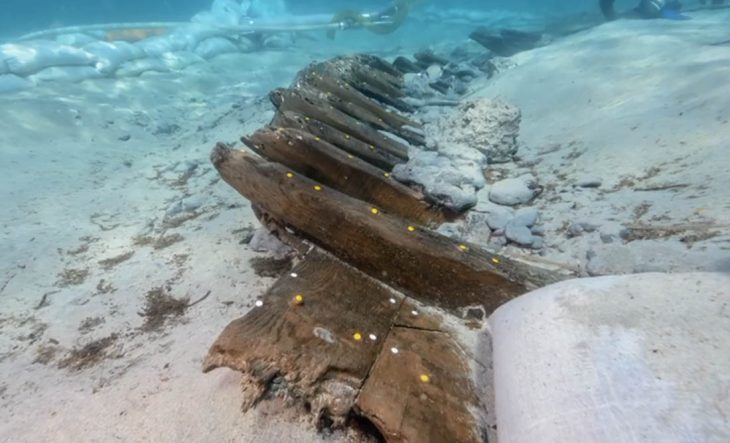
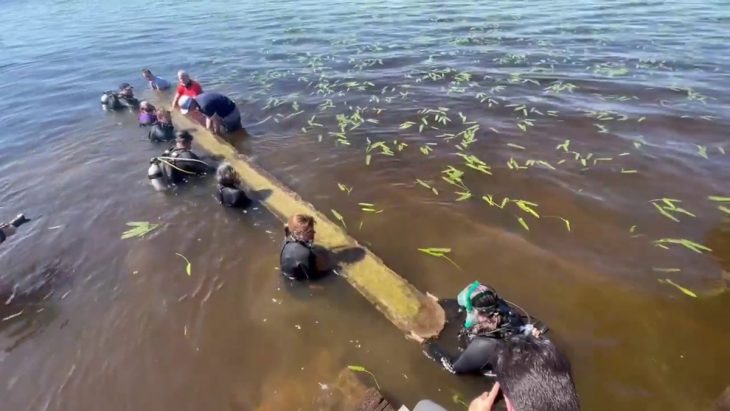
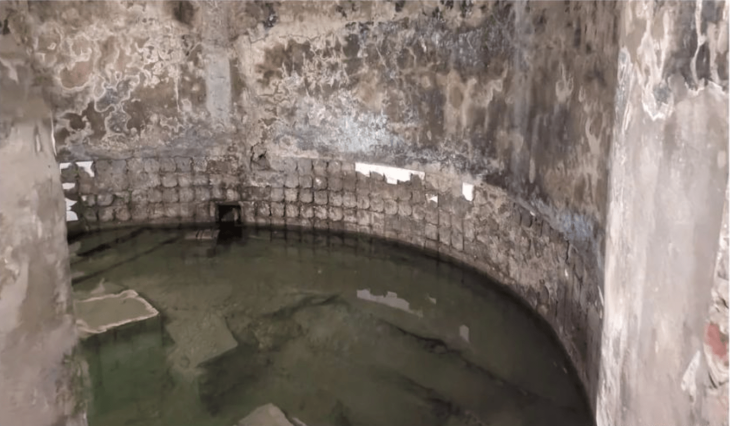
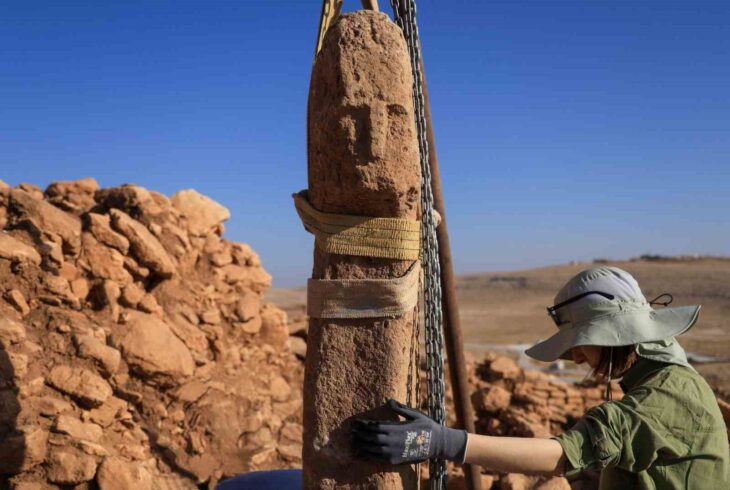
The team from the University of Chester, Heneb: the Trust for Welsh Archaeology (Clwyd-Powys region), and the Portable Antiquities Scheme have uncovered a Roman settlement and what is thought to be an extremely rare early Medieval longhouse in North East Wales.
