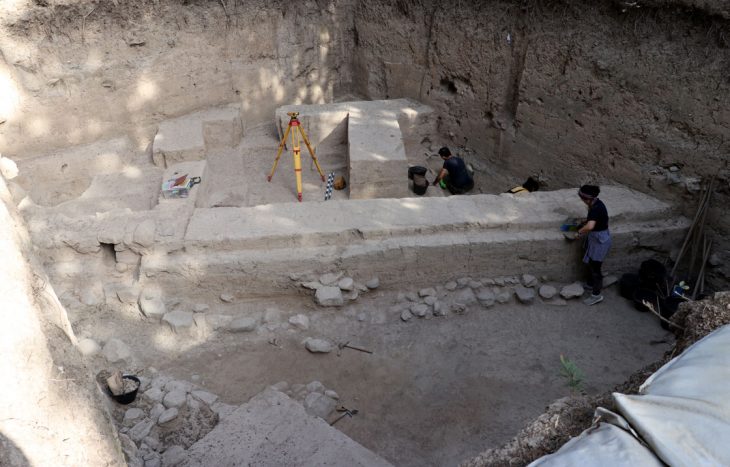
The Egyptian Ministry of Antiquities announced on July 15 that a team of Czech archaeologists, while excavating near the Giza Plateau, discovered a tomb belonging to a powerful Egyptian military commander who lived 2,500 years ago.
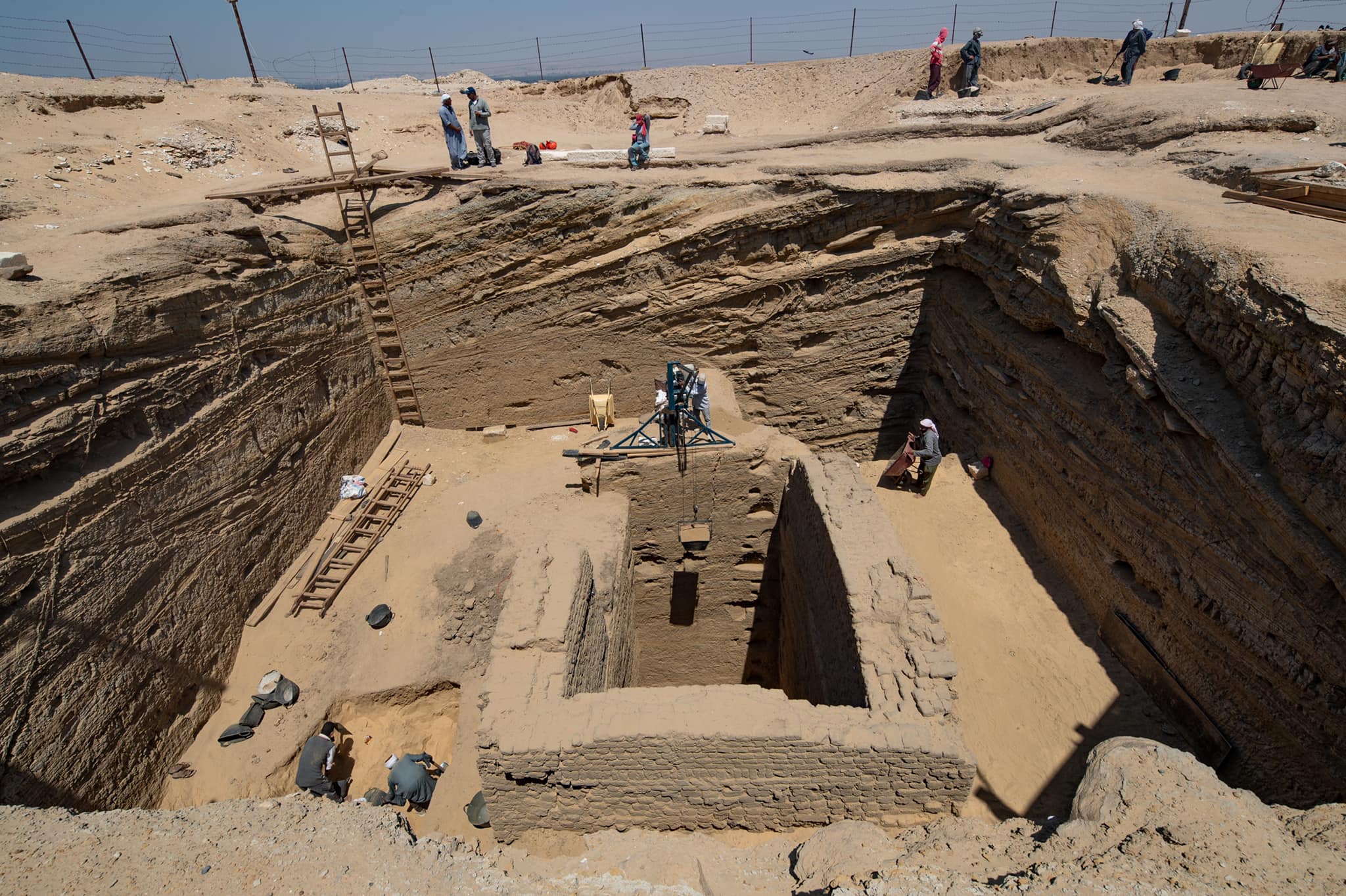
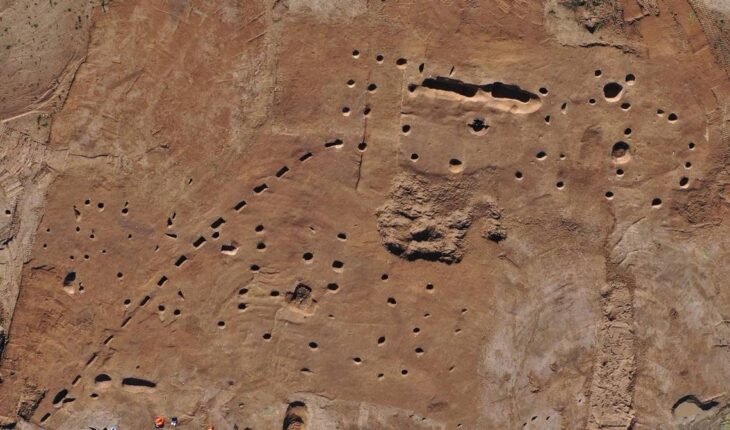
The ancient commander’s tomb was discovered by Czech researchers about 7.5 miles (12 kilometers) from the Pyramids of Giza, near the Old Kingdom cemetery and the Abusir archaeological site. Notably, the tomb was located near Wah-Ib-Ra Meri Nate’s embalming stash, which was discovered four months earlier. The finding of the latter suggested that the commander was buried nearby, so the archaeologists were not shocked to find this burial site where they did.
In a press release, the ministry said that the discovery is “unique of its kind” and provides new insight into the turbulent period of the beginning of the era of the Persian domination of ancient Egypt and puts forward the first evidence of true globalization in the ancient world. [The tomb also] offers a new insight into the turbulent period of the beginning of the era of the Persian domination of ancient Egypt.
