In Cambridgeshire village, the earliest evidence of a Roman crucifixion has been discovered.
Archaeologists investigating a previously unknown Roman roadside settlement in a Cambridgeshire village have discovered evidence of the first example of a Roman crucifixion in the UK.
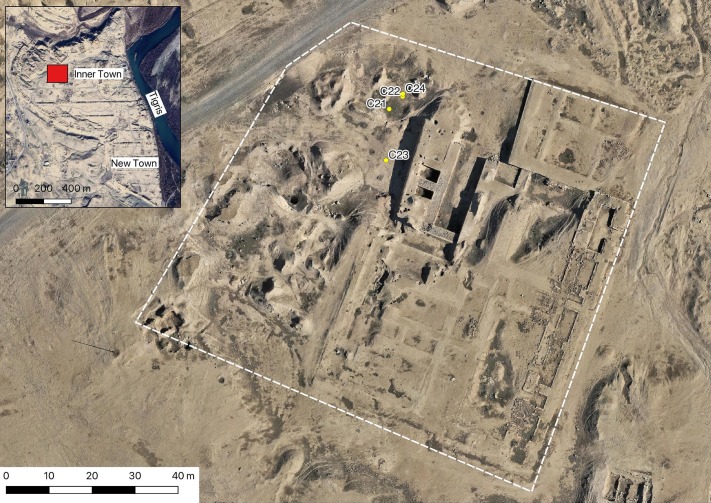
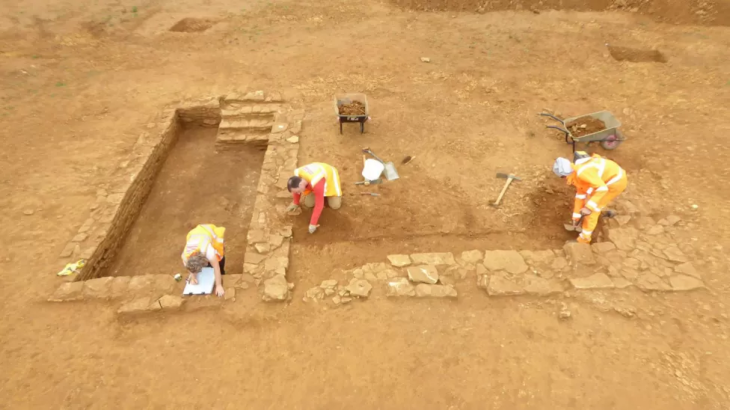
The astonishing and historically significant find was uncovered during archaeological digs at Fenstanton, between Cambridge and Huntingdon, in preparation for new housing development.
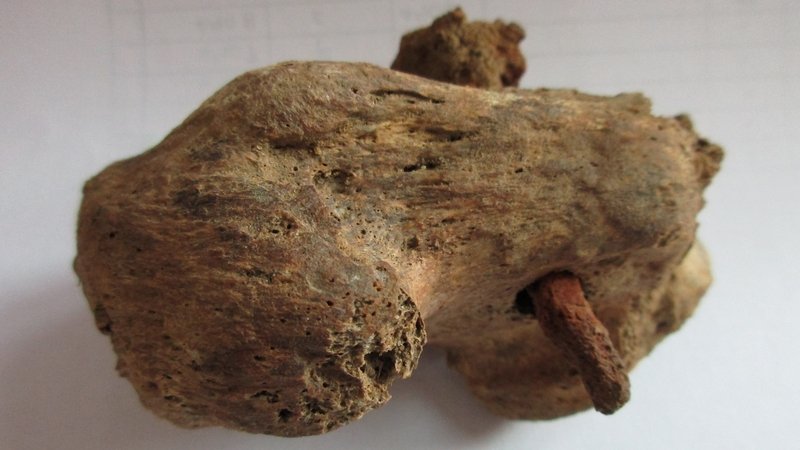
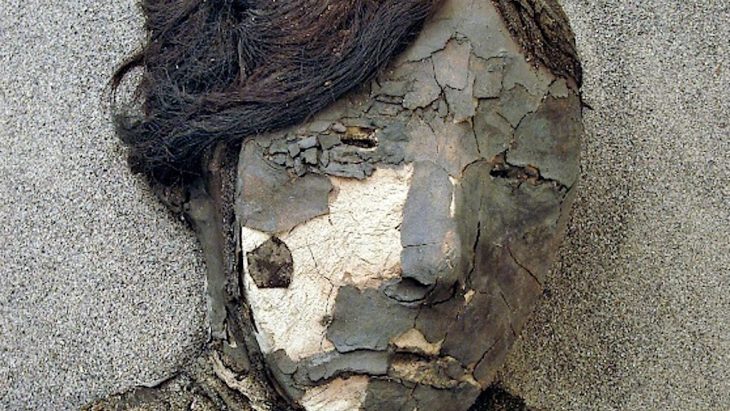
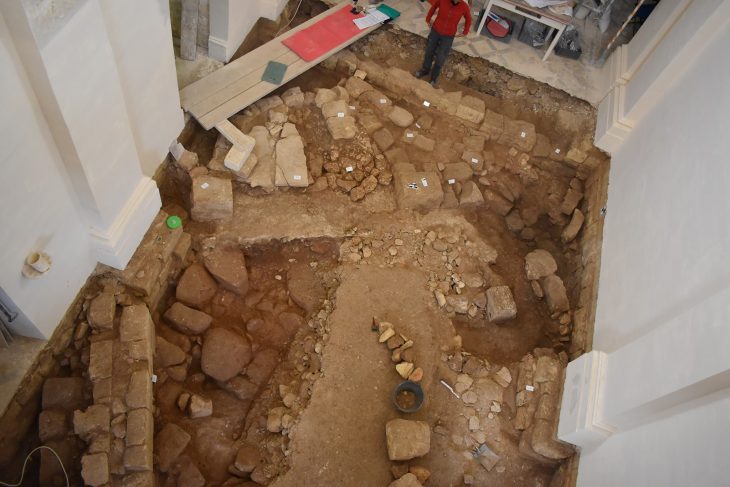
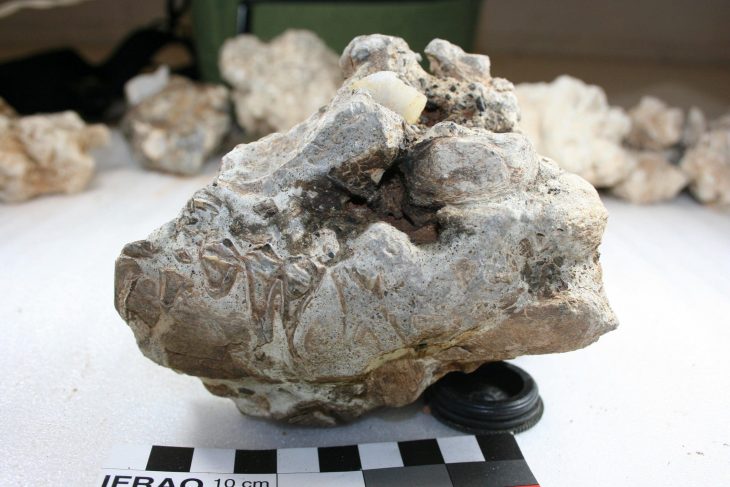
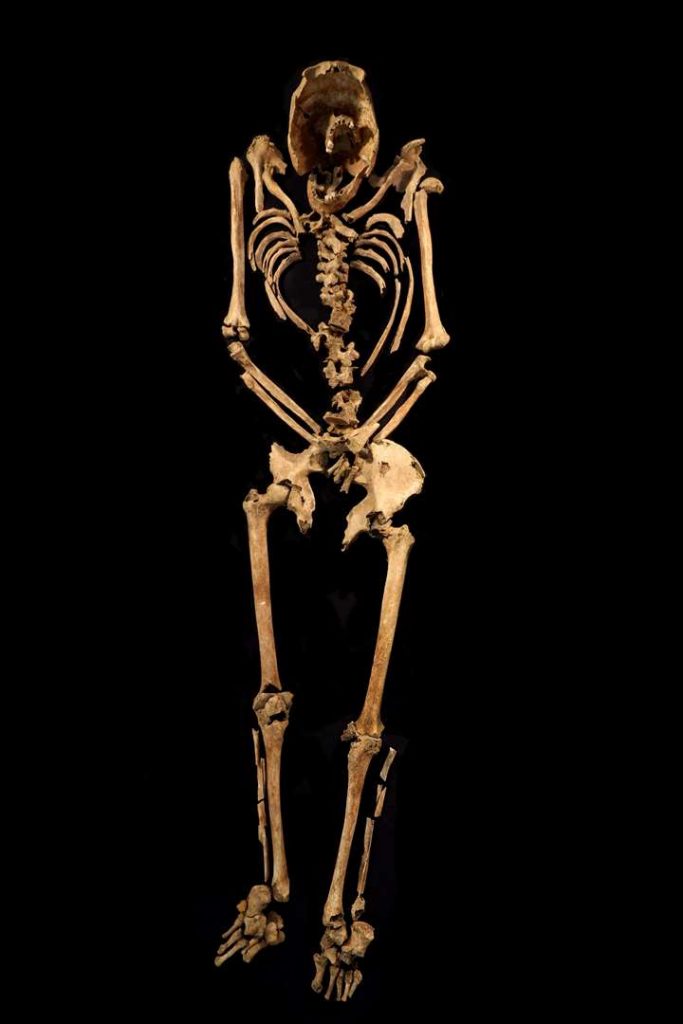
Archaeologists investigating a previously unknown Roman roadside settlement, which includes five small cemeteries, discovered in one grave the remains of a man with a nail through his heel.
