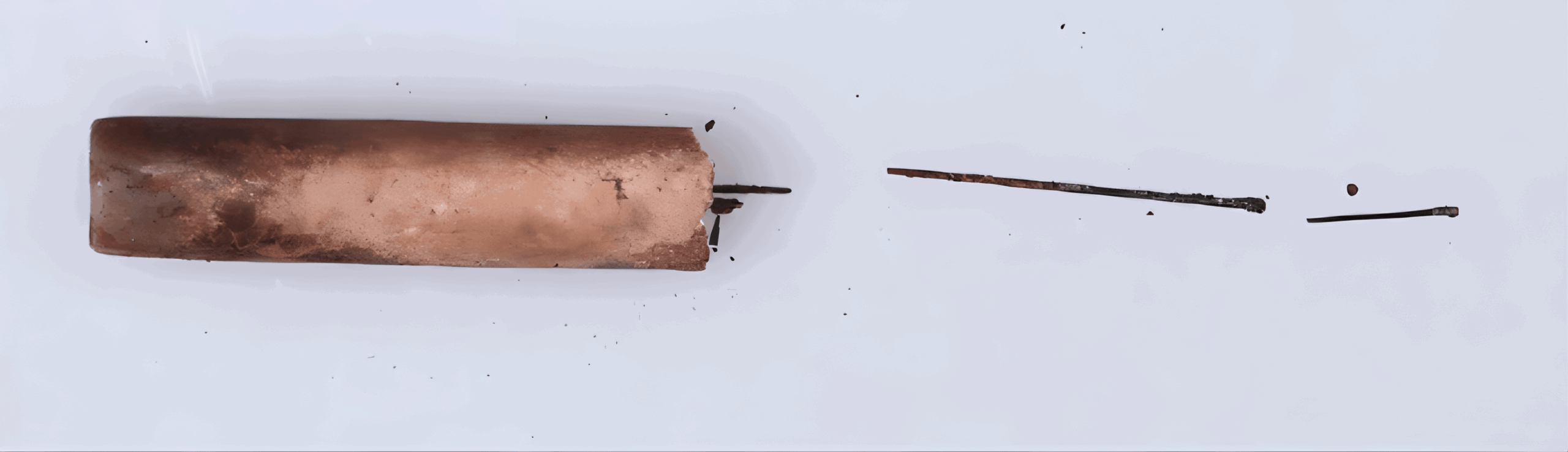
In a discovery that reshapes the history of traditional Chinese medicine, archaeologists have unearthed what experts now confirm to be the world’s earliest known steel acupuncture needles. The artifacts were found in the famed tomb of the Marquis of Haihun, located in East China’s Jiangxi Province, and date back over 2,000 years to the Western Han Dynasty (206 B.C.–A.D. 25).
A Breakthrough in Both Medicine and Metallurgy
According to a report sent to the Global Times by the Jiangxi Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, the needles were discovered inside a jade tube placed within a gilded lacquer box near the remains of Liu He, a briefly reigning emperor who was later titled Marquis of Haihun.
Though heavily corroded and fragmented, five needle remnants were identified. Researchers carefully analyzed those that had naturally detached, avoiding further damage to the rare artifacts. Remarkably, advanced metallurgical analysis revealed that the needles were made of steel produced via the ancient “frying” process—a sophisticated steelmaking method that allowed for the creation of needles as thin as 0.3 to 0.5 millimeters, comparable to those used in modern acupuncture.
Confirmed by Ancient Texts
Lying near the box was a wooden label inscribed with the phrase “Nine Needles Complete,” offering clear evidence of the needles’ intended medical use. This directly ties the find to ancient Chinese medical doctrines that describe nine types of acupuncture needles.
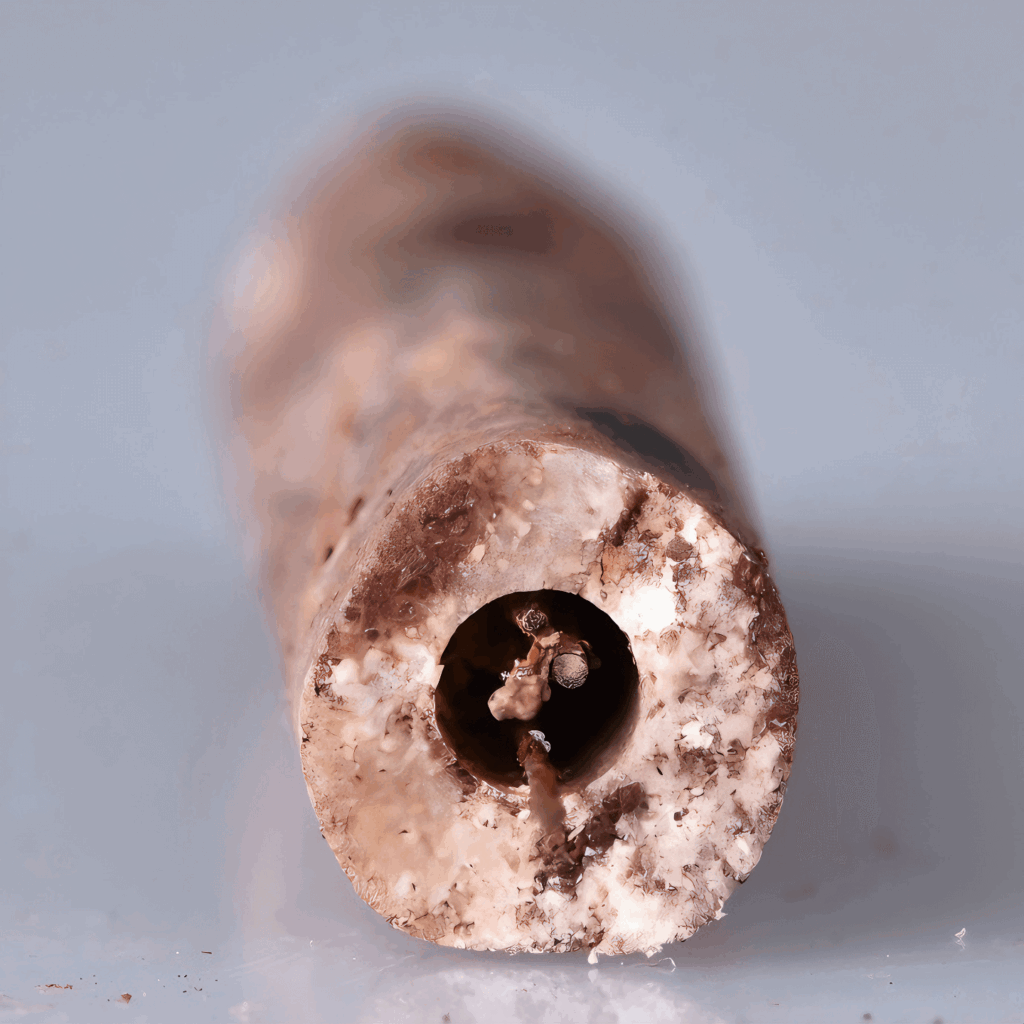

