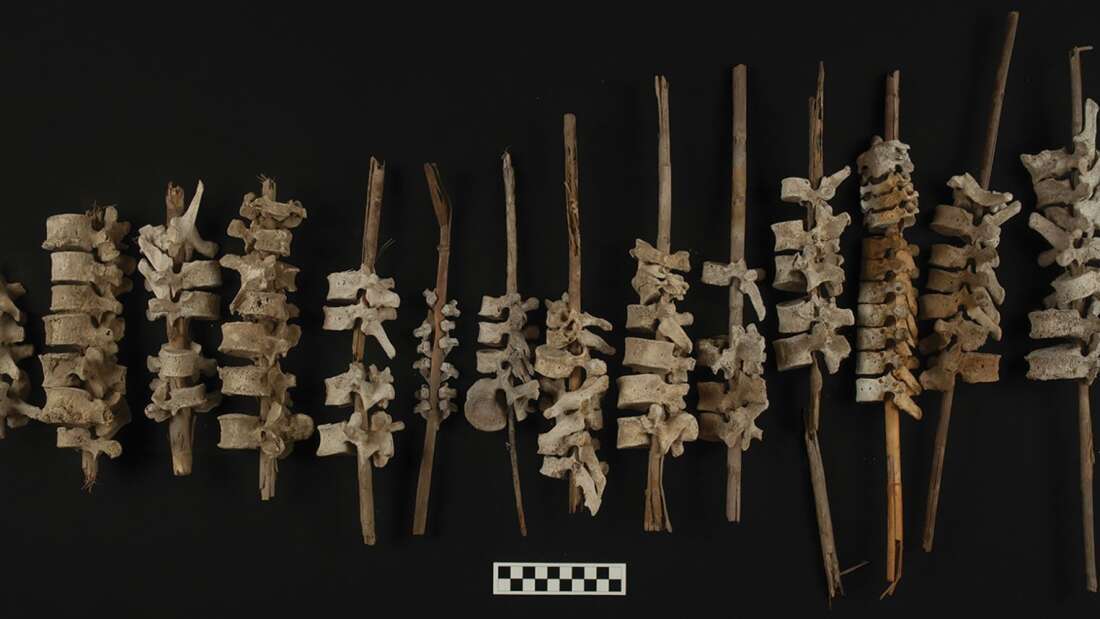
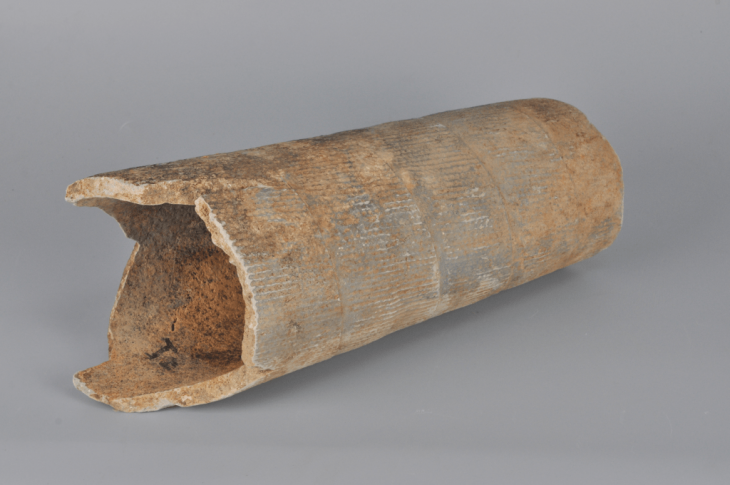
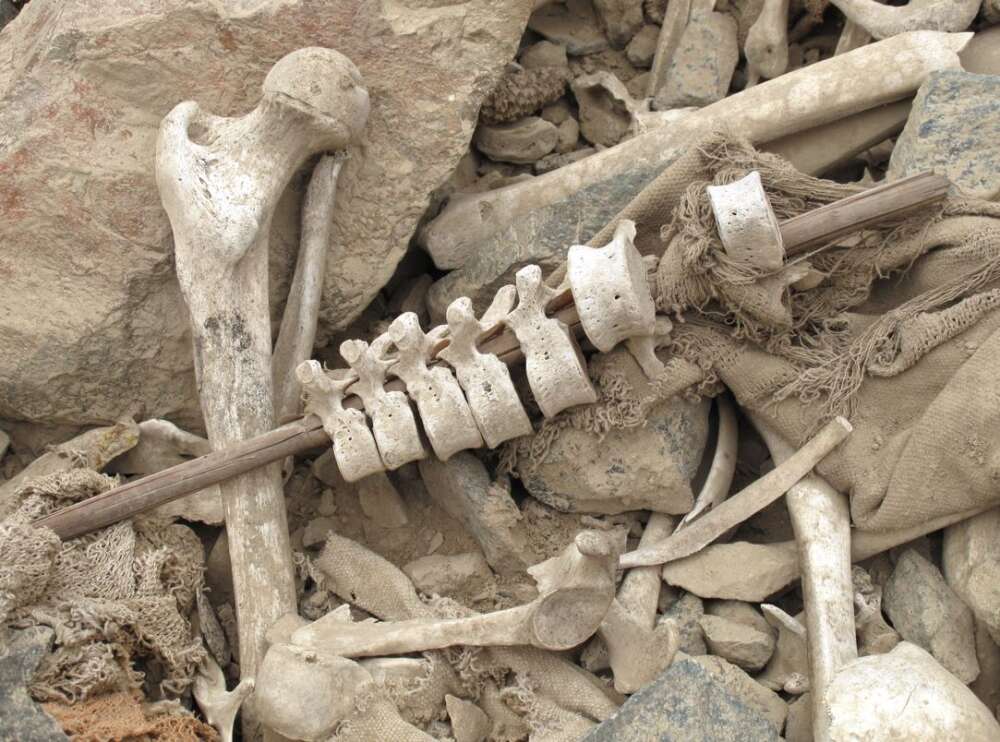
Archaeologists have found almost 192 examples of human vertebrae threaded onto reed posts 500 years ago in the Chincha Valley of Peru.