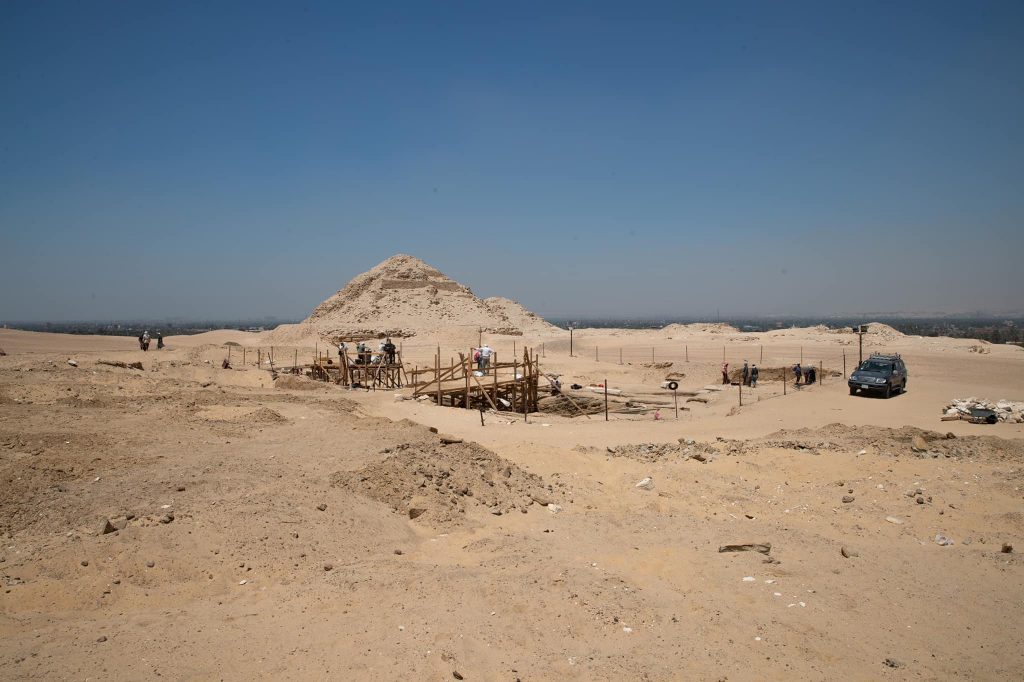

The cemetery documents a period when the ancient Egyptians lived in the 6th century BC. During this period, the Egyptians greatly expanded their sphere of influence. therefore, the kings of the 26th dynasty [664-525 BC] brought in foreign mercenaries and united them in many parts of the country, including the army.
Mostafa Waziri, Secretary-General of the Egyptian Supreme Council of Antiquities, stated in a ministry statement that the design of this good tomb was unsurpassed in ancient Egypt.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
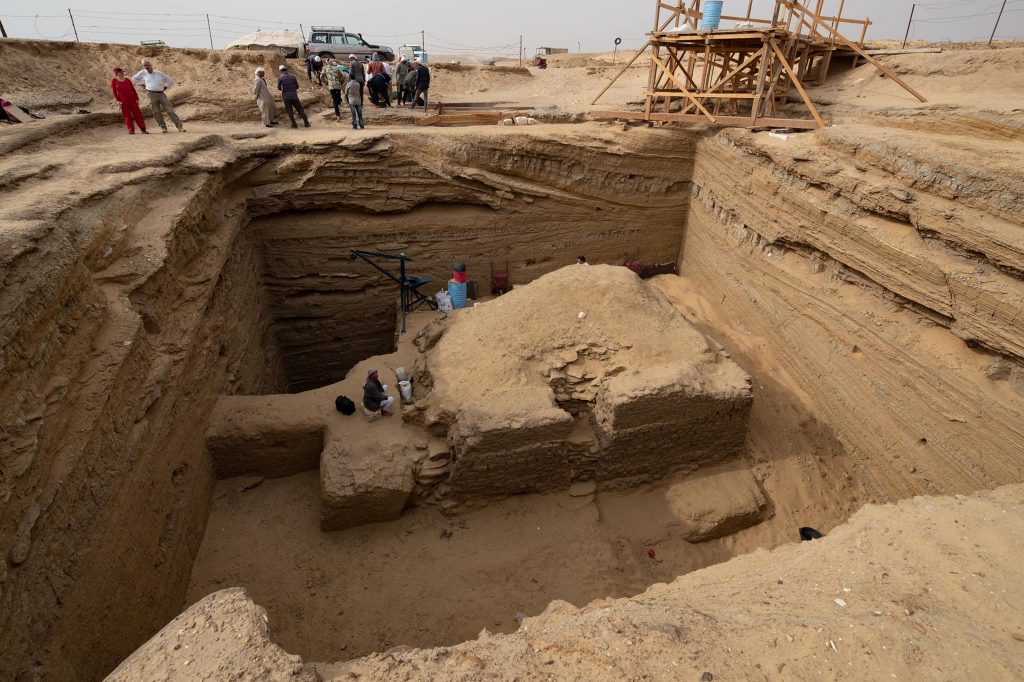

Wah-Ib-Ra Meri Nate was buried in a large, square tomb with two levels that were excavated especially to house the revered commander’s bones. The main shaft was around 45 feet by 45 feet (14 meters by 14 meters) in size and was nearly 20 feet (six meters) deep. Below it, a smaller shaft, rectangular in shape, 11 feet by 21 feet long, was dug into the bedrock (6.5 meters by 3.3 meters).