“This definitively identifies them as one type of the ‘Nine Needles’ described in ancient medical texts,” said Wang Chuning, a doctoral researcher at Peking University, as quoted by Xinhua News Agency.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Why Steel Mattered
Experts highlight the technological significance of using steel. Unlike gold or silver, which are too soft, and iron, which rusts and poses an infection risk, steel’s durability and precision allowed for more advanced techniques and longer needle retention in the human body.
“Iron needles rust easily, risking infection. Gold or silver needles are too soft to be made this thin,”
explained Zhou Qi, a research fellow at the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, in an interview with the Global Times.
“This is the earliest physical evidence of steel medical needles in China,” added Gu Man, director of the same institute.
Gu further emphasized that this discovery confirms the integration of cutting-edge metallurgy with ancient medical practice as early as the Western Han Dynasty.
“This breakthrough in material science directly fueled the evolution of acupuncture tools and the progress of medical practice itself,” Gu told the Global Times.
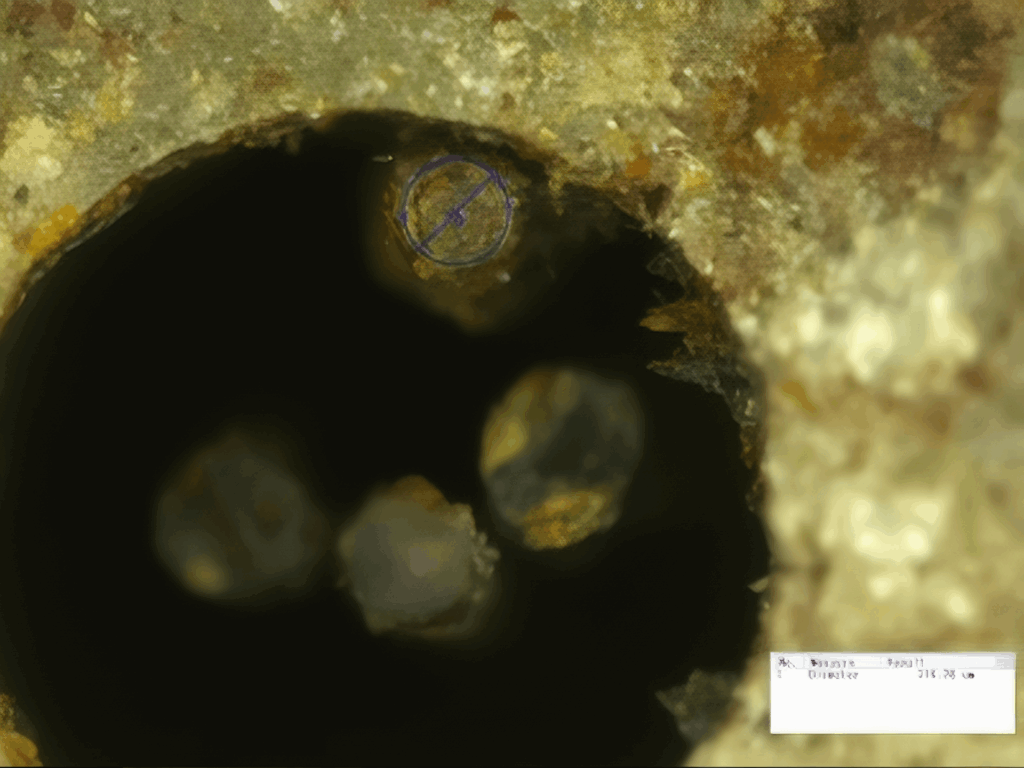

A Tomb of Wonders
The tomb of the Marquis of Haihun, first discovered in 2011, continues to be hailed as one of China’s most significant archaeological sites in decades. Alongside the needles, the site has yielded over 10,000 artifacts, including bronze coins, books written on bamboo and wood, weapons, and a rare set of fish-scale armor.
As researchers continue to excavate and analyze the site, discoveries like these offer rare glimpses into the sophistication of early Chinese science, technology, and medicine.
Cover Image Credit: Yang Jun – Global Times