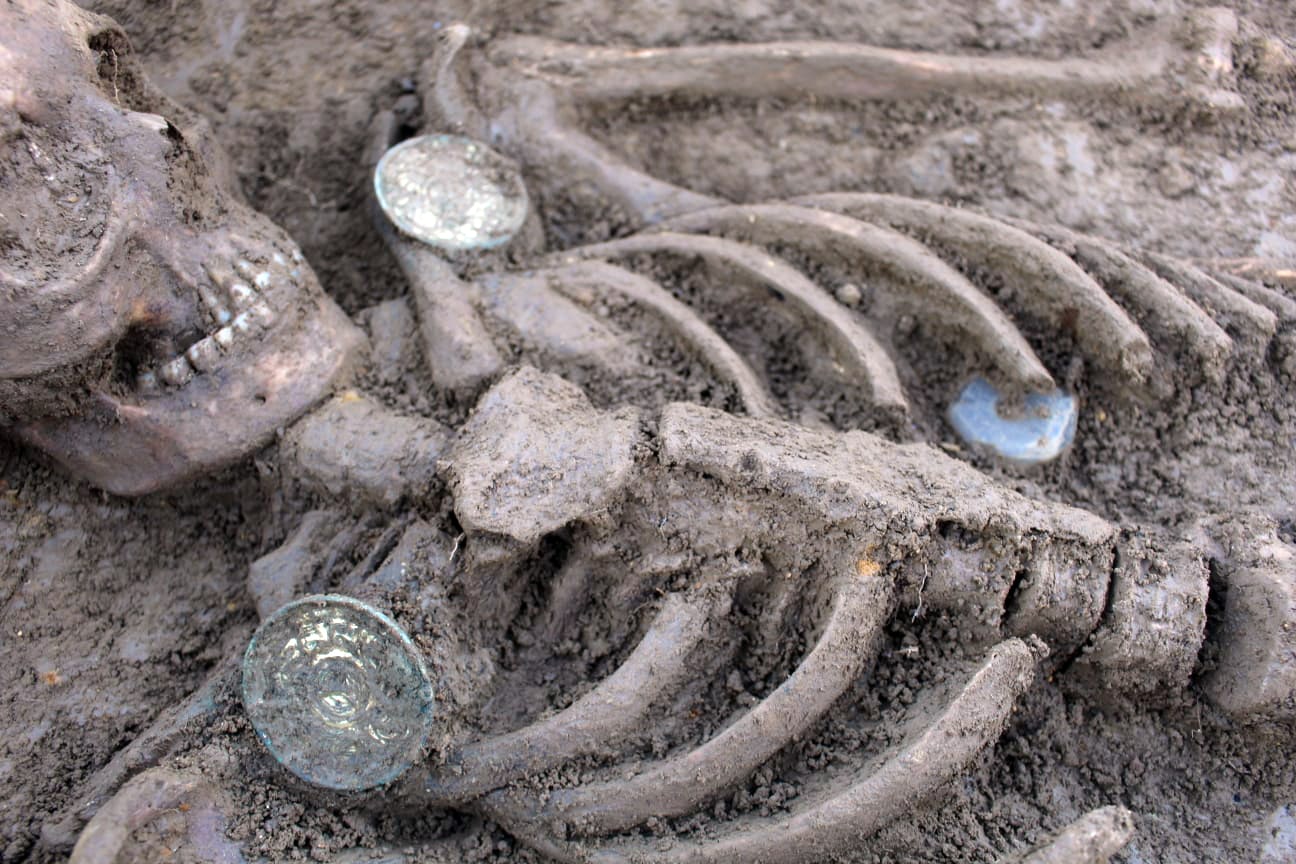
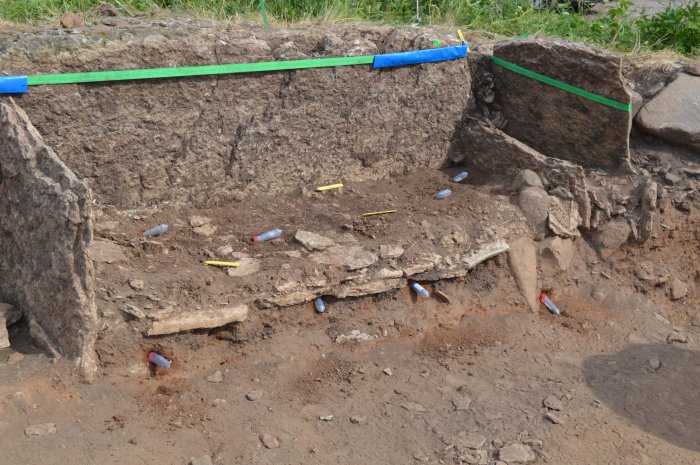
Archaeologists have found seven pairs of Anglo-Saxon saucer brooches, one pair in each of seven burials unearthed in an excavation in South West of England Gloucestershire.
