A dinosaur trove in Italy rewrites the history, geography, and evolution of the ancient Mediterranean area.
Italy is not exactly renowned for dinosaurs. In comparison to its excellent artistic and archaeological heritage, dinosaur fossils are very rare. Not surprisingly, the discovery of the first isolated remains from these animals, in the early 1990s, generated quite an excitement but was shortly after considered nothing more than an exception to a general rule. During the reign of dinosaurs, between 230 and 66 million years ago, the ancient Mediterranean area would have been hard to map, formed by countless small islands far from all major mainlands – Europe, Africa, and Asia – unsuitable to sustain large animals like the dinosaurs. Or so we believed.
Now, a new study published on Scientific Reports and coordinated by researchers from the University of Bologna unveils the first palaeontological site with multiple, exceptionally complete dinosaur skeletons from Italy: the Villaggio del Pescatore site, located in the Duino-Aurisina municipality, near Trieste, in north-eastern Italy.
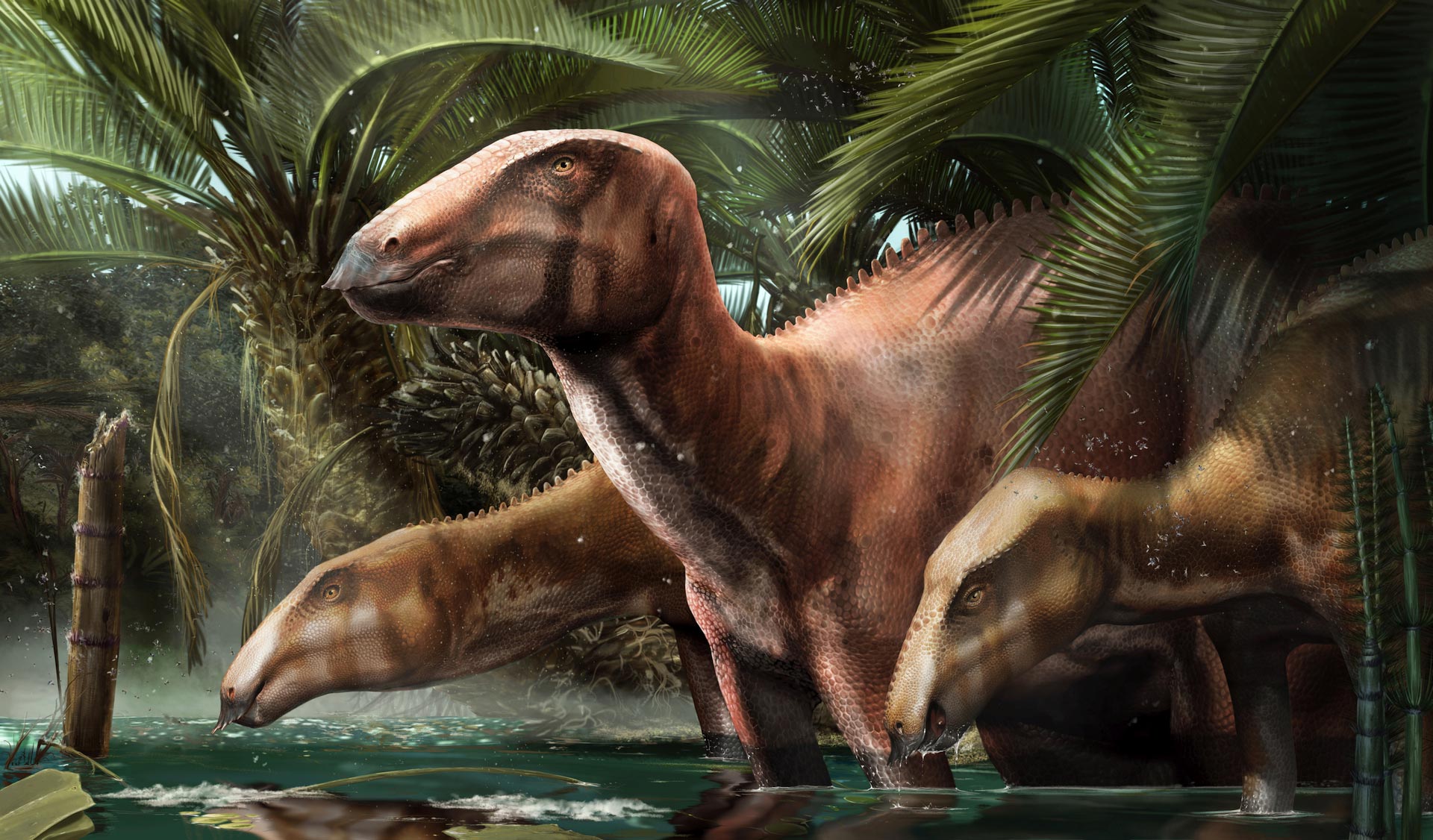
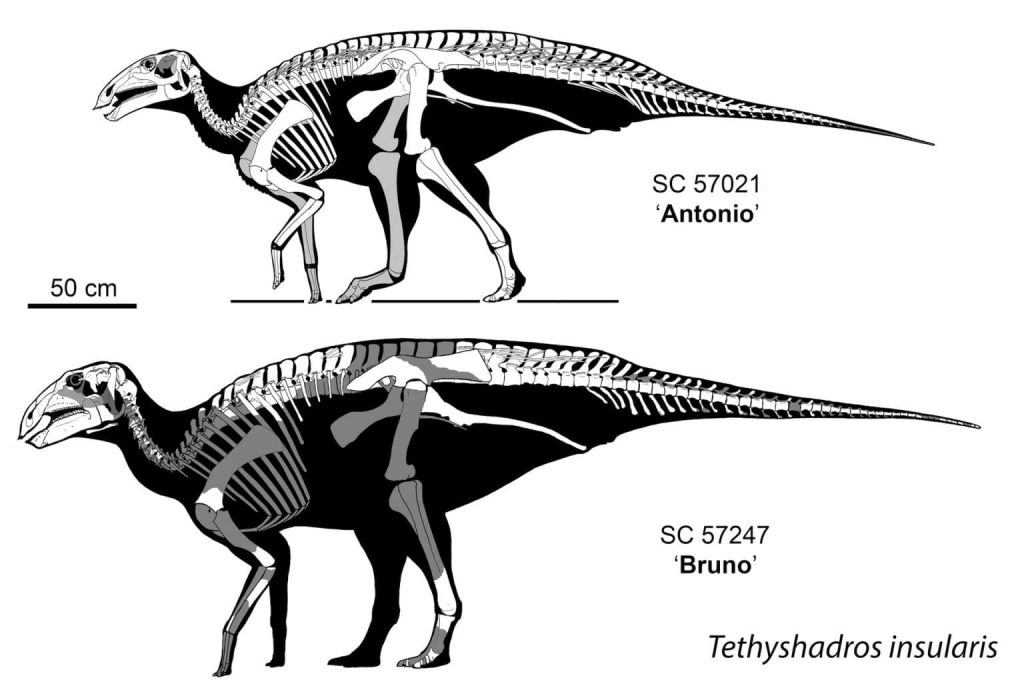
These beautiful skeletons belong to the species Tethyshadros insularis and represent the biggest and most complete dinosaur ever found in this Country. The team describes the skeletons of some of the most beautiful and pristine dinosaurs from the site (in particular of a new individual nicknamed “Bruno”) and highlights the occurrence of seven (probably eleven) individuals at the Villaggio del Pescatore.
Dinosaurs are not the only fossil remains from the site: fish, crocodiles, flying reptiles and even small crustaceans provide a vivid picture of an ancient ecosystem that has no equal worldwide. The unique fossils collected from the Villaggio del Pescatore can be admired in Trieste at the Museo Civico di Storia Naturale, granted on deposit by the Italian Ministry of Culture.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The study also reviews and rewrites many evolutionary hypotheses to interpret the ancient Mediterranean context. Originally, geologists interpreted the area that today is the Villaggio del Pescatore site as part of an island in the middle of a “proto-Mediterranean” ocean called Tethys. This supported the incorrect interpretation that the relatively small, first dinosaur skeleton found at the site (nicknamed “Antonio”), was actually a “dwarf” species, an example of the so-called “island rule” (the evolutionary miniaturization of bigger animals in an insular environment due to the scarcity of resources).
