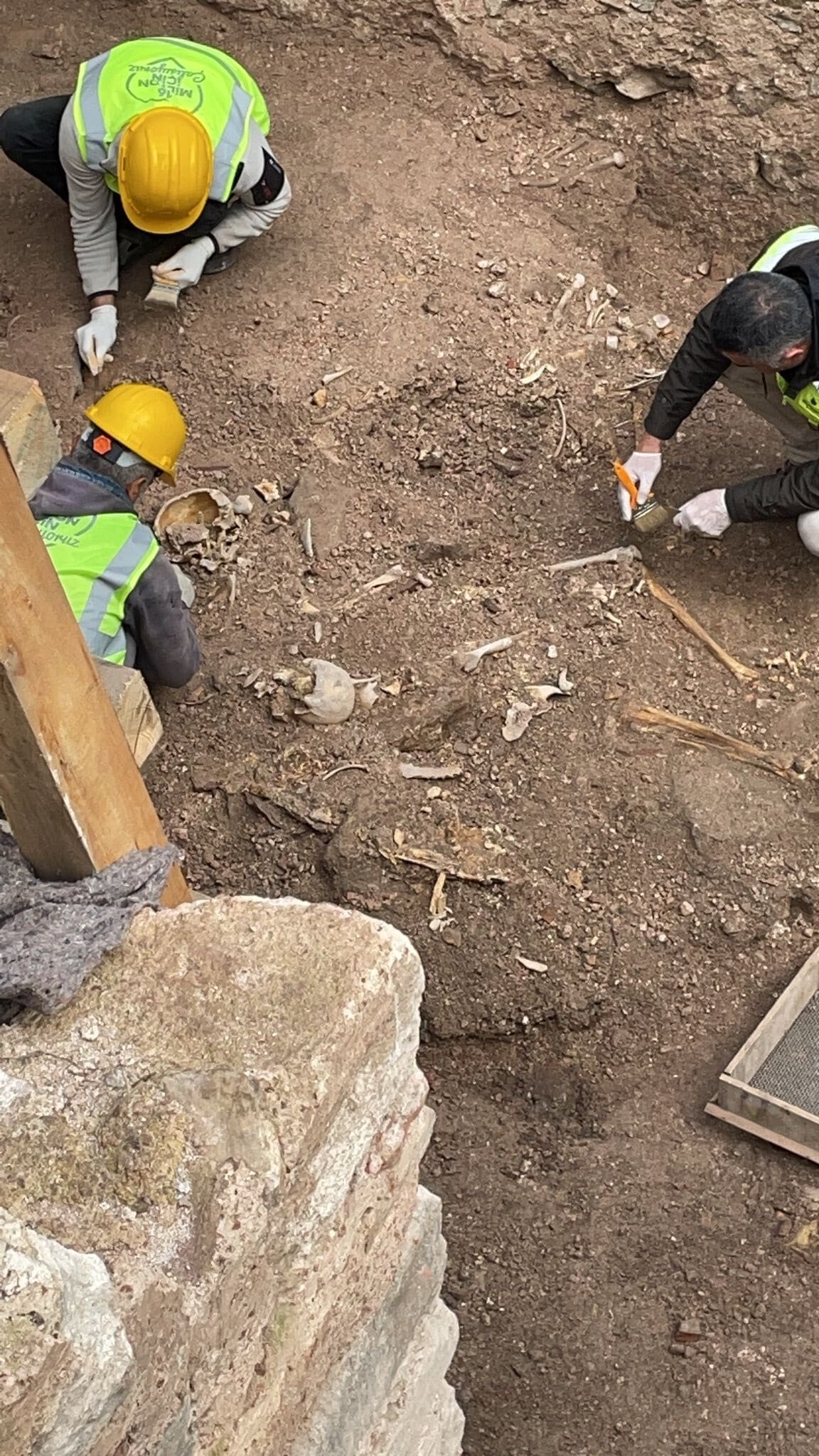
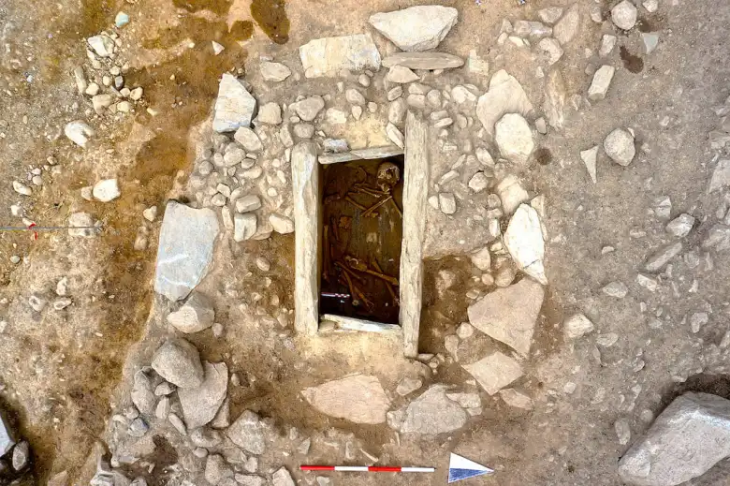
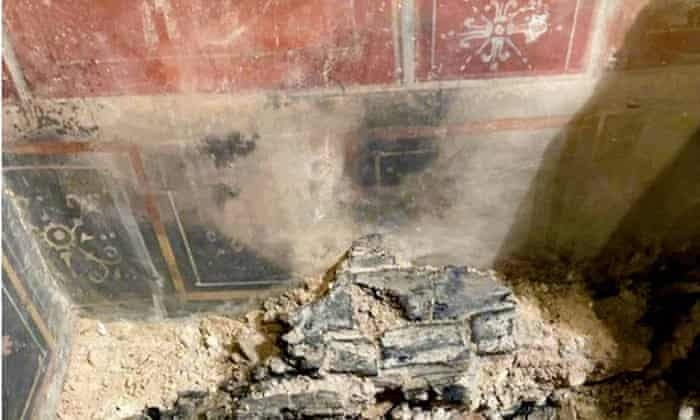
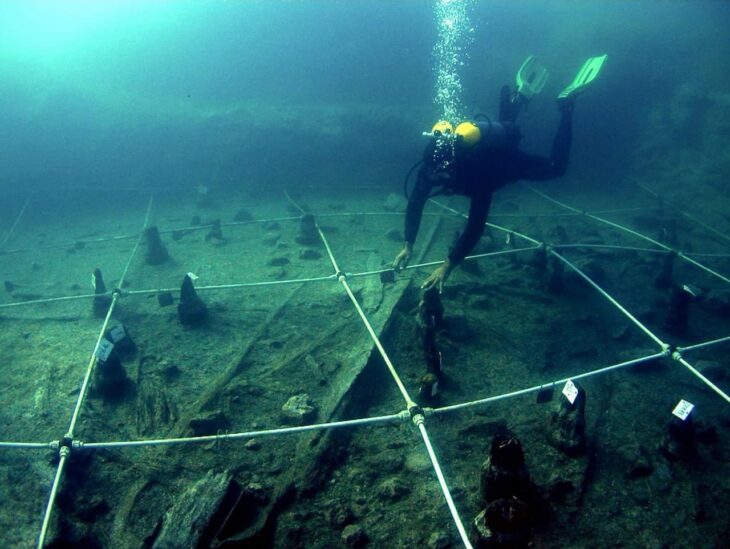
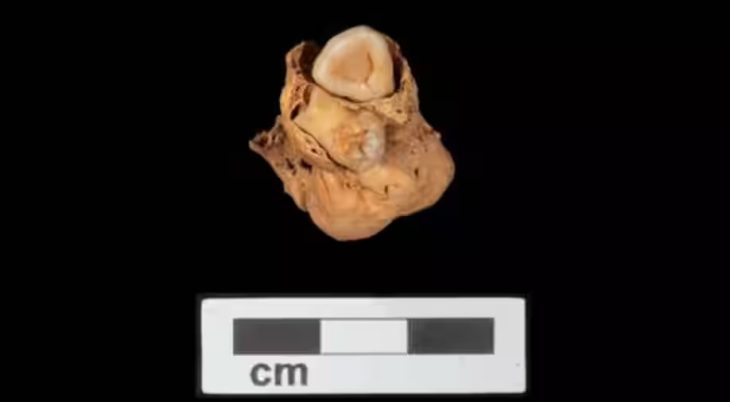
It is thought that the 7 skeletons messy found in the Bukoleon Palace excavations may be the victims of the massacre carried out by the Crusaders in Constantinople.