The wonderful discovery was announced on Twitter by Cotswold Archeology. At the site, the Cotswolds Archaeology team unearthed more than 70 Anglo-Saxon burials, some of which had luxurious grave goods. They are from the 5th or 6th centuries.
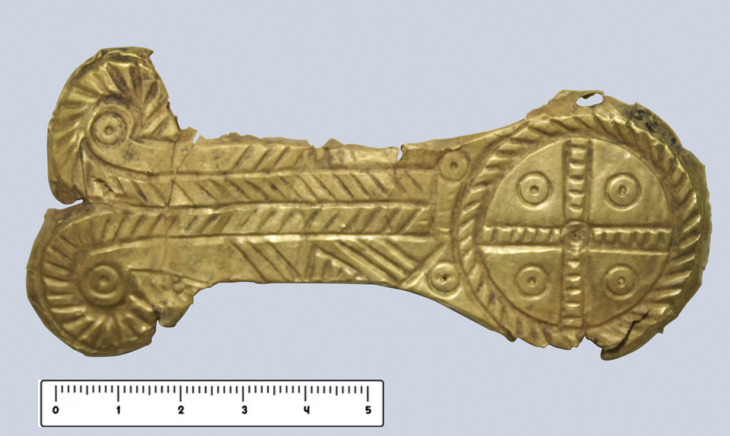
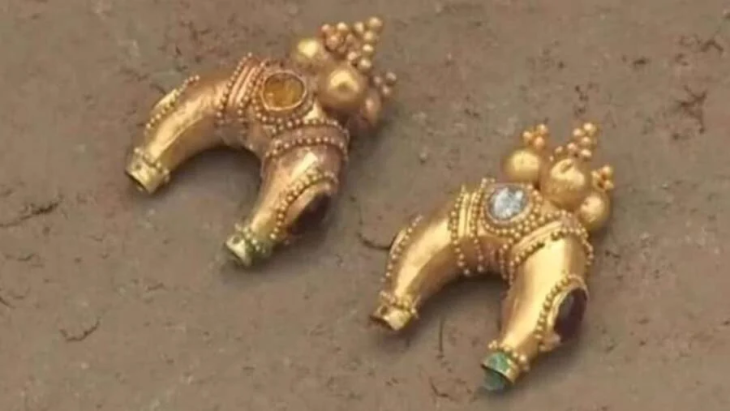
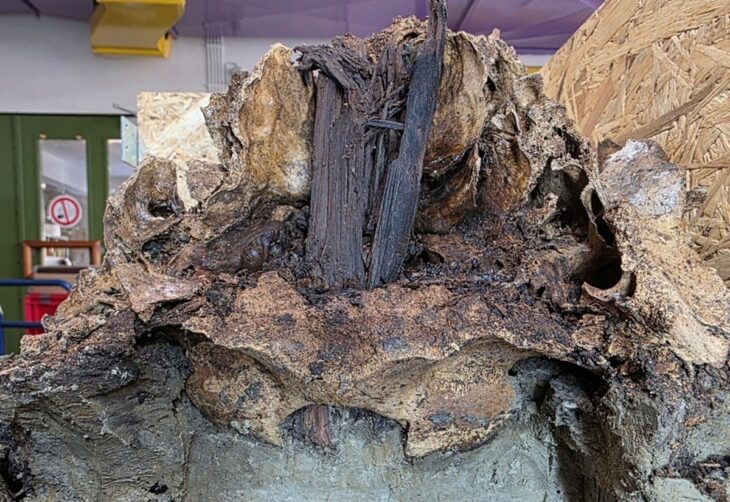
Seven pairs of gold-gilt plate (or saucer) brooches were found, in seven separate graves. Plate brooches such as these were decorative items, worn in pairs at the chest and used to fasten clothing.