Only one earlier example of crucifixion like this has been uncovered in the globe, in Israel, while two probable occurrences have also been reported in Italy and Egypt. The Fenstanton sample, on the other hand, is the finest maintained.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The exciting discovery follows on from previous digs across Cambridgeshire in recent years which have uncovered preserved Bronze Age buildings and artifacts at Must Farm in Whittlesey, pristine prehistoric occupation sites and burial monuments in Needingworth Quarry, and new Iron Age, Roman, and Anglo-Saxon settlements that emerged during the course of the recent A14 road improvement scheme.
Osteologist (human bone specialist) Corinne Duhig from Wolfson College, Cambridge, said: “The lucky combination of good preservation and the nail being left in the bone has allowed me to examine this almost unique example when so many thousands have been lost.
“This shows that the inhabitants of even this small settlement at the edge of empire could not avoid Rome’s most barbaric punishment.”
The grave of the man who was crucified was discovered during excavations in advance of a new housing development by Tilia Homes (previously known as Kier Living) south of Cambridge Road. The excavation was led by David Ingham of Albion Archaeology.
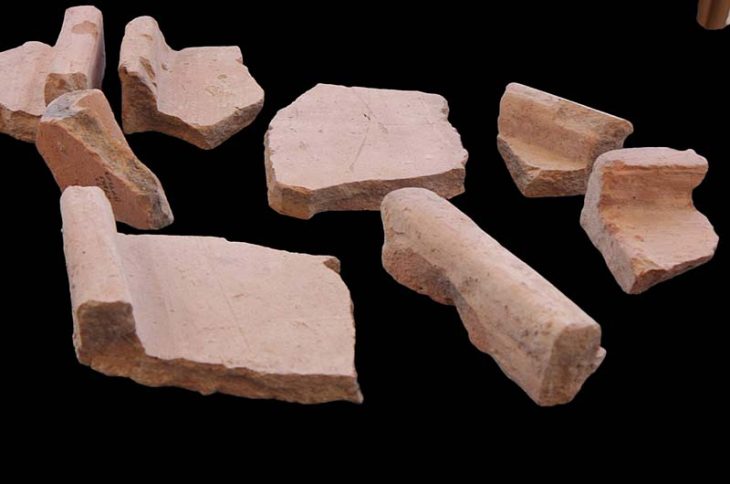
Inside the cemeteries, 40 adults and five children were buried, with a specialist study showing that some family groups were present. The Roman graves, now fully excavated, also included a number of archaeologically significant artifacts.
The results of the excavation will be formally published when analysis of the site’s finds and evidence has been completed.
Pic by Albion Archaeology.
















