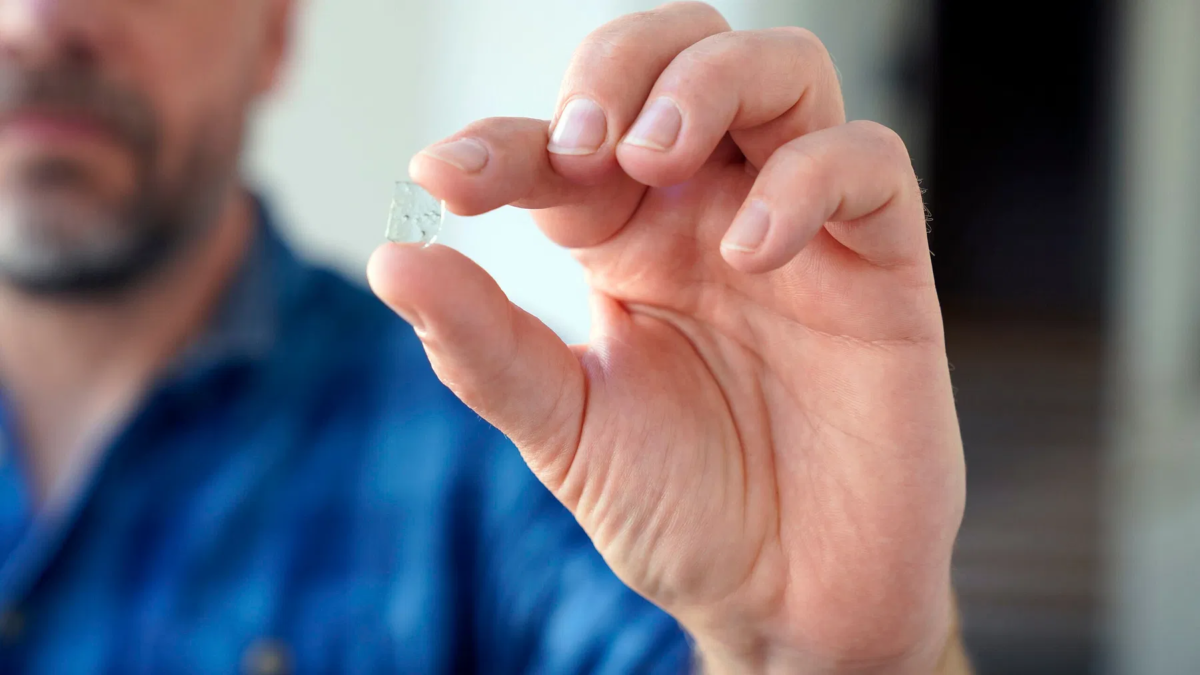
New research shows that Viking Age windows were created using stained glass in the 9th century, contrary to popular belief that stained-glass windows only emerged during the construction of medieval churches and castles in Denmark.
Researchers in Copenhagen analyzed 61 fragments of glass panes and concluded that the pieces of glass can be dated from long before the churches and castles of the Middle Ages and that Vikings had windows with glass panes between 800 and 1100. The Viking Age is considered to be from 793 to 1066.
“Several fragments of glass windows found on important Viking Age sites in South Scandinavia, made us wonder if it was just a mere coincidence that they were there,” says Torben Sode, the study’s lead author who first noticed the special find material. “And it wasn’t, they can be dated to the Vikings Age and most likely must have been in use in that time-period as well.”
The museum said glass windows were for the upper echelons of society and religious use, as was the case in the rest of Europe. These Viking Age windows were not the large, transparent windows we are accustomed to today. Instead, they likely consisted of smaller panes in various shades of green and brown, not meant for viewing the outside world but for infusing the interior of their buildings with colorful light.
