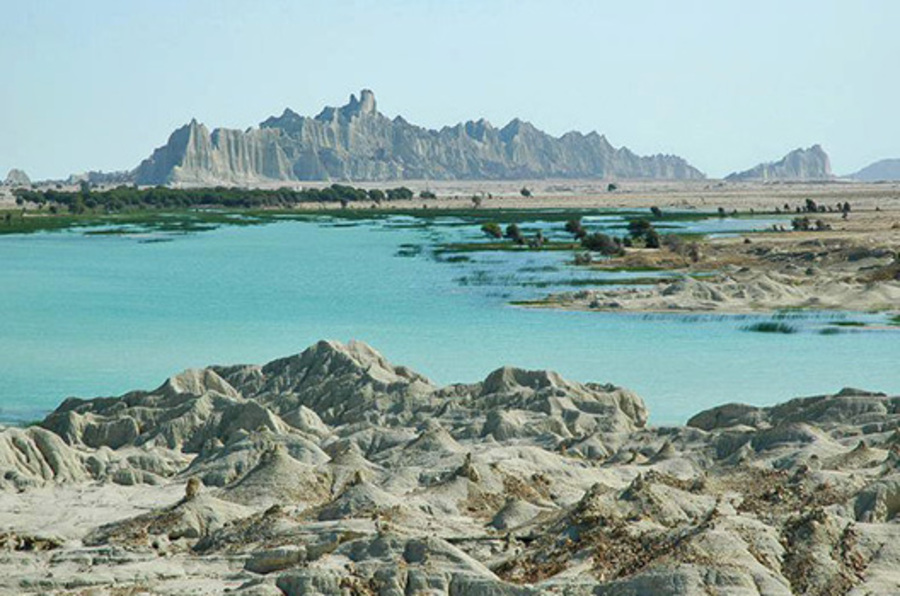
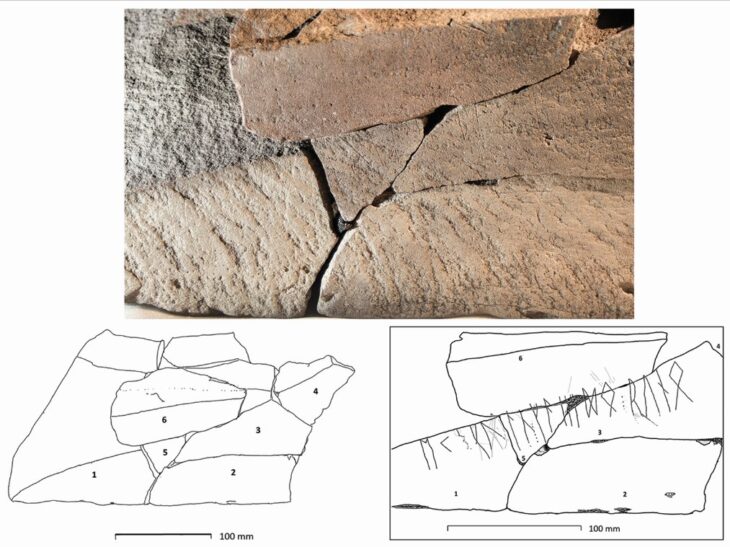
The Makran coast, a historically rich coastal stretch along the Sea of Oman, has once again drawn archaeological attention with groundbreaking discoveries revealing prehistoric maritime life and fishing activities.
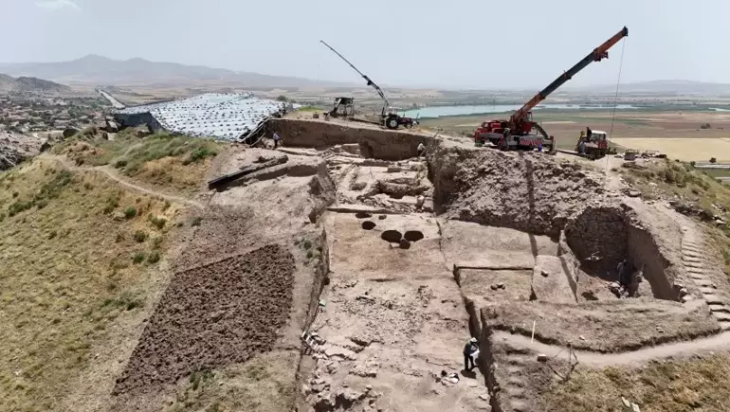
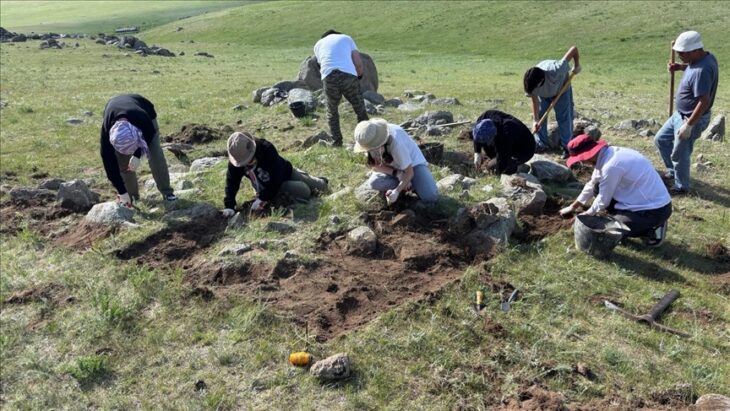
A team of Iranian archaeologists, led by Mortaza Hessari, has uncovered compelling evidence of ancient marine exploitation at the Kopal site in Dashtiari County, Sistan-Baluchestan province. These findings shed light on the continuous human reliance on the sea across multiple cultural periods, stretching as far back as the Paleolithic era.