At the bottom of this second tunnel, some 52 feet underground, the commander’s mummified body was placed (16 meters). He was interred in a complex double sarcophagus with an inner and an outer part. The inside coffin was fashioned from basalt and sculpted into the shape of a human body, while the exterior sarcophagus was built from two massive slabs of white limestone. The basalt sarcophagus’ overall dimensions were 7.5 by 6.5 feet (2.3 by 1.98 meters).
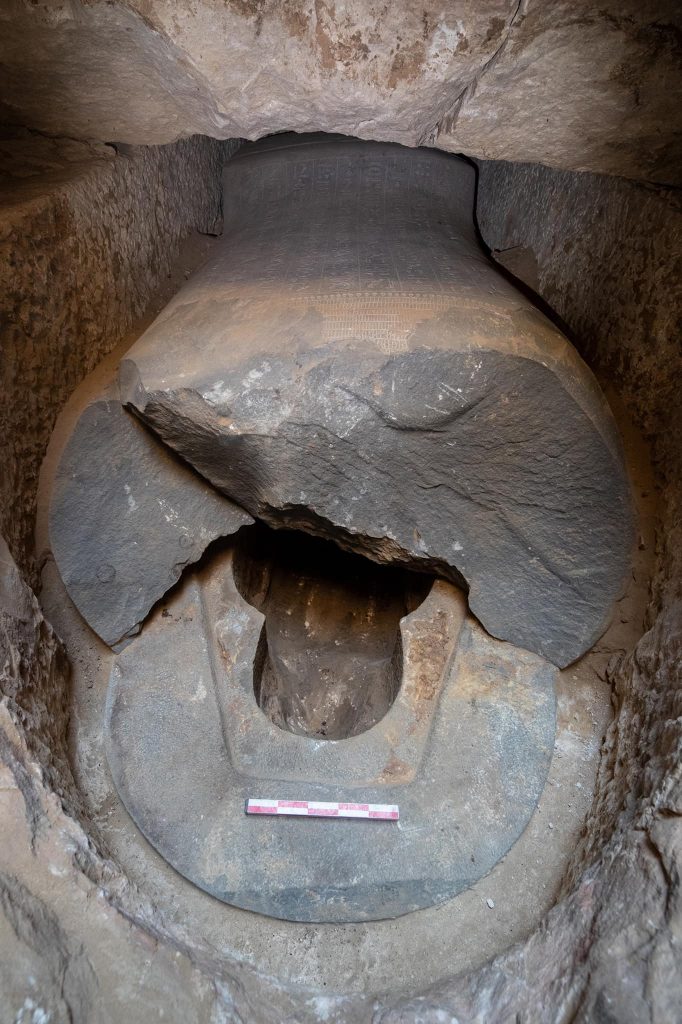

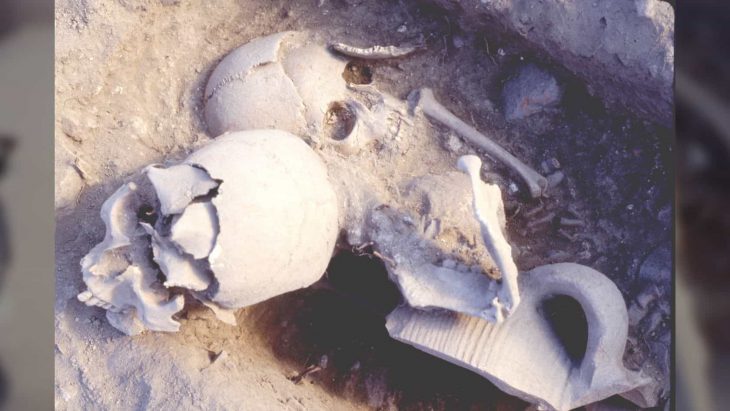
The archaeologists were disappointed to see that this great discovery was defeated by the tomb thieves and the sarcophagus was smashed open and the mummy of Wah-Ib-Ra Meri Nate was removed. Based on the finding of two pottery objects left within the tomb that belonged to the fourth or fifth century AD, they determined that tomb robbers had broken in and taken it more than 1,000 years ago.
