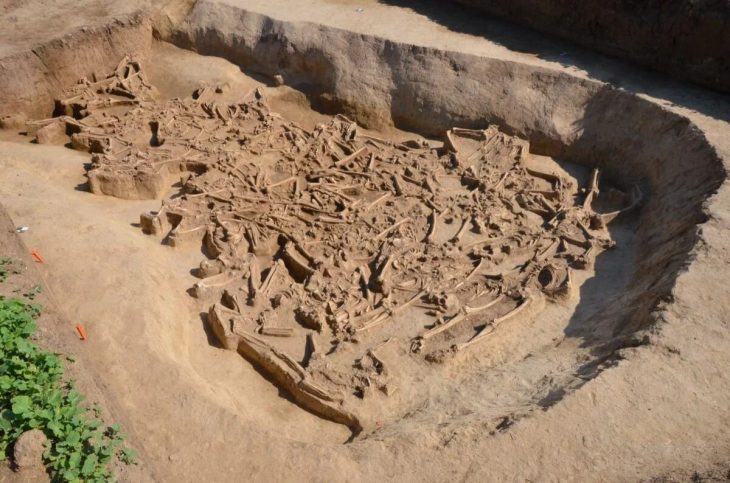
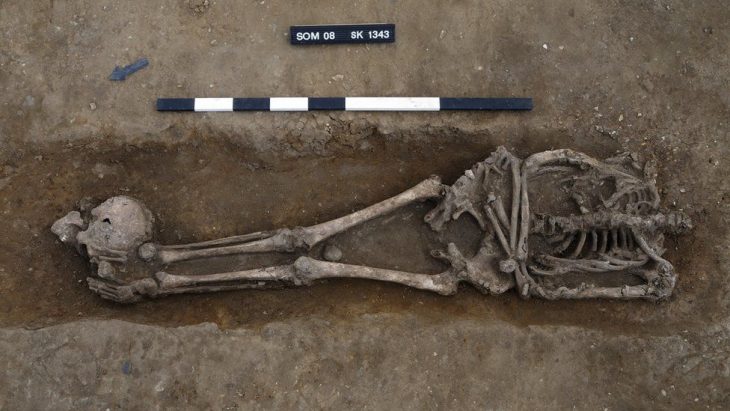
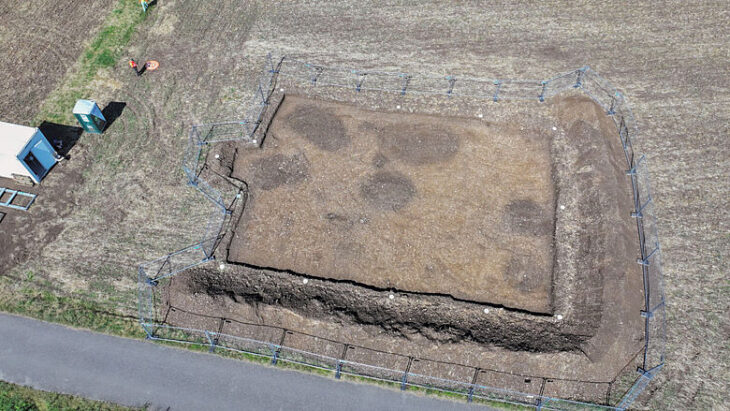
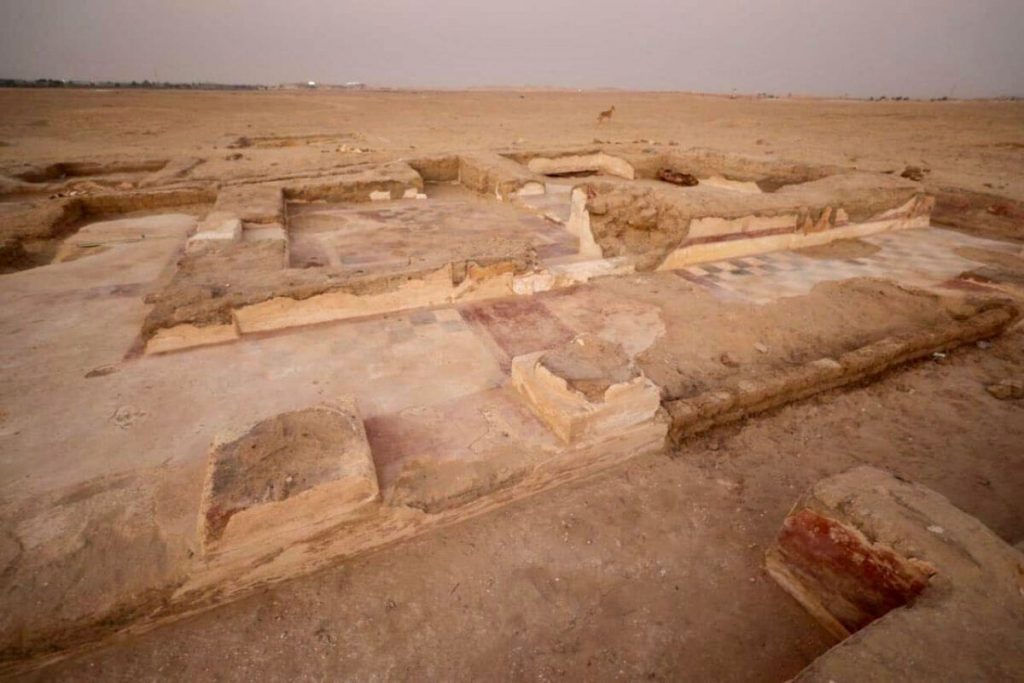
The Egyptian archaeological mission working in the Gerza archaeological site in Fayoum revealed a huge funerary building from the Ptolemaic and Roman periods, as well as a number of Fayoum portraits.
These are the first mummy portraits discovered at Fayoum during an archaeological dig since Flinders Petrie discovered 146 of them in a Roman-era cemetery in 1910–1911.
Dr. Mostafa Waziri, Secretary General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities, explained that what was discovered at the site illustrates the diversity and difference in the accuracy and quality of the embalming process during the Ptolemaic and Roman eras, which indicates the economic stature of the deceased, starting from high-quality embalming to simple burials.
