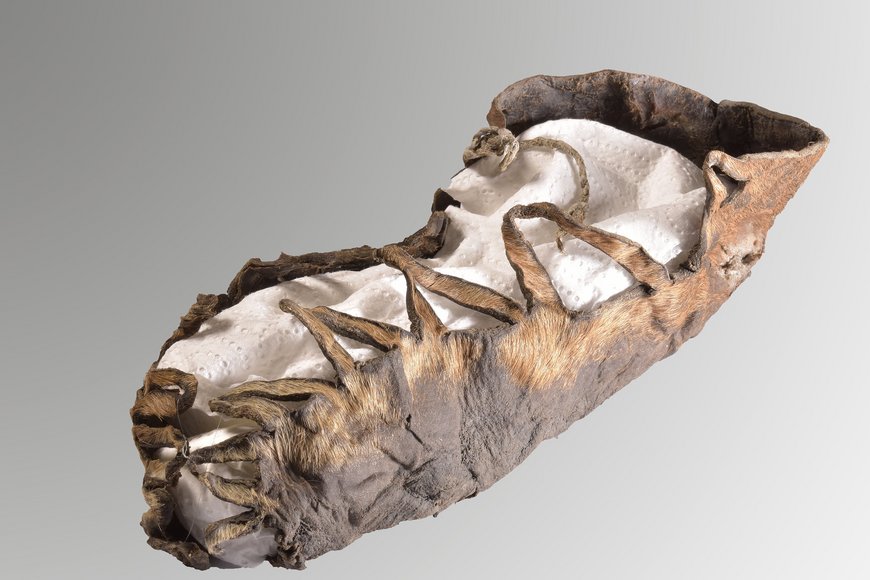
An “extremely well-preserved” Iron Age child’s shoe was discovered in Austria during excavations at Dürrnberg, near the historic town of Hallein.
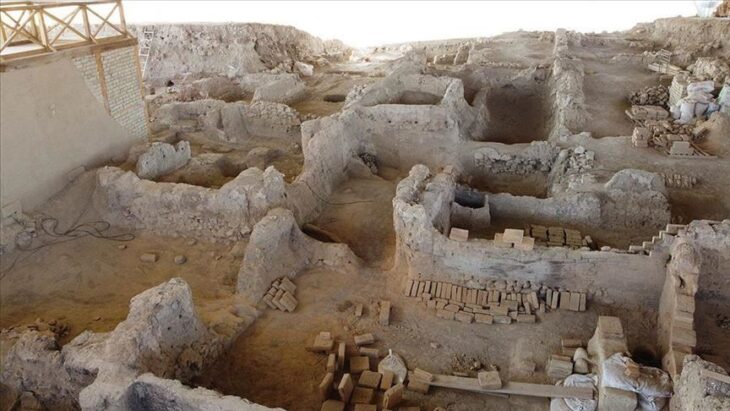
Since 2001, the German Mining Museum Bochum, Leibniz Research Museum for Georesources, has been conducting mining archeological investigations with its mining archeology research area on the Dürrnberg near Hallein. The Dürrnberg near Salzburg is known for its rock salt mining, which already occurred in the Iron Age.
Due to the preservation effect of the salt, organic remains are particularly well preserved, in contrast to other excavations, where such finds are in short supply. During this year’s campaign in the Georgenberg tunnel, a children’s shoe made of leather came to light.
The shoe is made of leather and roughly corresponds to today’s shoe size 30 (12.5-inch). The shape, as well as the lace-up closures, which were likely made of flax or linen, are still intact. The shoe’s design provides additional indications of its manufacture, which was most likely in the second century B.C.
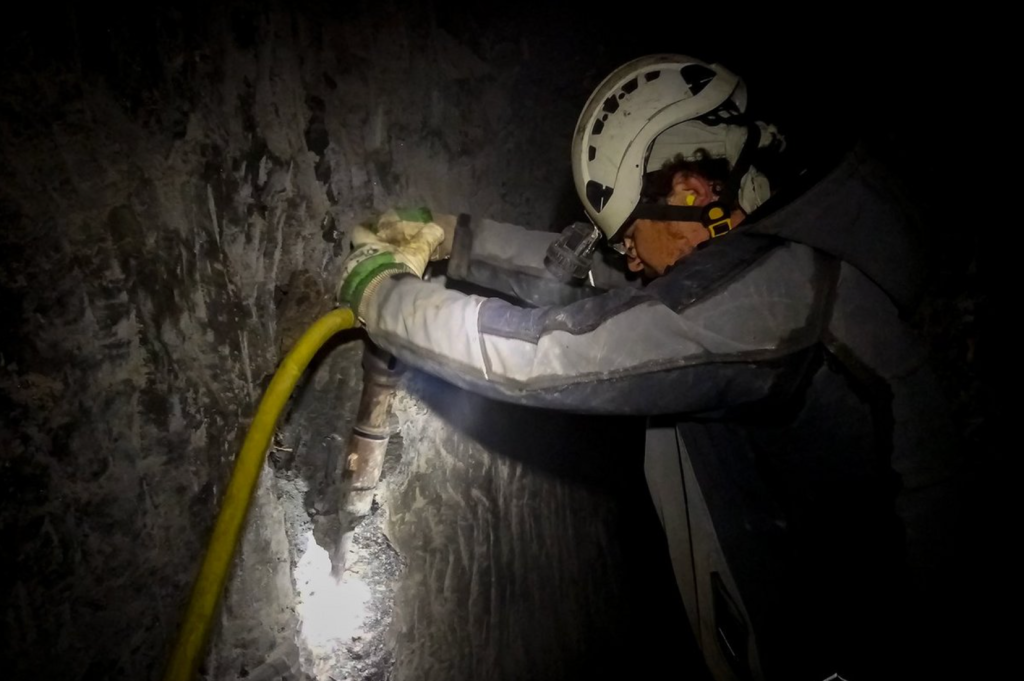

“For decades now, our research activities on the Dürrnberg have repeatedly provided us with valuable finds in order to develop the earliest mining activities scientifically. The condition of the shoe that was found is outstanding,” says the head of the research area, Prof. Dr. Thomas Stöllne. “Organic materials usually decompose over time. Finds such as this children’s shoe, but also textile remains or excrement, such as those found on the Dürrnberg, offer an extremely rare insight into the life of the Iron Age miners.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Several finds of leather shoes are already known from the Dürrnberg, but a child’s shoe is always something special, as it proves the presence of children underground. In addition, in this case, as an exception, a remnant of a lacing made of flax or linen has been preserved. In this way, conclusions can be drawn as to how the shoes were laced.
In the vicinity of the well-kept find, archaeologists also found other organic materials, namely a fragment of a wooden shovel in the shape of a blade and the remains of fur with lacing that possibly belonged to a fur hood.
The research work on prehistoric salt production at Dürrnberg near Hallein in Austria is part of a long-term research project. The work is funded by Salinen Austria AG and Salinen Tourismus and is carried out in cooperation with the Institute for Archaeological Sciences at Ruhr University in Bochum.
Cover Photo: German Mining Museum