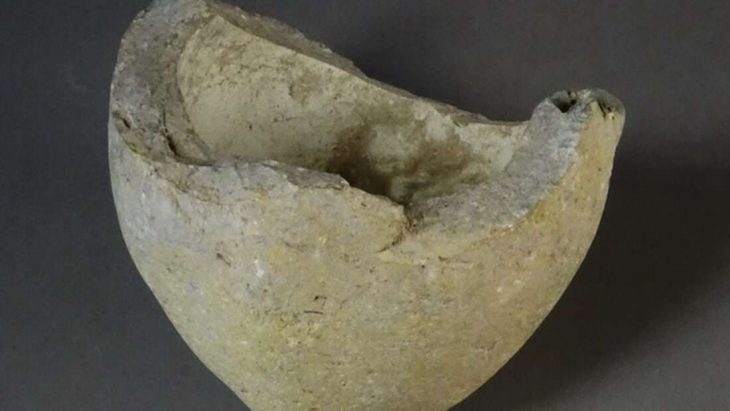
In addition to the absence of a mummy, the area inside the basalt sarcophagus was devoid of grave goods. Only a scarab delicately carved into the shape of a heart and an amulet supposed to be worn on the head was discovered.
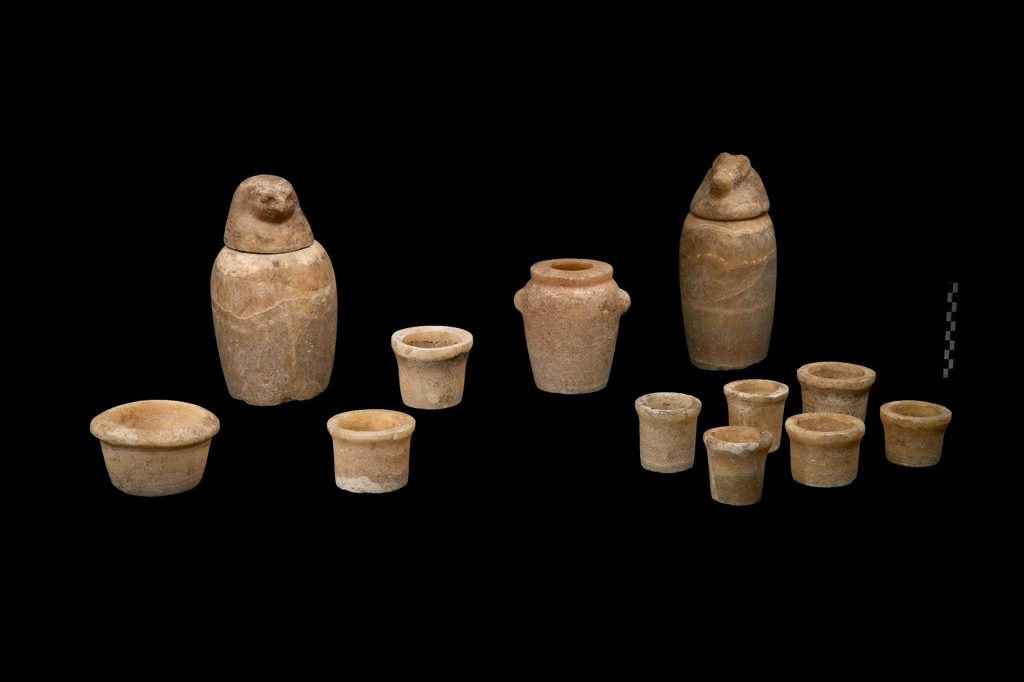

However, the mission found on the eastern side of the necropolis many intact archaeological relics that were part of the funerary belongings, including 402 Ushabti statues made of faience.
Ushabtis, which are little figurines that were placed in ancient Egyptian tombs along with mummies that often had writing from the Book of the Dead, was thought to represent the departed and carry out tasks for them in the hereafter.