Also, a rare terracotta statue of the goddess Isis-Aphrodite was also found in one of the burials inside a wooden coffin.

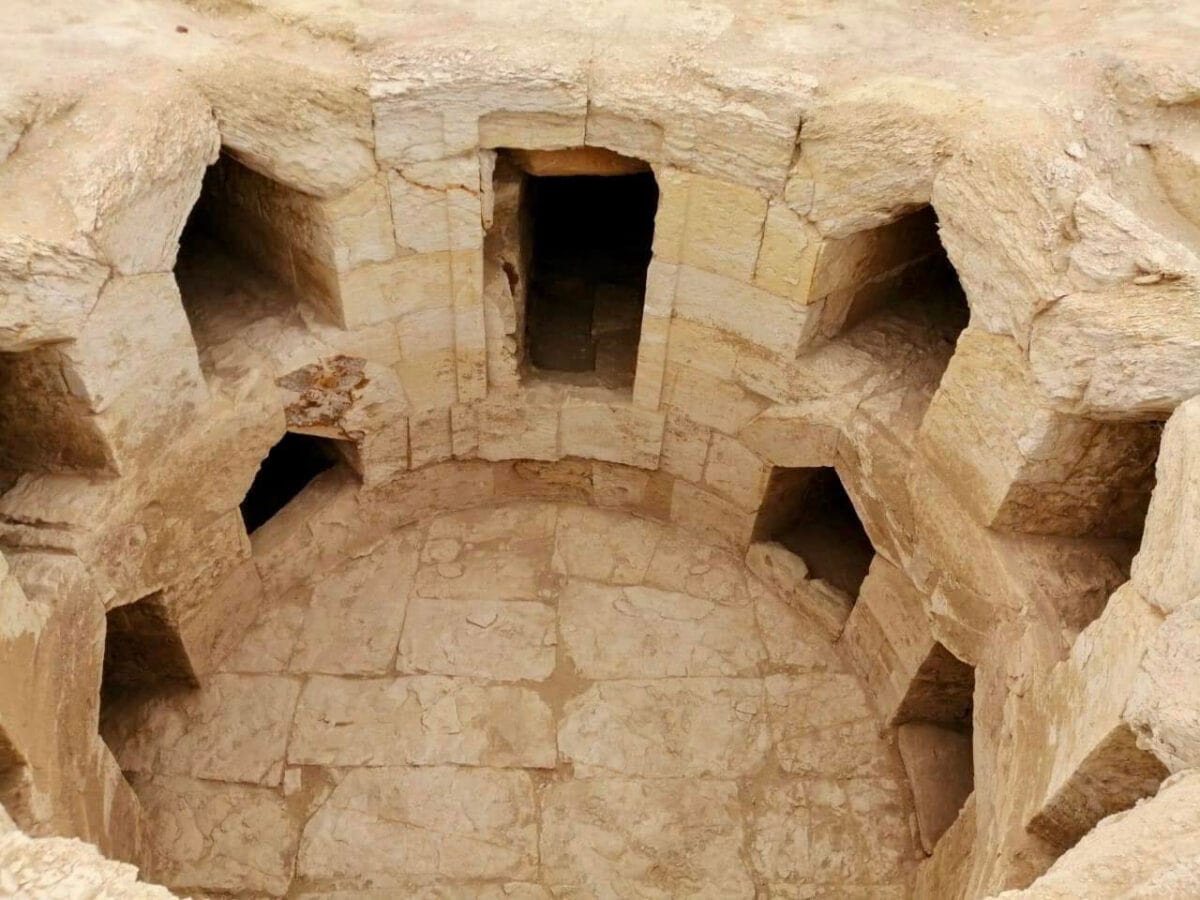
Regarding the architectural remains, Dr. Adel Okasha, head of the Central Department of Egyptian Antiquities in Central Egypt, indicated that what has been found is a huge building of funerary house type, with a floor made of colored lime mortar and decorated with interchangeable tiles. On its southern side, there is a colonnade of which four columns survive. Through the building, there is also access to a narrow street.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
He added that among the many and diverse artifacts found and recorded, the portraits of mummies, or what is known as Fayoum portraits, are of great importance.
