Archaeologists in Scotland have discovered medieval remains during excavations for construction work, and they are exposing mysteries about the industrial history in Inverness, the Scottish Highlands’ capital.
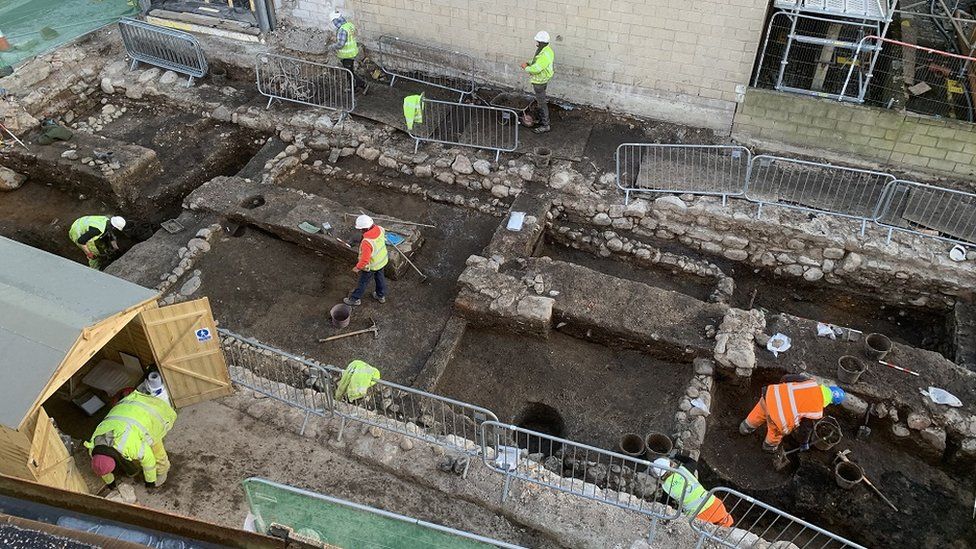
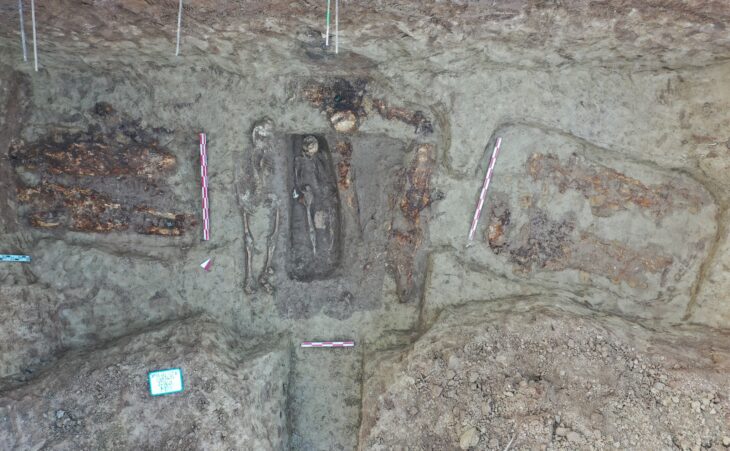
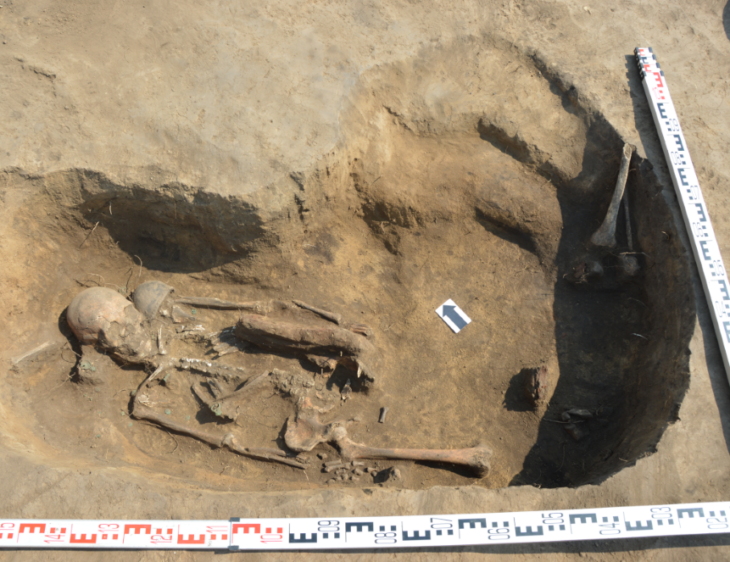
The city’s 99 Church Street has uncovered evidence of iron industry, including three smithing hearths used in the metal’s manufacture. Carved bone pins, medieval coins, iron implements, and bronze decorative items are among the artifacts discovered.
