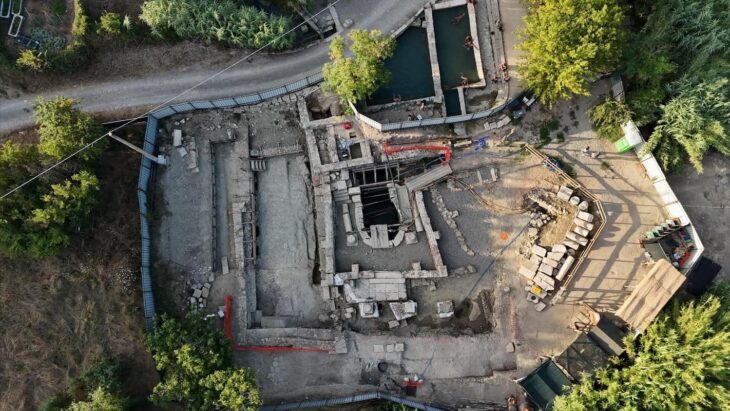
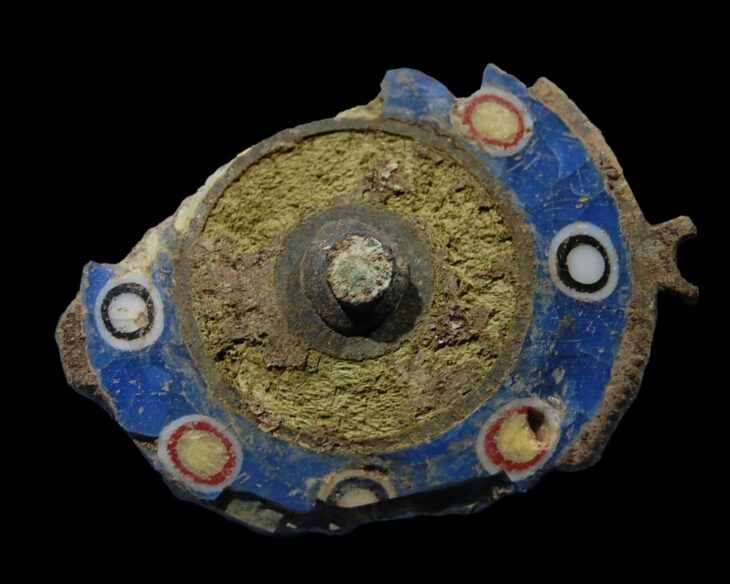
The Romans are long regarded as heroes in the history of ancient civilizations because of the legacy they have left behind. However, the lives of many emperors continue to be a subject of curiosity. And what about you? Have you ever wondered what a Roman emperor smelled like?
Julius Caesar’s “Telinum” perfume has been re-created by the Scent Culture and Tourism Association, which promotes ancient perfumes.
According to research, the Romans liked perfumes with simple formulas. Made with rose oil and the sweat of gladiators, rhodium was the most widely used formula in ancient Rome. because gladiators’ dirt and sweat, rather than their blood, were valued enough to be used in sculpture and painting.
In Antique Rome, besides rhodium with rose, narcissus, and crocus with saffron, metopium with bitter almonds was among the most loved perfume mixtures.
However, the scent of an emperor would undoubtedly have been more special and different. Especially, high-level executives, generals, priests and the rich would import different perfumes from all over the world to smell different from everyone else or order leading perfumers of the age to make special perfumes for them.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
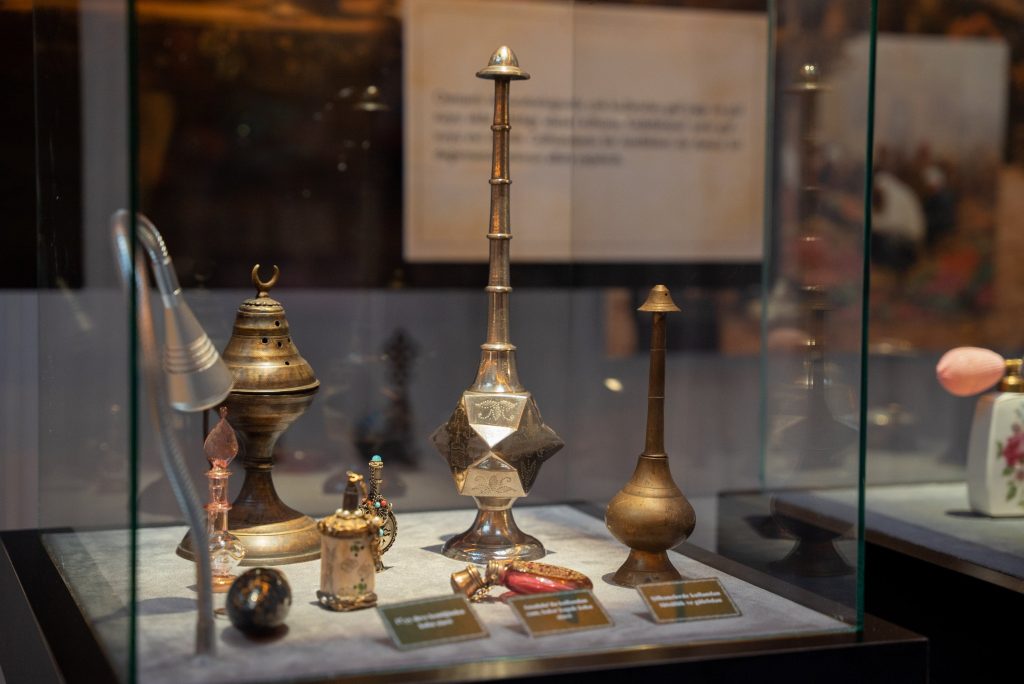

This special study was carried out under the supervision of Associate Professor Cenker Atila from the Archaeology Department of Sivas Cumhuriyet University, with the support of Milan perfumers and the expertise of renowned Perfume Designer Bihter Türkan Ergül.
The perfume, the product of a long work, contains ancient scents from rock rose to citrus and from oud to amber. The perfume will be on sale simultaneously in Türkiye, France, and Italy as of October.
The Scent Culture and Tourism Association made a statement about the new perfume, saying that Caesar (100 – 44 B.C.), who visited all of Europe, Anatolia, Greece, the Aegean islands and Egypt during his years as a general, perfumes and cosmetics were extremely popular throughout the Mediterranean world in ancient times and had a huge commercial potential.
“Caesar was a very famous general and dictator, and he always attracted the attention of the public with his lifestyle and clothing. The perfumes he used were also followed with great interest by the public. What Caesar smelled like, what was in his perfume, where he got his perfume or who made it for him had always been a matter of great curiosity. According to information provided by both ancient writers and works of his close friends, the contents of his perfumes have been largely determined. This perfume, signed by perfume designer Ergül, consists of the scents determined in the light of archaeological and historical data,” the statement added.
In addition to scents like mint, rose, lemon, bergamot, lavender, jasmine, water lily, violet, oud cedarwood, patchouli, and amber, the association said that the perfume includes iris flower and rock rose, which were highly sought-after and hard to locate in ancient times.