In this new study, the research team documents that “Antonio” is an immature individual, whereas “Bruno,” which is bigger in size, represents an older individual – and that could have been still growing at the time of its death.
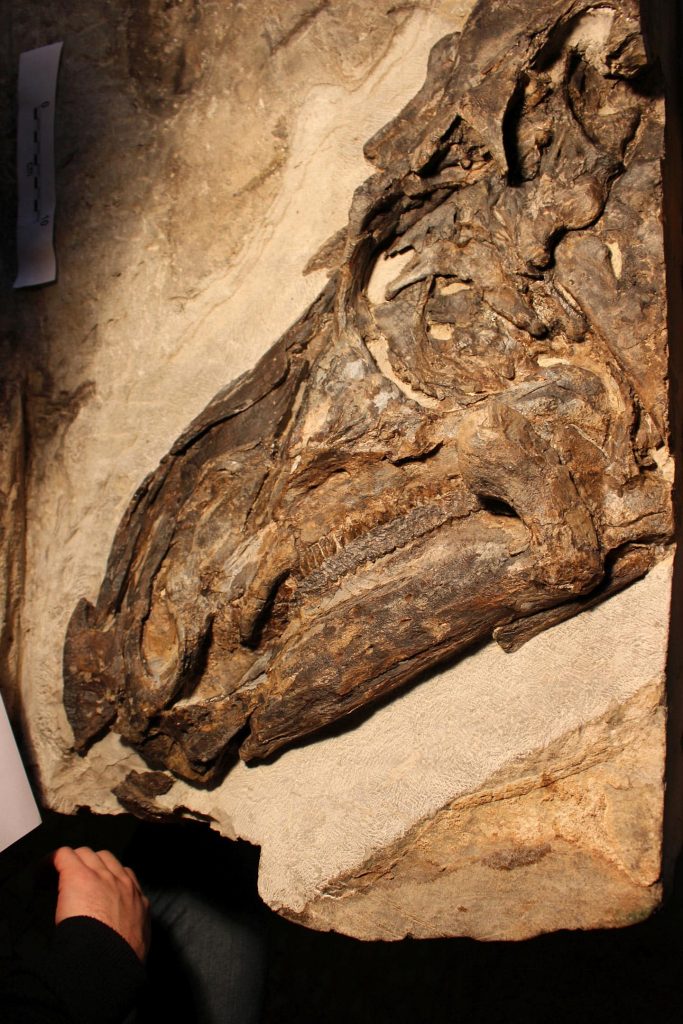

New geological data gathered by the team also provided the age of the site and its fossils: approximately 80 million years ago, in the Cretaceous period. This is about 10 million years older than previously thought: quite a long time even when dealing with dinosaurs. At that time, what is now north-eastern Italy was a land facing a vast ocean but connected to western Europe and Asia. This means that not only small islands characterized the ancient Mediterranean, but many migratory routes for large terrestrial animals like the dinosaurs might have been possible across land bridges of what we nowadays call Italy.
This new research highlights not just a first in terms of exceptional findings, but most importantly the pivotal role of the Italian dinosaur fossil record for evaluating important scientific hypotheses on these ancient animals. As the site is already protected from the Italian institutions, new research and didactic activities may represent an opportunity to include the geological and paleontological heritage in the “must-see” list while visiting the “Belpaese.”
Reference: “An Italian dinosaur Lagerstätte reveals the tempo and mode of hadrosauriform body size evolution” 2 December 2021, Scientific Reports.
The researchers involved in the study are Alfio Alessandro Chiarenza (University of Vigo), Matteo Fabbri (Field Museum of Natural History, Chicago), Lorenzo Consorti (the University of Trieste and Geological Survey of Italy – ISPRA), Juan Cantalapiedra (Universidad de Alcalá), David Evans (Royal Ontario Museum and the University of Toronto), Federico Fanti and Marco Muscioni (University of Bologna).
Cover Photo: An adult and two juvenile individuals of the dinosaur Tethyshadros insularis show the different appearances exhibited by immature and mature specimens in the ancient environment of Villaggio del Pescatore, the first locality in Italy preserving many dinosaur individuals of the same species. Credit: Davide Bonadonna