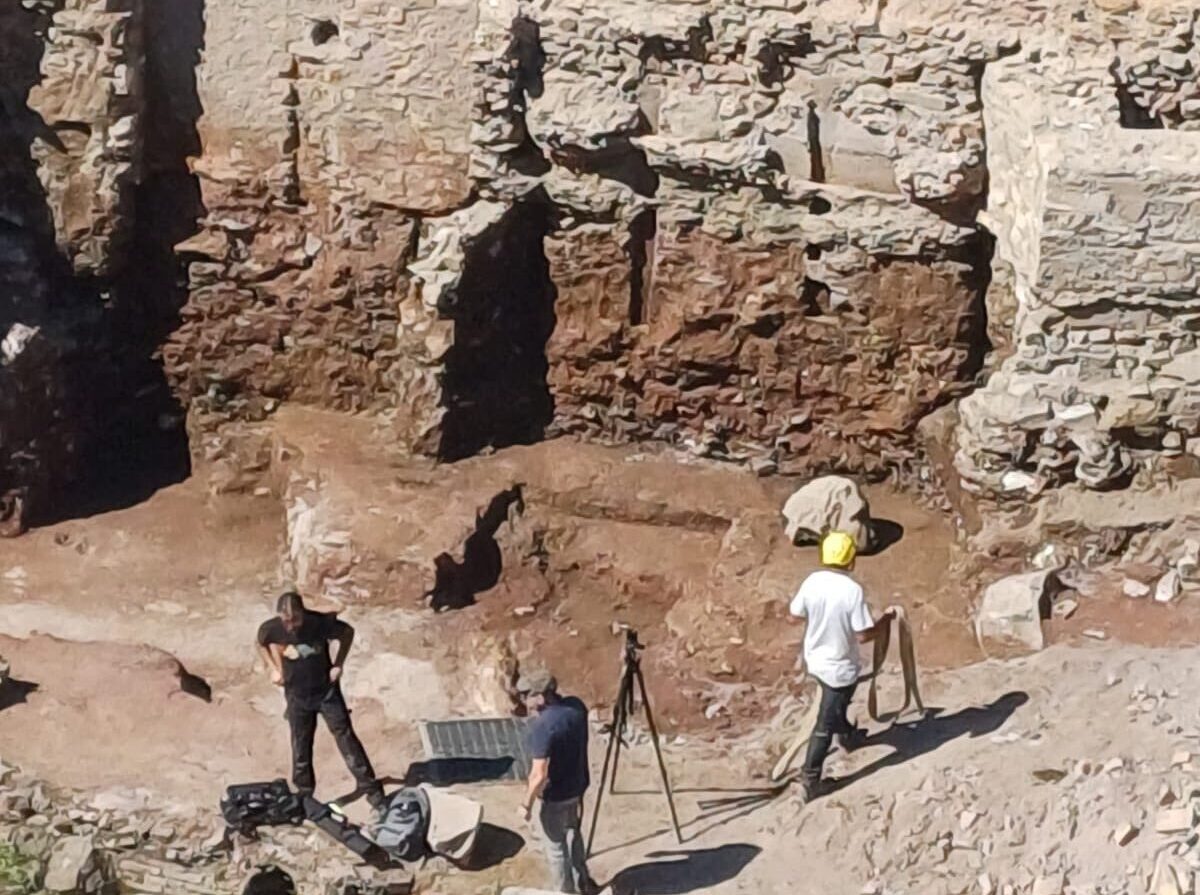
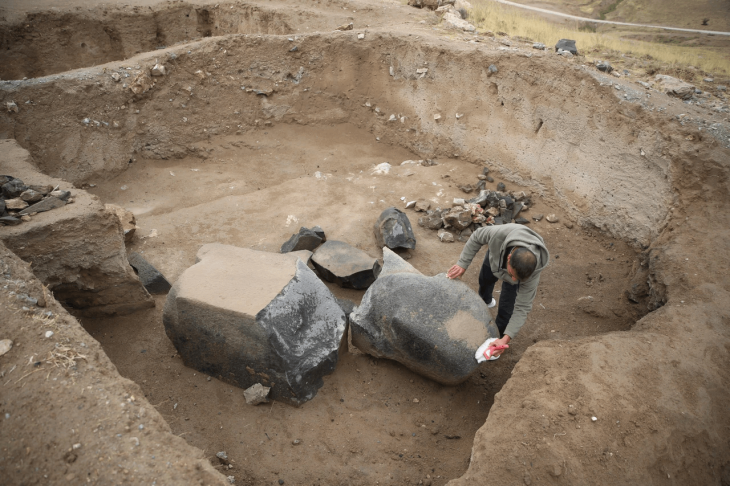
A remarkable archaeological discovery has emerged from the heart of imperial Rome. During recent excavations on Via Alessandrina—funded by Italy’s National Recovery and Resilience Plan (PNRR)—a colossal marble head was unearthed beneath the square of Trajan’s Forum. The find has generated excitement among archaeologists and city officials, as it could represent either an imperial figure or a deity like Dionysus, the god of wine.