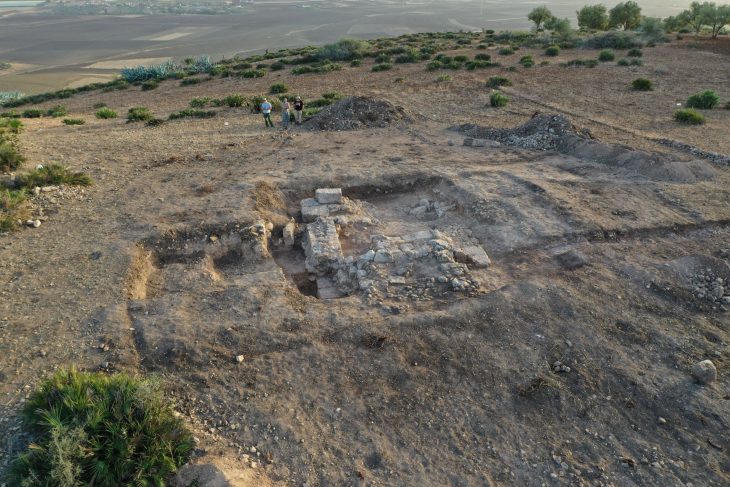
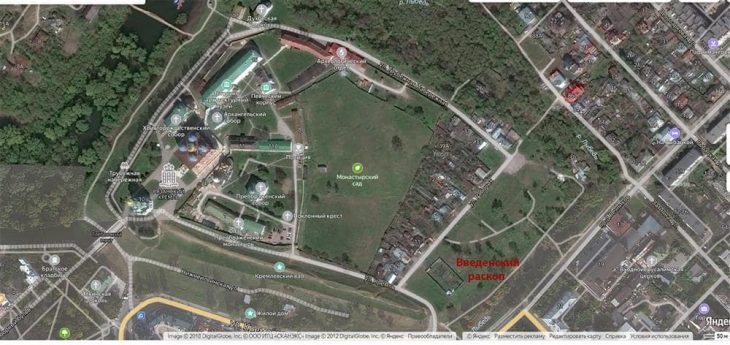
The restoration of the Bukoleon Palace, which is a branch of the restoration and excavation works initiated by the Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality in recent years, continues.
