Archaeologists have discovered the earliest evidence of forest management at the La Draga Neolithic site in northeastern Spain.
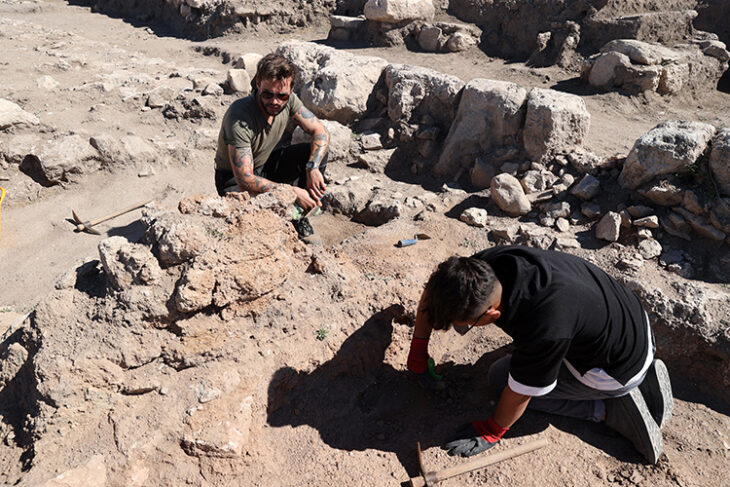
A scientific team from the Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB) has identified the oldest evidence of forest management, based on the analysis of several anthropic marks located on pillars of laurel wood (A noble laurel) from La Draga (Banyoles, Girona), the only Neolithic lake site in the Iberian Peninsula, of between 7,200 and 6,700 years old.
The research has been carried out by Oriol López-Bultó, Ingrid Bertin, and Raquel Piqué, researchers from the University’s Department of Prehistory, and the archaeologist Patrick Gassmann, and has been published in the International Journal of Wood Culture after its presentation at the congress From forests to heritage held in Amsterdam (Netherlands).
Marks such as the ones found at La Draga had been previously identified at a site located in Switzerland, the Hauterive-Champréveyres site, but were at least 1,000 years younger than the ones found at La Draga.
“The discovery is of great importance due to the extreme difficulty in finding archaeological evidence on when and how the first groups of humans managed these forests, given the natural degradation of the wood over time”, points out Oriol López-Bultó, first author of the article.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
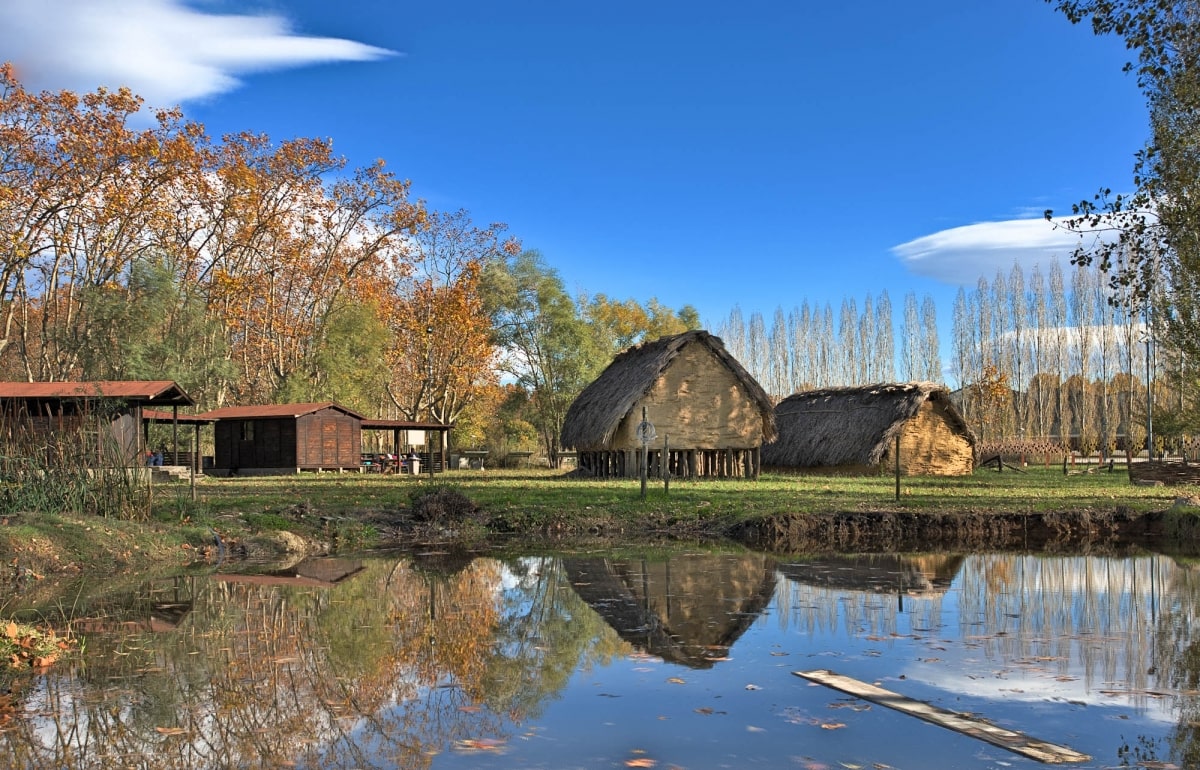
La Draga is one of the few European sites to register wooden remains in good conditions, due to being submerged in water on the edges of Lake Banyoles.