A new dig unearthed important structural features and materials dating to the Roman era and, from initial indications, the early Medieval period, during an excavation at a site near the Holt Roman tile and pottery works, in Wrexham.
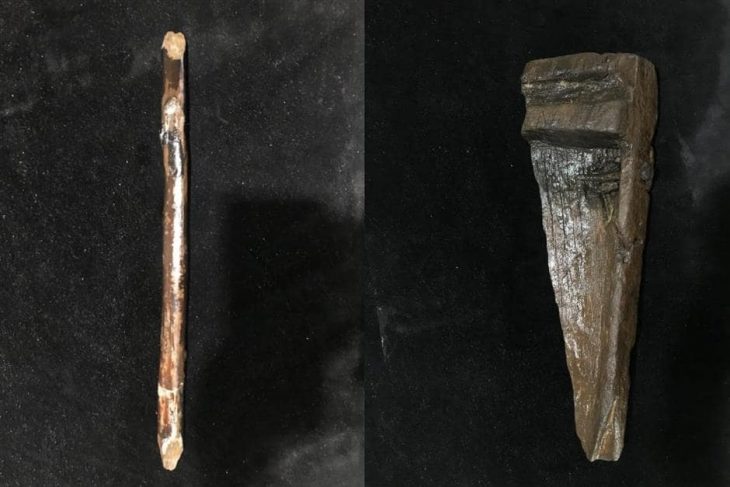
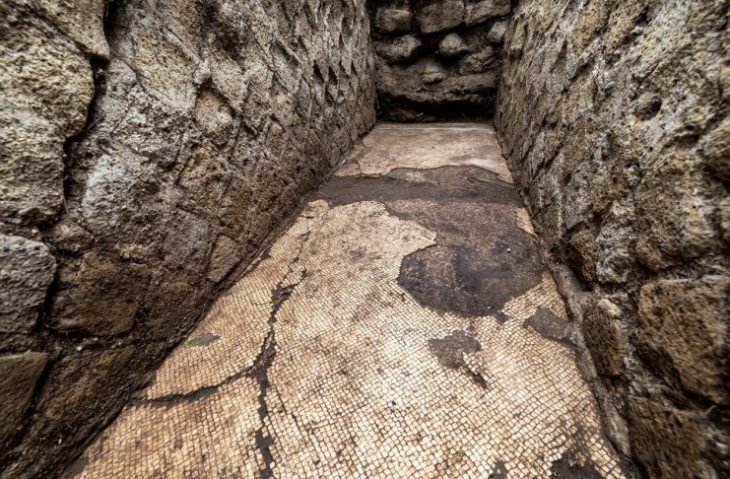
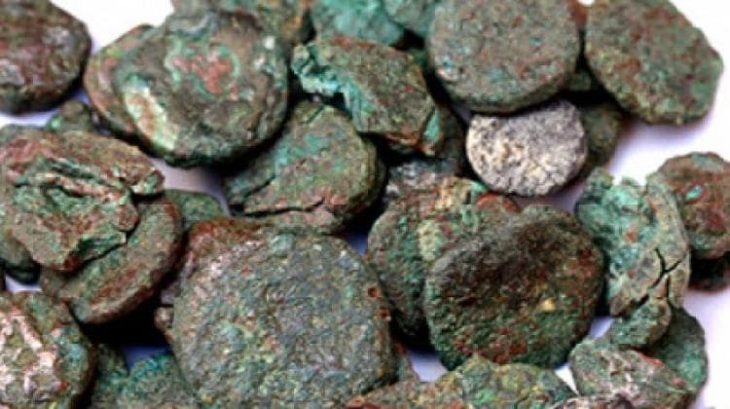
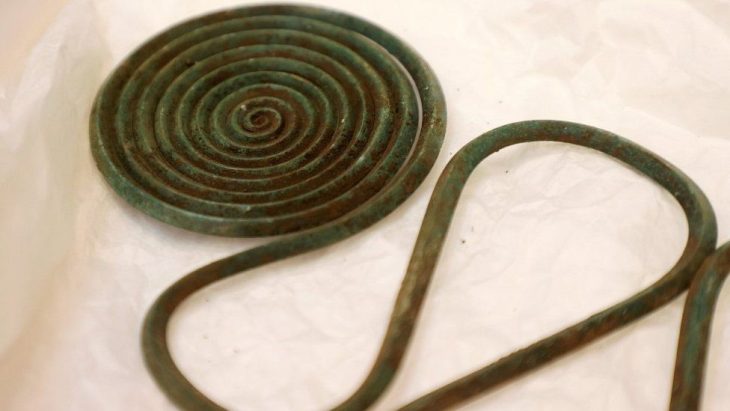
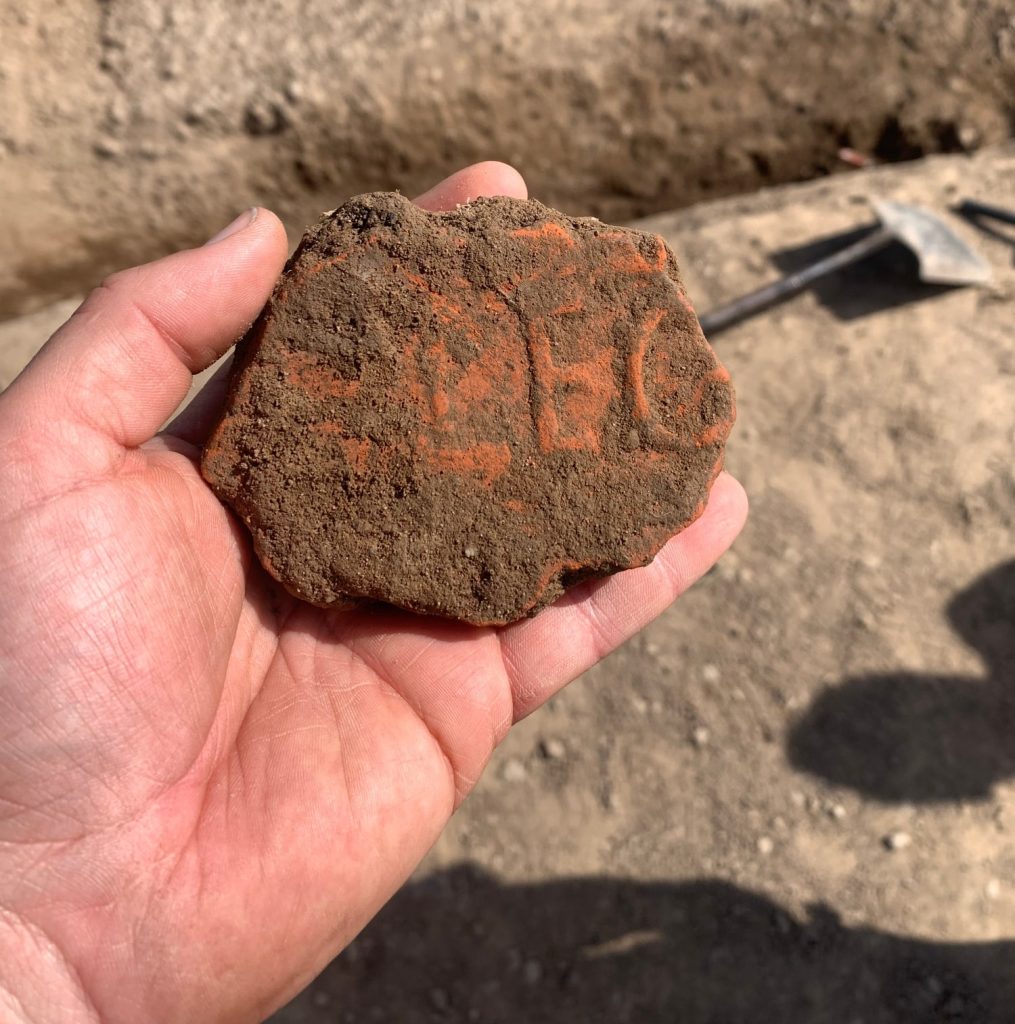
In addition to a trackway, buildings, building materials, ceramics, including a stamped legionary tile, and a fragment of a brooch that suggests there was also a Roman settlement at the site, the team, which included volunteers from the community and students from the University of Chester, appears to have discovered the structure of an early Medieval longhouse, a long, narrow building for communal dwelling.
The project was led by Chris Matthews of Heneb, Dr Caroline Pudney of the University of Chester and Steve Grenter, former county archaeologist and Heritage Services Manager at Wrexham County Borough Council, with support from Dr Susie White, Finds Liaison Officer for the Portable Antiquities Scheme (PAS Cymru).