Rome Mayor Roberto Gualtieri announced the discovery on social media, describing the marble head as “a male face, with thick hair and an intense expression, hidden for centuries under the Forum’s square.” The artifact was found within a medieval layer of brick and lime mortar, suggesting it had been repurposed as construction material long after the fall of the Roman Empire.
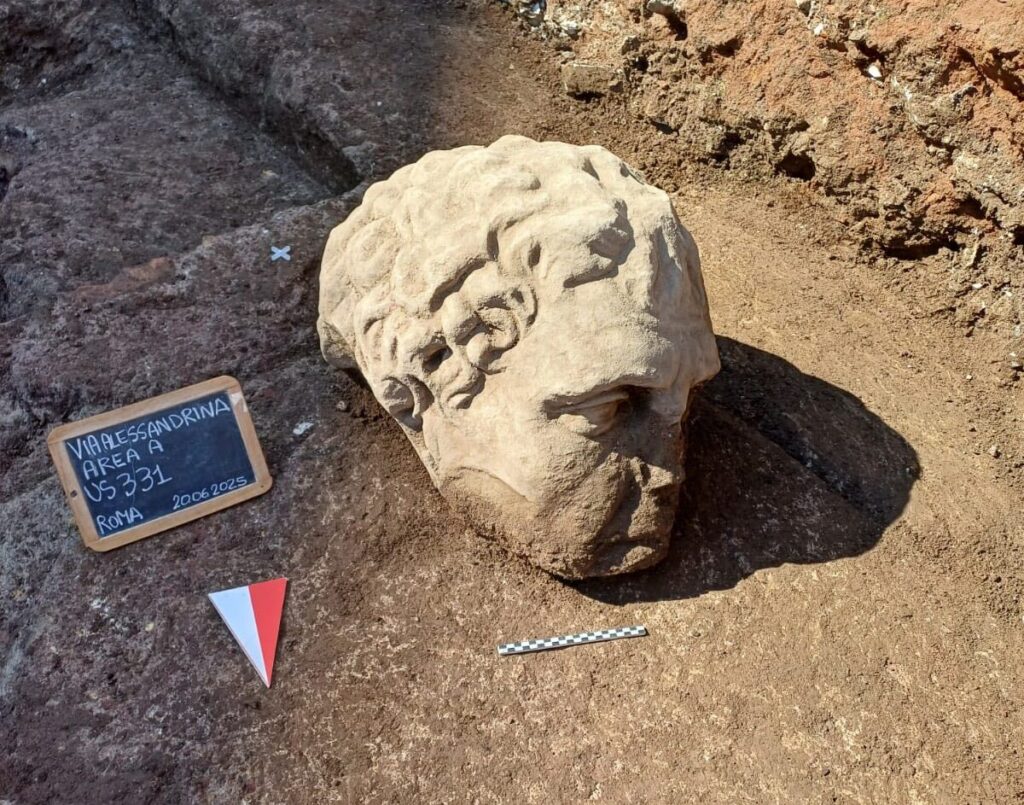

The head’s style and craftsmanship hint at imperial portraiture, potentially dating it to the central years of Emperor Trajan’s reign (105–115 A.D.). Its physical features—wavy hair, high cheekbones, and focused gaze—closely resemble existing depictions of Trajan himself. However, due to the presence of another similar head found years earlier with Dionysian attributes, some experts believe it might represent the god Dionysus.