Rare Prehistoric Fishing Tools Discovered
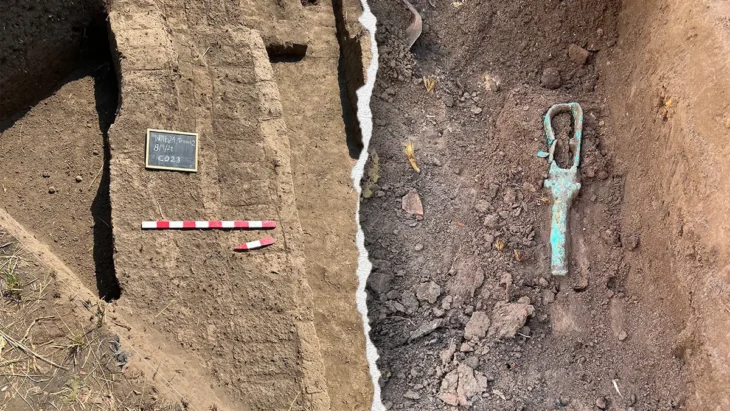
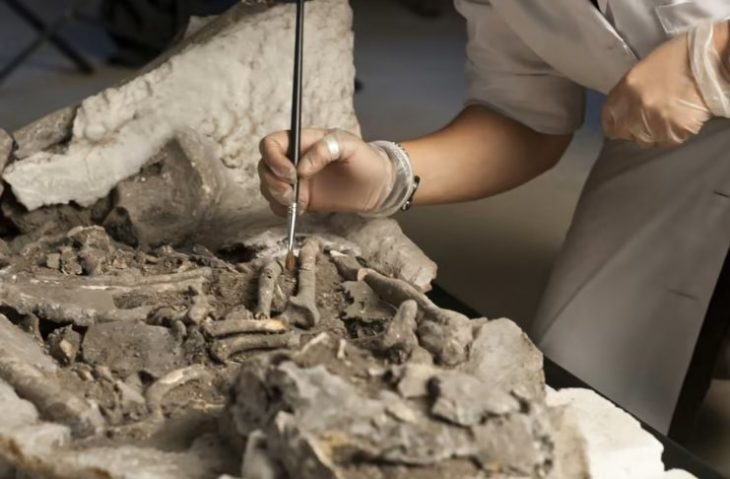
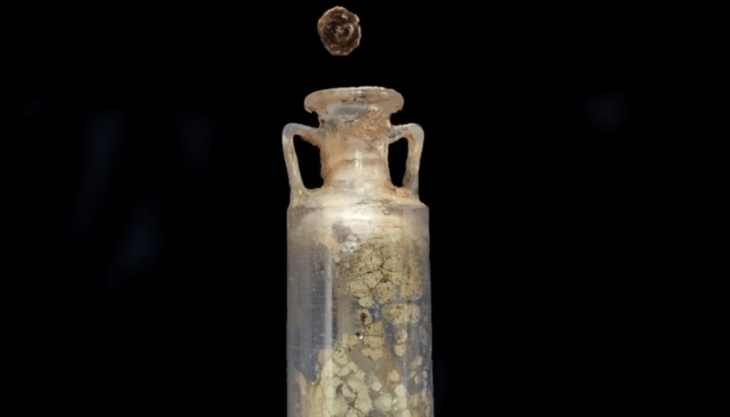
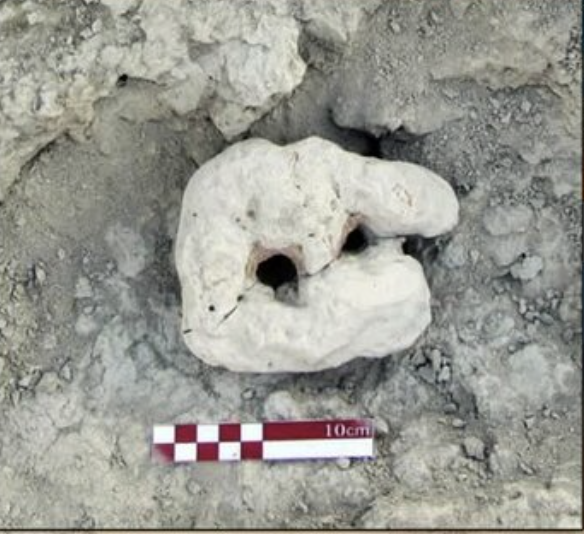
Among the most striking discoveries are stone fishing hooks, net weights, shell deposits, and bones of marine animals—unearthed alongside ceramic fragments dating to the 4th millennium BCE. These artifacts suggest that early coastal communities engaged in organized fishing practices and sustained marine resource utilization thousands of years ago.