Archaeologists said houses and associated local industry would have been built along this street from the late 12th Century.
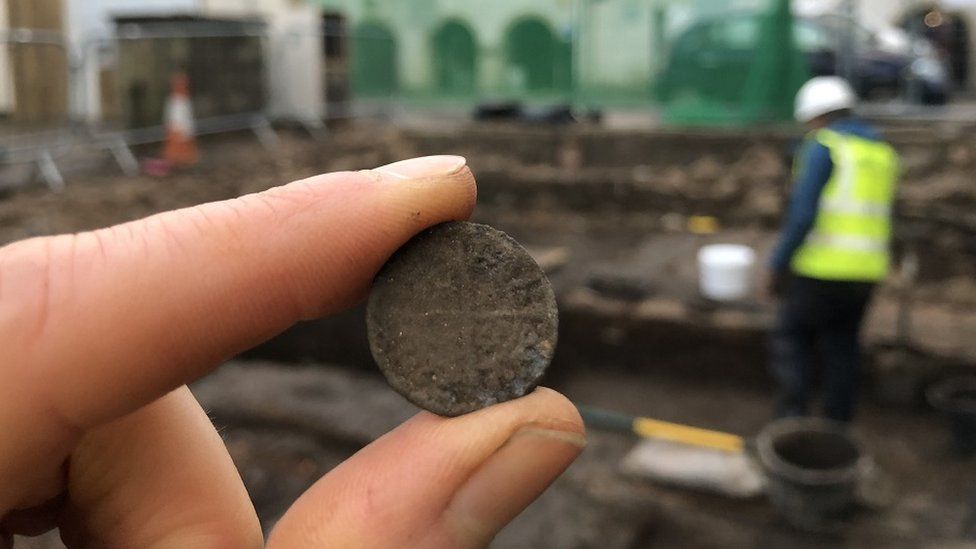

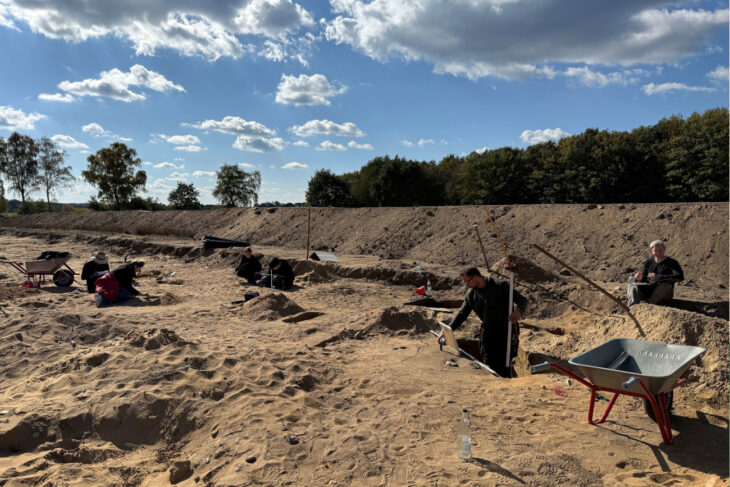
The ruins were preserved beneath 19th-century structures and were uncovered by recent construction work. The site is roughly in the vicinity of a 12th Century medieval church and Dominican Friary on neighboring Friars Street.