Mummy portraits, also known as Fayum portraits, are the most amazing body of painting to have come to us from the ancient world; they are remarkable for their social significance as well as their artistic quality.

” Fayoum Portraits ” is the name that has been given to describe them because more have been found in the Fayoum Oasis than anywhere else in Egypt.
For his part, Dr. Basem Jihad, the supervisor of the central training unit and head of the mission, said that the mission also succeeded in uncovering a number of coffins of different styles, some of them in the human form and others in the Greek form with a gabled roof.
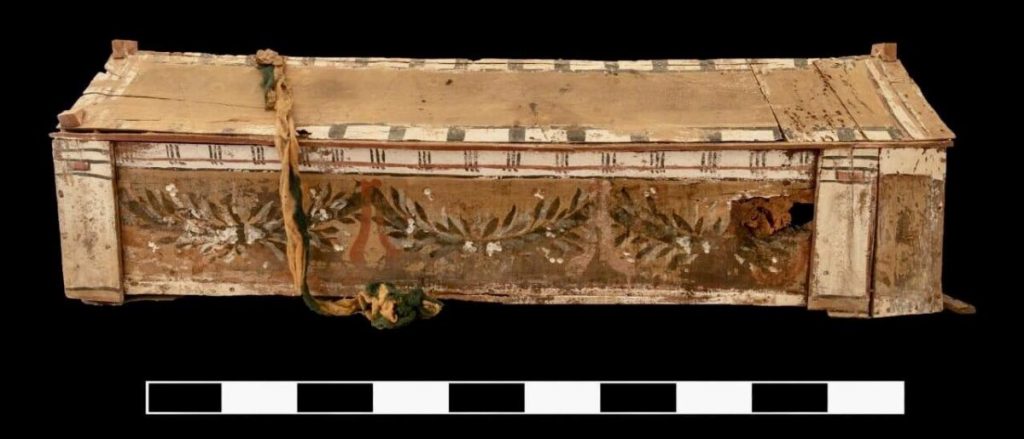

Under the rule of Ptolemy II Philadelphus, the village of Gerza was established as Philadelphia (309–246 BC). Since 2016, there have been ongoing excavations, and many artifacts have been found that date from the city’s founding to Roman rule in the third century A.D.