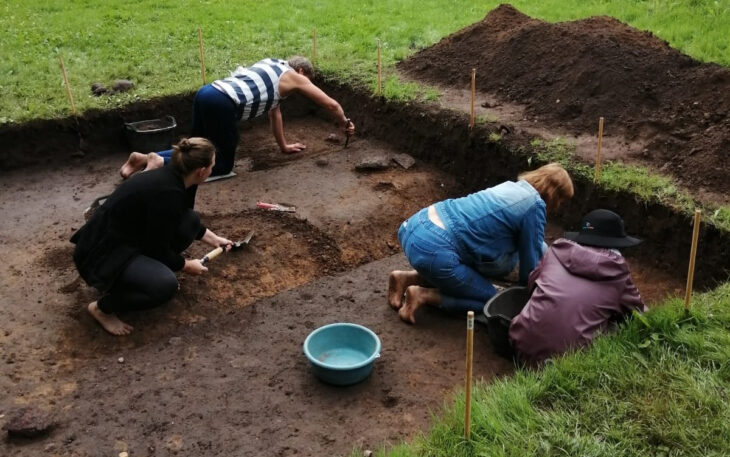
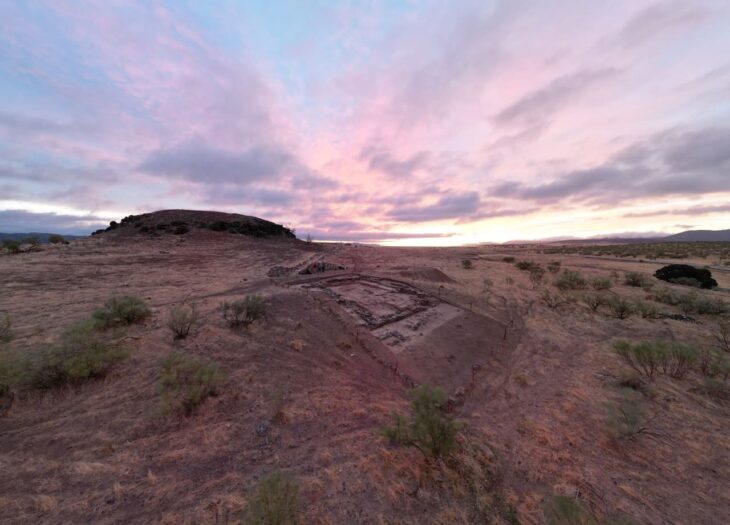
Excavations are set to resume next week at the ancient Kurul Castle in Ordu, the first scientifically excavated archaeological site in Türkiye’s Eastern Black Sea region.
Recent and past discoveries continue to illuminate the sacred and political life of the Hellenistic Pontic Kingdom, with striking links to the cult of Dionysus and its royal patron: King Mithridates VI Eupator.
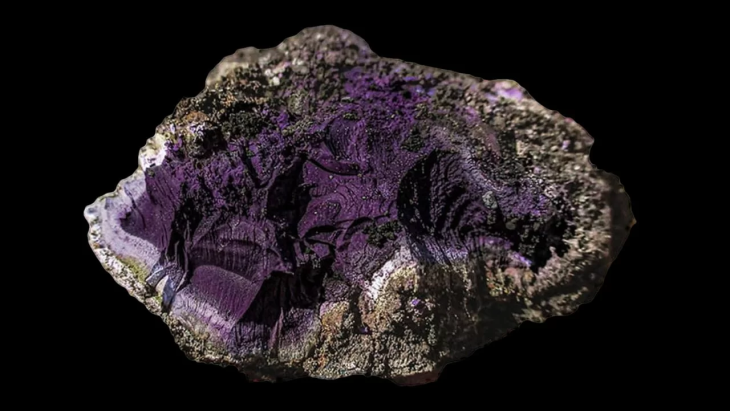
Led by the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism with support from the Ordu Metropolitan Municipality, the site has been under systematic excavation since 2010. The dig, now entering its 16th season, has brought to light more than 5,000 artifacts—including the celebrated statue of the Mother Goddess Cybele, dating to approximately 2,100 years ago.