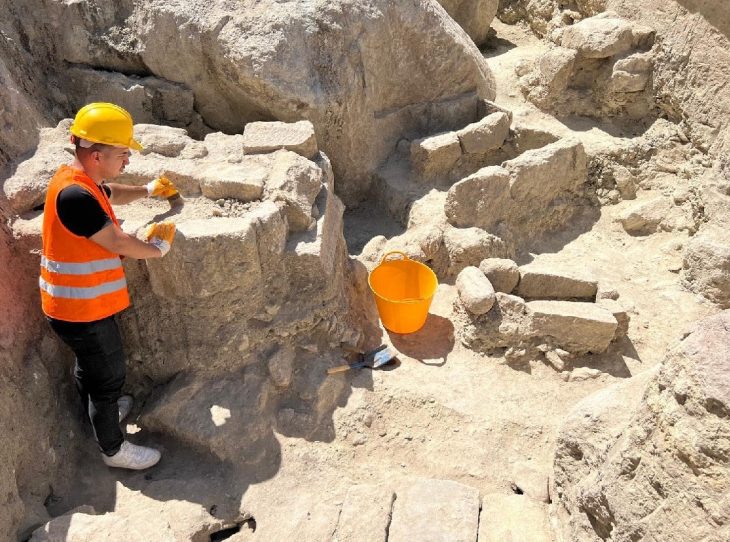
AOC Archaeology discovered two well-preserved, burnt-down wattle and daub medieval houses, as well as subsequent stone-built structures with internal walls, wooden floor joists, and cobbled surfaces.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
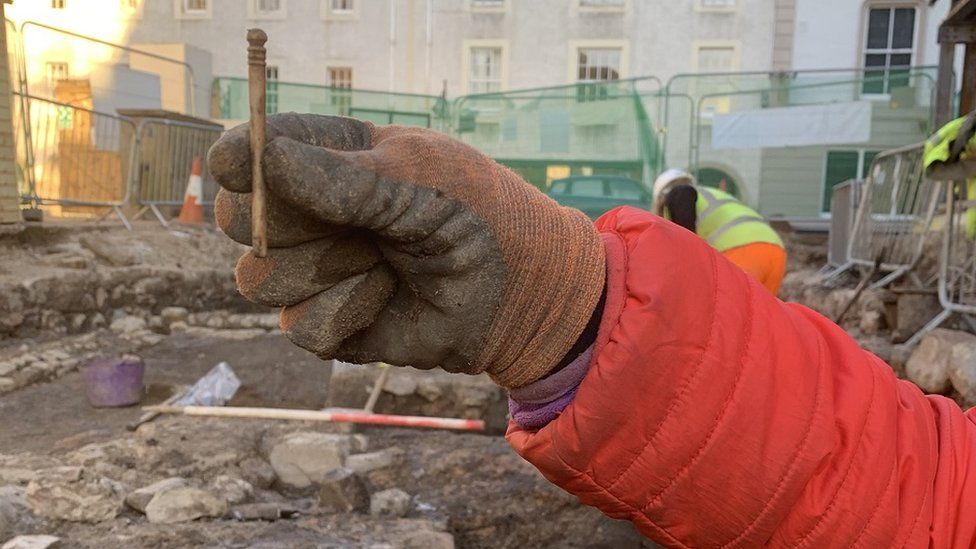

The two well-preserved burnt-down buildings are revealing to archaeologist the skills behind medieval “ wattle and daub ” architecture.
Archaeologists stated that this demonstrated how the site was used again and again repeatedly over centuries.
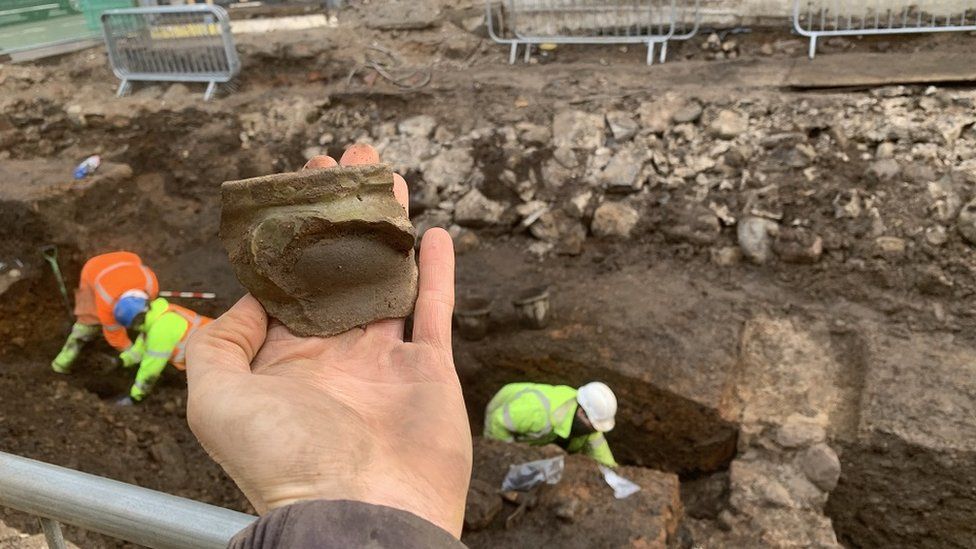

Lindsey Stirling, the archaeologist who supervised the excavations, said: “This was an amazing and rare chance to experience first hand these moments in time preserved after activities had ceased and buildings had been abandoned, and to see the overlapping of successive occupation.”
According to AOC Archaeology, the excavations revealed a level of preservation of historic artifacts not frequently encountered in previous Inverness city center projects.
The dig was supported by funding from the developer Ark Estates.
Source: AOC Archaeology