The fact that glass windowpanes were uncommon in Denmark until several centuries later, when medieval churches and castles were built, is what makes the discovery so astonishing. This new information highlights the fact that the Vikings were much more advanced than commonly believed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

What shapes our architecture today was not common for a long time: window glazing was first documented in Roman times. However, this equipment was previously reserved for exclusive housing, and later church buildings were outfitted with transparent components. Until now, it was assumed that the spread of glass windows in the early Middle Ages was limited to the Christian-Roman cultural area. If the pagan Vikings had windows at all, they were most likely covered with translucent animal skins. Only in the later Middle Ages were stained glass windows clearly documented in Scandinavia’s first churches and castles.
“This is yet another shift away from the image of unsophisticated barbaric Vikings swinging their swords around,” told National Museum’s senior researcher Mads Dengsø Jessen. “In fact, we are talking about a cultivated Viking elite with royal power that equalled that, for example, of Charlemagne, king of the Franks. This is something that is often omitted in the simplistic Hollywood portraits of Vikings,”.
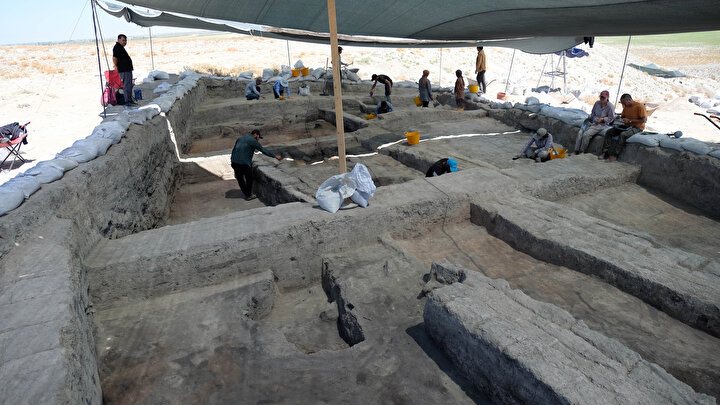
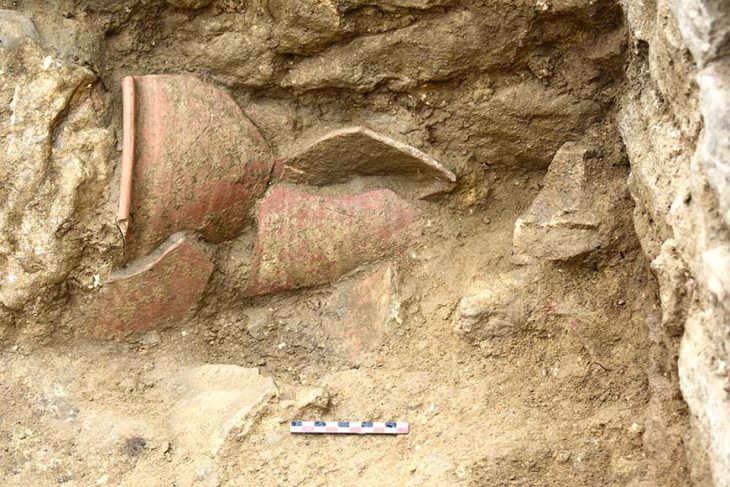
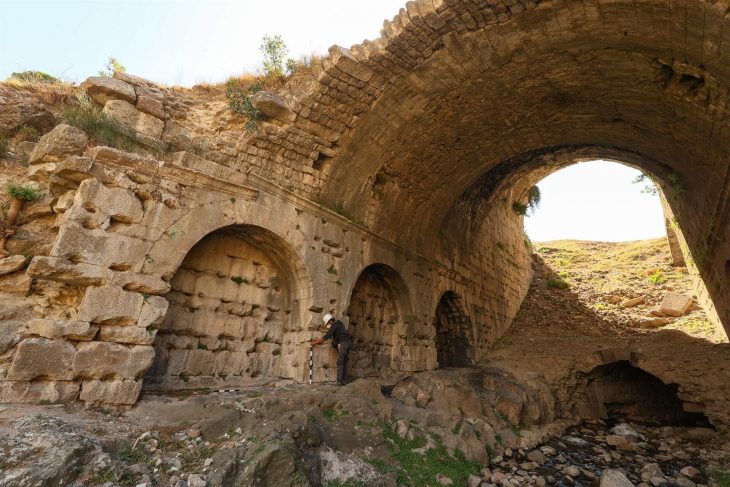
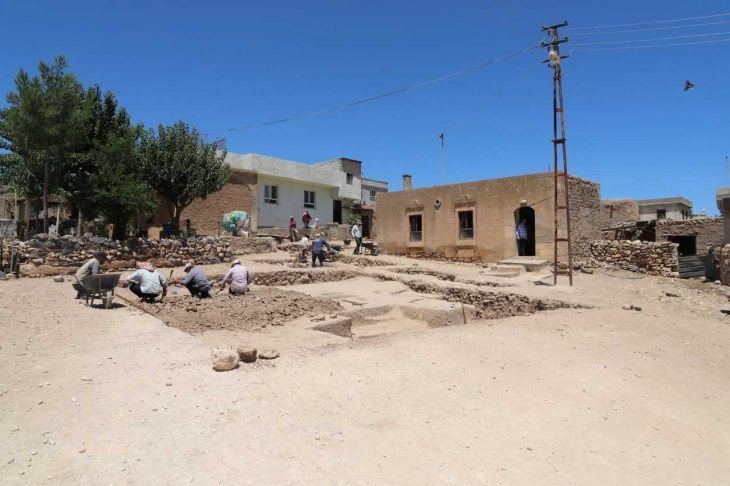