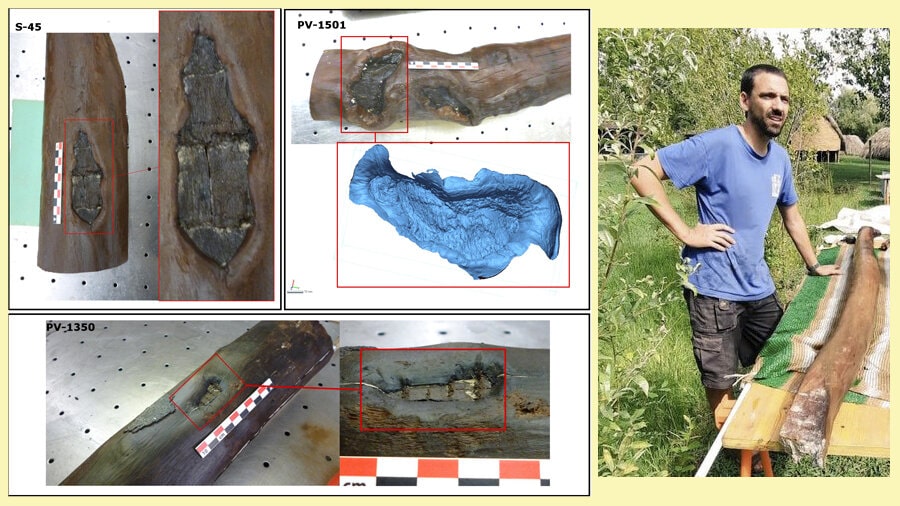

“There are signs that the communities at La Draga managed the forests, but until now we have not been able to demonstrate this with enough physical evidence”, explains Raquel Piqué, co-author of the research. “The results allow us also to confirm the presence in the area of a group of people inhabiting La Draga years before the settlement was established and who selected, marked, and controlled the forest”
Wood rarely used in the Neolithic
Bay tree wood was rarely used in the Neolithic in Europe, despite it being readily available in areas mainly located close to lakes. In the case of La Draga, it is documented in the remains of fires, tools, and in very few elements used for building, with a very secondary role when compared to oak: of the 1,200 posts recovered to date from the site, bay tree wood represents only 1.4%, in comparison to the 96.6% of posts made out of oak.
The marks of forest management at La Draga however were only discovered on bay tree posts, and this opens the door to questioning the reason why this type of wood was intentionally marked. “It could have been a way to avoid the use of this wood, for practical reasons, such as marking different territories, or even for symbolical reasons, but more studies will be needed clarify this question”, researchers point out.
Profound knowledge of natural resources
Researchers confirmed in earlier studies that the inhabitants of La Draga had a profound knowledge of the natural resources surrounding the settlemen. They managed plants and animal herds and used oak for practically everything, with an accurate selection of shapes and dimensions when building the posts that would later be used to build their cabins.
“The management of forests is a very relevant economic and social activity, which requires expertise, planification and social organization to succeed. Once again, our study demonstrates the economic importance and evolution of the inhabitants of La Draga and, in general, of the Neolithic groups of the western Mediterranean”, states López-Bultó.
To conduct the study, researchers used a combination of different methodologies, such as direct observation and registration, traceology and experimental archaeology, 3D scanning, taxonomic identification and dendrochronology.
The discovery of forest management at La Draga is significant because it shows that people were actively shaping their environment thousands of years ago. It also provides insight into the complex relationship between humans and nature. The researchers hope that their findings will help us to better understand how humans have impacted the environment throughout history.
The archaeological site of La Draga, discovered in 1990, lies on the eastern shore of Lake Banyoles and is one of the earliest farming and livestock-rearing settlements in the northeastern part of the Iberian Peninsula, as well as one of the first lakeside Neolithic sites to exist in Europe (5200-4800 BCE). While it was inhabited, the settlement formed the shape of a peninsula inserting itself into the lake, with a soft and continuous downward slope. Based on the prospecting work, it is estimated that the settlement measured some 8,000 square meters.
Cover Photo: ‘La Draga’ Neolithic Park