“These findings are unprecedented in the region,” stated excavation leader Mortaza Hessari. “They not only highlight Paleolithic stone tools but also provide strong archaeological evidence of systematic fishing practices in prehistoric times.”
One particular trench revealed a fishing weight adjacent to shellfish remains and pottery, offering a snapshot into the diets and technologies of ancient coastal societies. Experts believe that laboratory analysis of these remains could identify specific aquatic species harvested in the region, offering deeper insights into environmental and economic aspects of prehistoric life.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Site at Risk Amid Modern Development
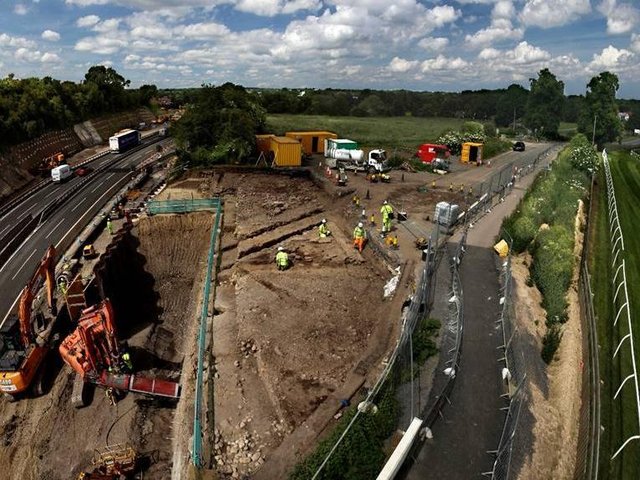
Despite the significance of the Kopal site, it faces an imminent threat due to road construction projects. This prompted a salvage excavation, initiated under the Cultural Heritage and Tourism Research Institute, to rescue vital archaeological data before it is lost.
“The urgency of our work is tied to modern development,” Hessari noted. “We’re racing against time to preserve a critical piece of Iran’s maritime heritage.”
The excavation team credited the support of local officials, including Governor Abdolaziz Miaei of Dashtiari County, and the Chabahar Cultural Heritage Department, for facilitating this critical research.
“Their cooperation has been invaluable in allowing us to progress swiftly and efficiently,” Hessari added.
Looking ahead, Hessari expressed optimism that these efforts could lay the foundation for a Makran Cultural Heritage Studies Center. Such an institution would serve as a regional hub for research, education, and preservation of the unique cultural and maritime heritage of southeastern Iran.

Makran Coast: A Maritime Crossroads of Antiquity
The Makran coast, or Savahel-e Makkoran in Persian, has long held strategic and cultural significance as a maritime corridor between the Middle East, South Asia, and East Africa. Archaeological and historical records suggest the region was once part of early trade networks, linking ancient Persia with civilizations as far afield as Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley.
With its semi-arid terrain hugging the Sea of Oman, this region was not only a geographic bridge for trade and migration but also a cradle of early coastal settlement and marine subsistence.
Recent archaeological discoveries, including Paleolithic stone tools, fishing implements, and marine remains, have revealed that human interaction with the sea in Makran dates back to prehistoric times. These findings underscore the region’s significance not just as a strategic waypoint for ancient seafarers and merchants, but as a thriving center of early maritime culture, where fishing, shell gathering, and seaborne trade played a central role in daily life. The Makran Coast thus offers invaluable insights into how early societies adapted to and harnessed marine environments long before the advent of written history.
These recent findings add another chapter to the long and diverse story of Makran, reinforcing its role as a cradle of human innovation and coastal adaptation.
Cover Image Credit: Fatemeh Aman
Source: Tehran Times