Between AD 1000 and 1400, the Chincha Valley was home to the sophisticated Chincha Kingdom. They established an alliance with the Inca Empire and were eventually consolidated into it.
The discovery, published in the journal Antiquity, highlights an Andean burial tradition that has only been found in this specific area of Western Peru, which is known as the Chincha Valley.
The Ancient spines threaded were recovered from burial sites in the Chincha Valley, where the local community was decimated by famine and disease epidemics following the arrival of Europeans.
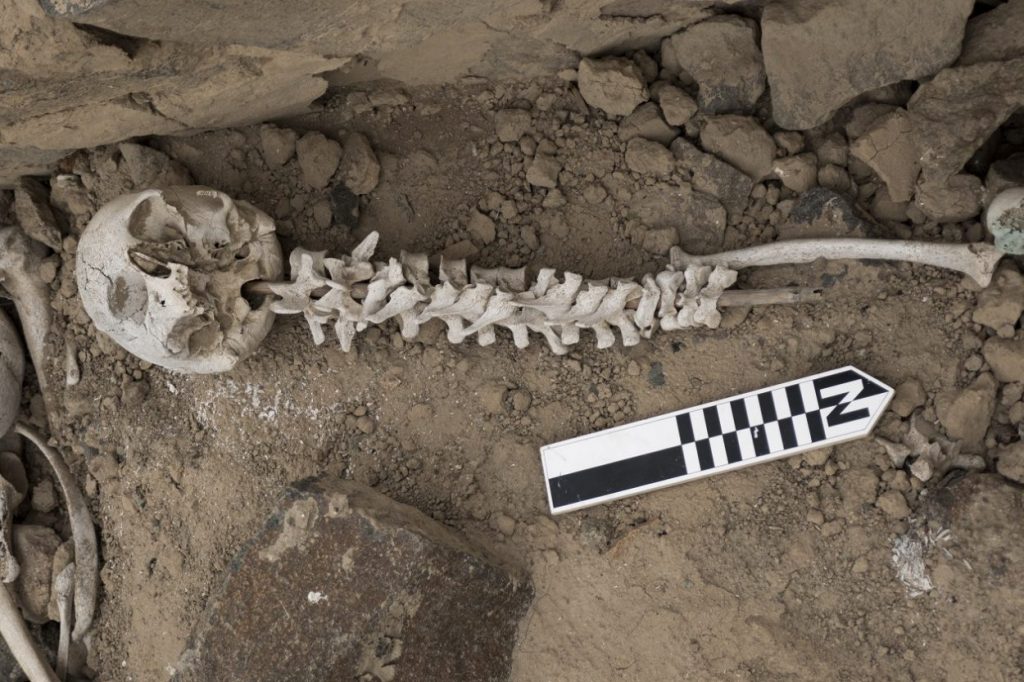

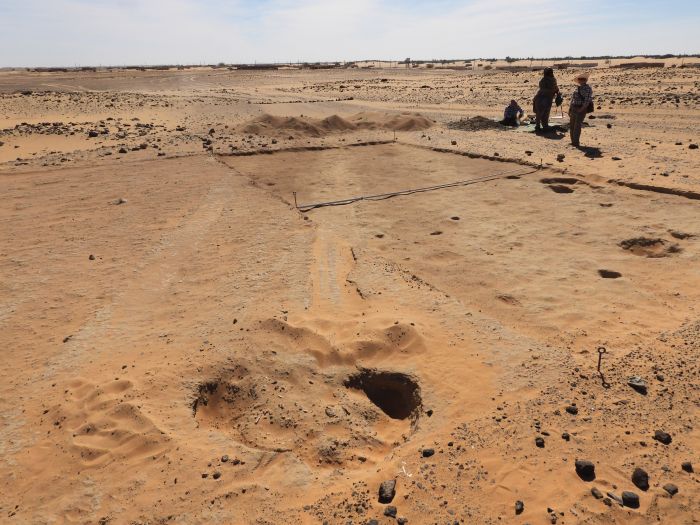
The team was excavating elaborate indigenous graves known as chullpas, where they found human vertebrae threaded onto reed posts that date from the 16th century AD.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
According to the researchers, the Chincha population declined from over 30,000 households in 1533 to just 979 half a century later, and many of the dead would have been ritually buried along with precious items made of gold.
It is therefore telling that all of the vertebrae-on-posts were dated to between 1450 and 1650 CE, a period when European colonialists raided and destroyed large numbers of indigenous graves in the region.
“Looting was primarily intended to remove grave goods made of gold and silver and would have gone hand in hand with European efforts to eradicate Indigenous religious practices and funerary customs,” explained study author Dr. Jacob L. Bongers from the University of East Anglia.
It is thought that the spines were reconstructed and held together with reeds many years after death, possibly due to the graves being looted and damaged by European settlers. The dead being buried intact was an important part of the culture of the Chincha people, so their reconstruction and reinterment would have been highly significant.
The discovery was made by an international team of researchers. Find out more.