The excavation site is located near the Porticus Trisigmentata, a monumental colonnade that once stood at the entrance of Trajan’s Forum. This grand structure, designed by Apollodorus of Damascus, featured 40-foot-high marble columns and housed statues, battle trophies, and intricate reliefs.
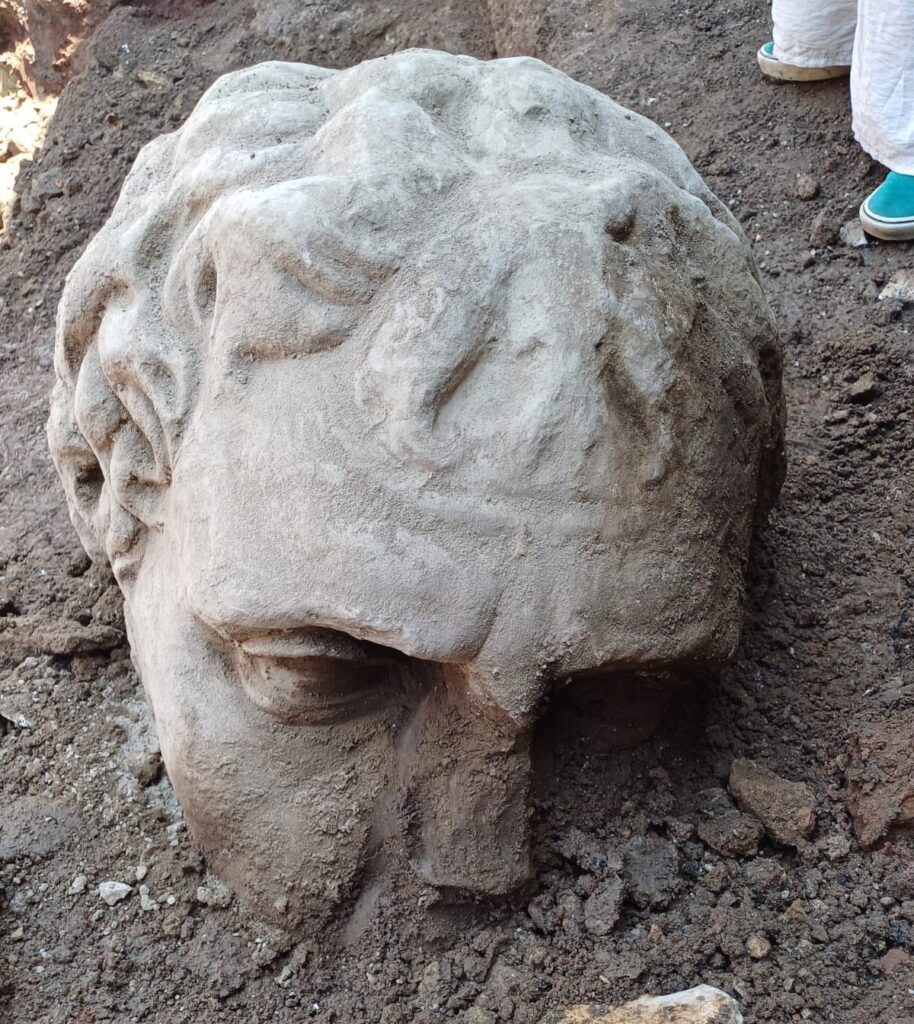

As archaeologists continue to study the find, petrographic analysis will be conducted to determine the marble’s origin and possibly confirm the statue’s identity. Once restored, the sculpture will be displayed at the Museums of the Imperial Forums, adding another chapter to Rome’s vast archaeological legacy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Rome never ceases to amaze,” said Mayor Gualtieri. “Beneath our feet lives a millennia-old story that continues to inspire the world.”
Cover Image Credit: Image shared by Rome Mayor Roberto Gualtieri on his official Facebook page.