The study is based on analyses of glass pane fragments that were discovered over a 25-year period in six different excavations, including Viking noblemen’s farms, pre-Christian temples, and early urban environments. Five of the excavations were conducted in southern Scandinavia, and one was conducted in Hedeby, northern Germany.
Although the existence of glass has been known for a long time, no one analyzed it until now. This is because we only associated early window glass with the Middle Ages, therefore assuming that the glass could not originate from the Viking Age, but must have been the result of ‘pollution’ from later periods.
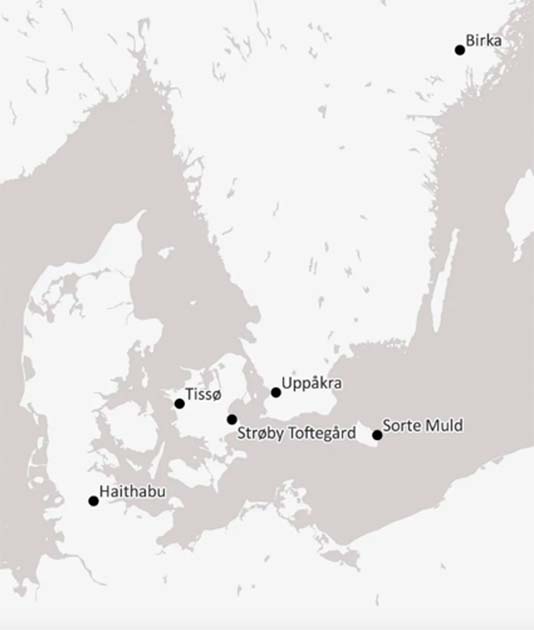
Now, however, chemical isotope analyses of the glass panes show that the glass was made of soda glass, a practice from Egypt and the Near East, or potash glass that was made in Germany, and can be dated to between the years 800 and 1150.
The Vikings probably couldn’t have produced the material themselves, say the scientists. These could therefore have been looted items from their infamous raids. The glass panes were probably acquired through trade: “We know that well-known Vikings like Harald Klak visited the south, where the Vikings had a political network and close trade connections. And of course they also knew about glass panes from the buildings of the upper classes of society,” says Mads Dengsø Jessen from the Danish National Museum.
The team concludes that it can now be assumed that the finds are shards of glass panes that were already in windows in the Viking Age. As in the rest of Europe, they probably only adorned the houses of the upper social class or ceremonial buildings among the Vikings.
DANISH JOURNAL OF ARCHAEOLOGY
