“Kurul Castle is exceptional because it was home to a single ancient civilization, allowing us to explore uninterrupted cultural layers,” noted Uğur Toparlak, Ordu’s Director of Culture and Tourism. “This is not only a heritage site but also a rare archaeological window into religious and political life.”

A Dionysian Cult in the Mountains of Pontus
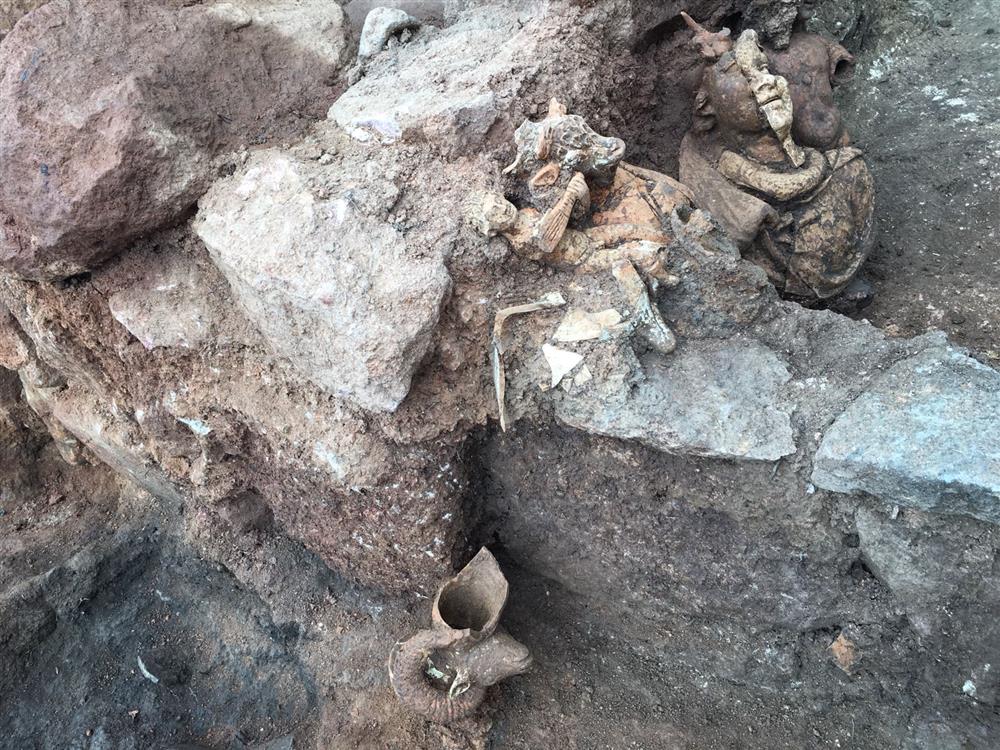
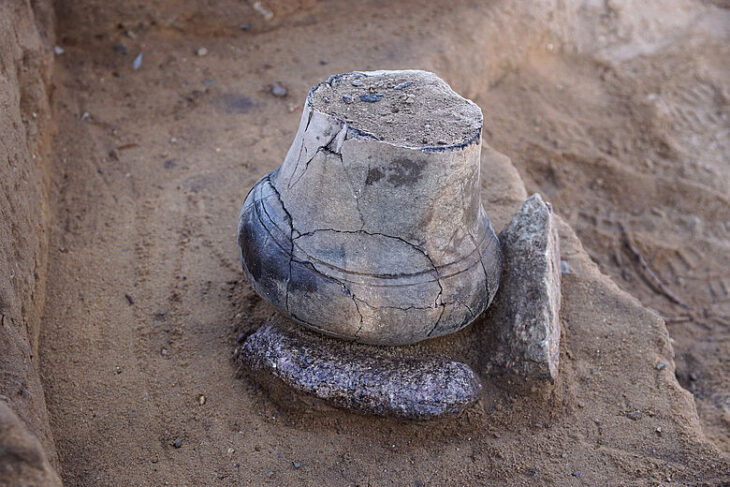
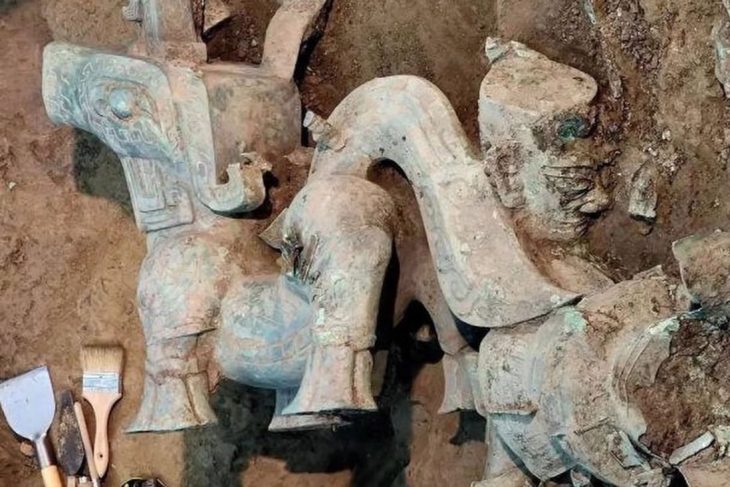
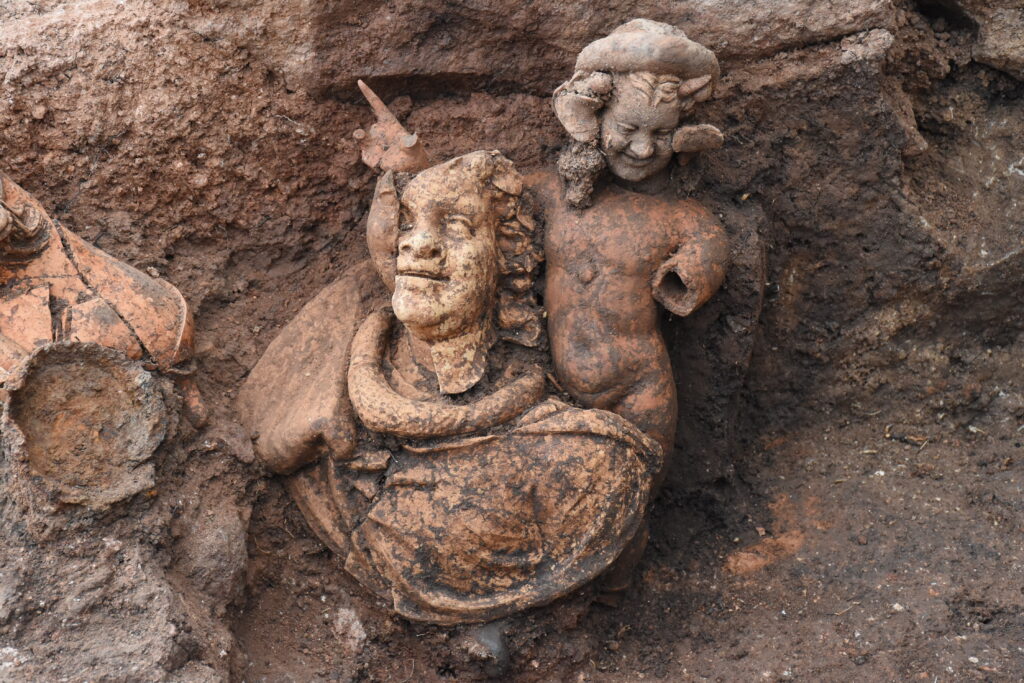
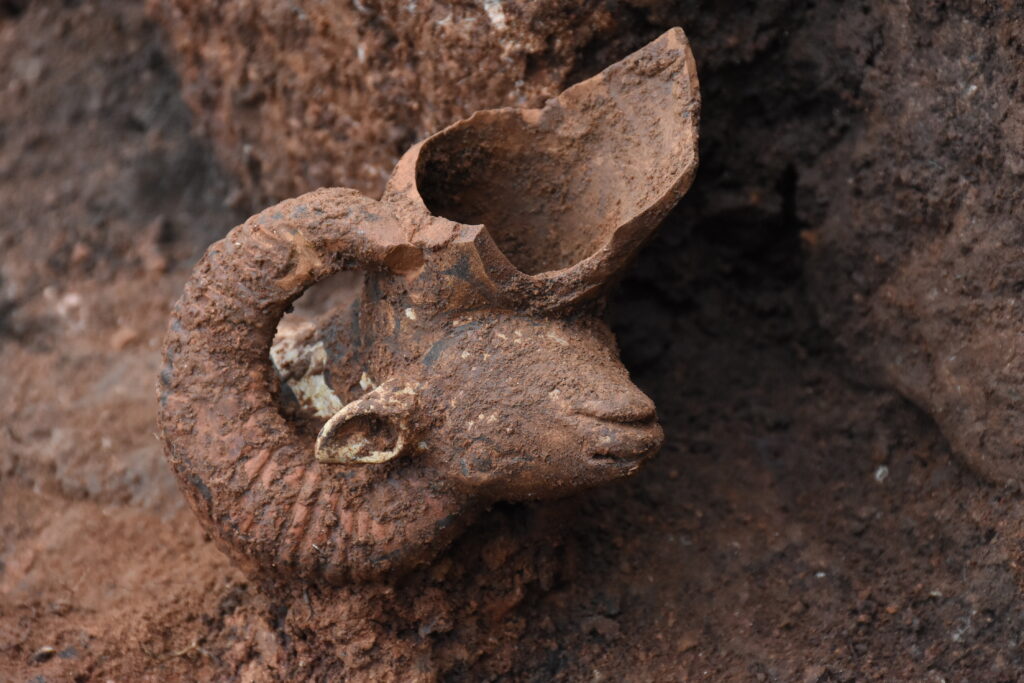
In previous years, archaeologists uncovered a group of terracotta figurines in what is believed to be a ritual or temple space. The set includes a young Dionysus, the pastoral god Pan, and goat-shaped ceremonial vessels—all indicative of Dionysian cult practices. These figures, likely used in sacred ceremonies, reflect the deep-rooted spiritual culture that once thrived in the region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