A short documentary on the excavations and discoveries is due to be released later this year.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr Pudney, Senior Lecturer in Archaeology at the University of Chester said: “We were very hopeful of finding evidence of Roman life due to previous discoveries and geophysical surveys in the area, not to mention the presence of the legionary tileworks a few fields away, but did not expect our excavations to uncover what is believed to be an early Medieval longhouse.
“The discovery of a Roman settlement is extremely important in building a bigger picture of Roman Wrexham and although early Medieval longhouses have been found in other parts of Wales, to unearth evidence of such a building in North East Wales is extremely rare.”
Mr Matthews, Project Archaeologist and Geophysicist with Heneb added: “While we are yet to begin the post-excavation investigations, during which all the findings will be analyzed, the samples processed and scientific dating obtained, this is potentially a very exciting new find for the region, which could help us to fill in current gaps in understanding about the construction and use of Medieval longhouses.”
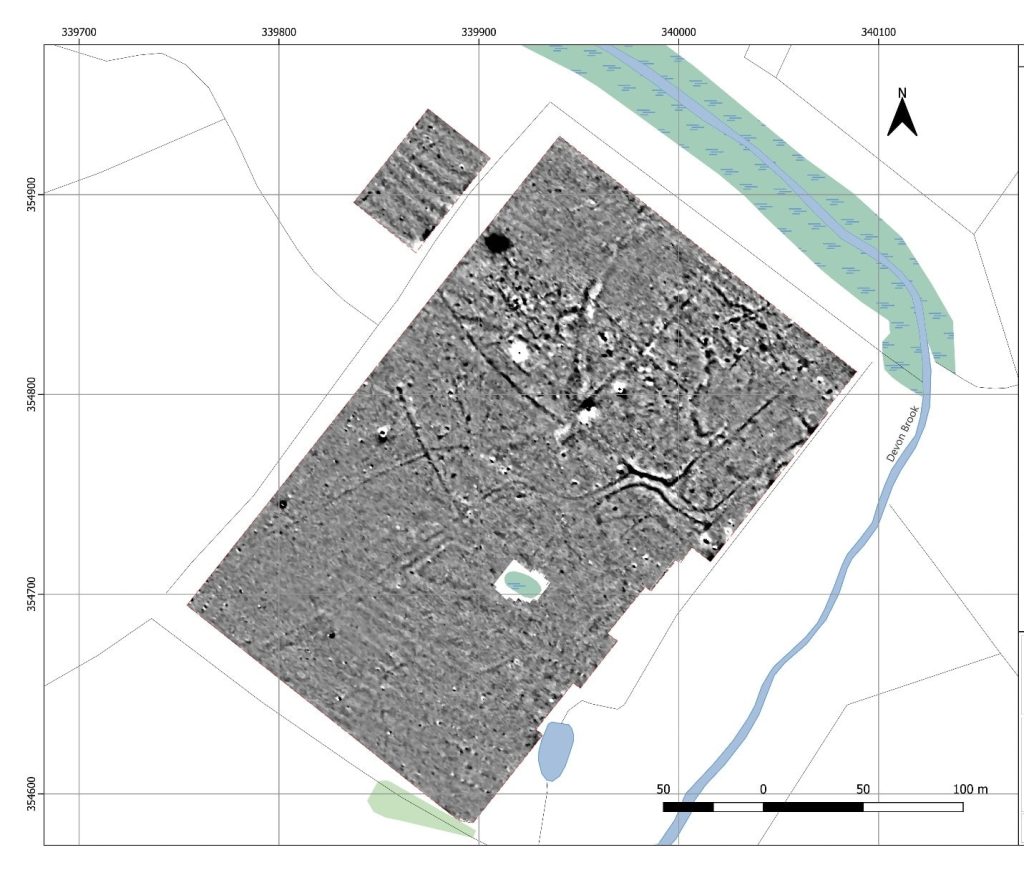
The dig followed trial trenching carried out by the Holt Local History Society between 2013 and 2017, during which a significant quantity of Roman ceramics and other objects were recovered. An examination of these artifacts, some of which are now held by the Wrexham Museum, led to Heneb and the University of Chester undertaking geophysical surveys which further enhanced the site’s archaeological potential.
Despite unfavorable geological conditions, the surveys, which comprised high-resolution magnetometry, revealed a clear outline of a gridded settlement and road system, as well as distinct rectangular structures just outside the settlement boundaries.
cover Image: University of Chester
