They’re known as saucer brooches after their shape: a circular central body with a raised rim. They are made of gilded copper alloy and were relief-cast (cast from a single piece of sheet metal) with decorative motifs in geometric patterns. The designs on cast saucer brooches are based on geometric motifs. The commonest design is the running spiral, so-called because each of the spirals is linked to the next and they run around the brooch, normally with a pellet in the center. The commonest number of spirals is five or six, but there are occasionally more.
Cast saucer brooches are similar to button brooches, with the upturned rim that gives them their name. They were worn in pairs, so in graves, it is normal to find two very similar, but not mould-identical, brooches together.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
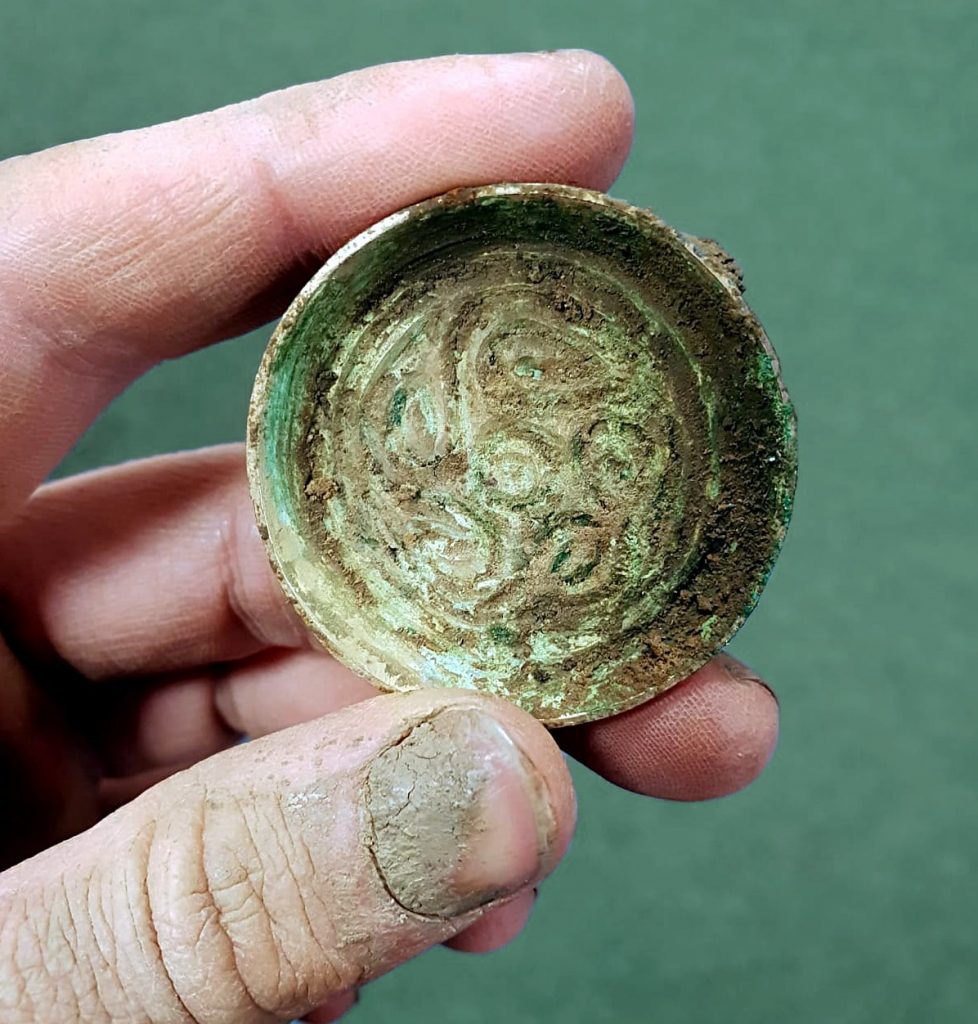

The saucer brooches are still a high-status signifier for burials from this early period of Anglo-Saxon history in England, often found in tandem with other expensive pieces of jewelry.
Ranging in size from 20-70 mm in diameter, saucer brooches were worn in pairs across the chest to fasten garments. Their designs are more simple than, for example, the long square-headed brooches which were so large they offered much more space to create complex, highly sophisticated designs.
“Those we uncovered were either positioned one on each shoulder or two next to each other on the left shoulder with an associated clothing pin, giving a vivid impression of how they once looked on their wearers,” they wrote on their Cotswold Archeology Facebook page.