7 skeletons unearthed in a scattered state during the restoration works of the Bukoleon Palace created a great mystery.
What event could the skeletons be victims of?
Unearthed skeletons, an earthquake disaster? Victims of a political murder? Or the victims of the Crusader army massacre in Constantinople? Answers to these questions are sought.
Mahir Polat, Deputy Secretary-General of IBB, informed on his Twitter account that the skeletons found in the excavations of Bukoleon Palace maybe people killed by the Crusaders who attacked Constantinople in 1204 and made a great massacre there.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

In his tweet series, in which he started with “I want to bring a very important issue to your attention,” Mahir Polat conveyed the following information.
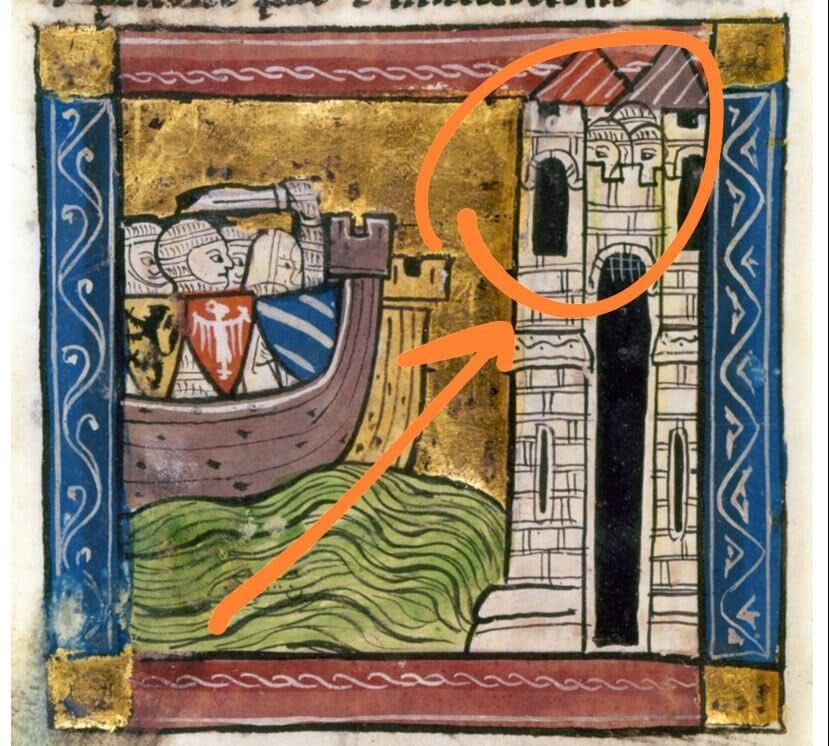
“You see an 800-year-old manuscript miniature depicting the Crusader army attacking Istanbul in 1204, probably in front of the Bukoleon Palace in Istanbul.
The mass body finds we uncovered during the restoration are of great historical importance.
If in the besieged palace during the 4th Crusade if it is about a conflict and a massacre that followed, this miniature is the historical proof of that.
This event was the most important historical fact of the split between the Orthodox East and the Catholic West. This mass murder site, which we uncovered after centuries during the restoration of the Bukoleon Palace, may be the largest surviving remnant of such a great historical event, despite the lack of public and media attention yet.
The background of the famous phrase “I would rather see a Turkish turban than a Latin headdress in Constantinople”, said by Lukas Notaras, who was in the ranks of Byzantium in the 1453 conquest, is of this massacre 200 years ago.

It is very important for the history of Istanbul in terms of the effects of the 4th Crusade
“We will continue to work on this very important archaeological find for the history of Istanbul.
We will determine the age of the corpses, especially with archaeometric studies and C14 examination.
This miniature, which is very valuable to us, is in The Granger Collection.
I would like to draw your attention to the point where the soldiers are in this miniature building, which was attacked by the Sea of Marmara and which we think is the Bukoleon Palace with its wide arched opening.
This point coincides with the part of our excavation where we found the bodies.
Now let me come to the most important point.
These corpses may be the corpses of the soldiers we see in the picture.
Here is the story of an incredible archaeological find that is worth getting excited about. As Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality Heritage, we held our breath during the restoration of the Bukoleon Palace.
We continue to work,” he said.