What makes the discovery especially significant is its likely connection to King Mithridates VI Eupator, the famed ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus (r. 120–63 BCE), who deliberately identified himself with the god Dionysus—a political and religious maneuver that positioned him as both mortal king and divine agent of rebirth, transformation, and power.
One of the most striking historical pieces of evidence supporting this identity comes from an inscription at Delos, dated to 94/93 BCE, in which Dicaeus, a priest of Sarapis, made a dedication on behalf of the Athenians, Romans, and explicitly, “King Mithridates Eupator Dionysus.” The fusion of king and god was not metaphorical—it was public, official, and strategic. Mithridates styled himself as a liberator of the East from Roman dominance, using Dionysus’s symbolic role as a boundary-crossing, world-reversing deity to legitimize his authority.
“To find not only Cybele, the ancient Anatolian mother goddess, but also ritual objects tied to Dionysus and Pan, gives this site a mythological richness rarely encountered in northern Anatolia,” explained excavation head Prof. Dr. Süleyman Yücel Şenyurt of Gazi University.

Kurul Castle: Bridging Nature, History, and Mythology
Dating back approximately 2,300 years, Kurul Castle overlooks the Black Sea from a dramatic mountain ridge near Ordu’s Altınordu district. Built during the reign of Mithridates VI, the castle served not only military functions but appears to have housed significant religious activity tied to the Dionysian mysteries.
“Preparations for this year’s excavation are complete. Once preservation and site development efforts are finalized, we aim to open Kurul Castle to tourism,” said Toparlak. “Ordu has long been known for its natural beauty—but now, it will also shine through its ancient cultural heritage.”
With archaeological findings of regional and international importance, Kurul Castle is poised to become a major destination for those seeking to explore the fascinating intersection of myth, monarchy, and sacred space.
Cover Image Credit: Ordu Provincial Directorate of Culture and Tourism