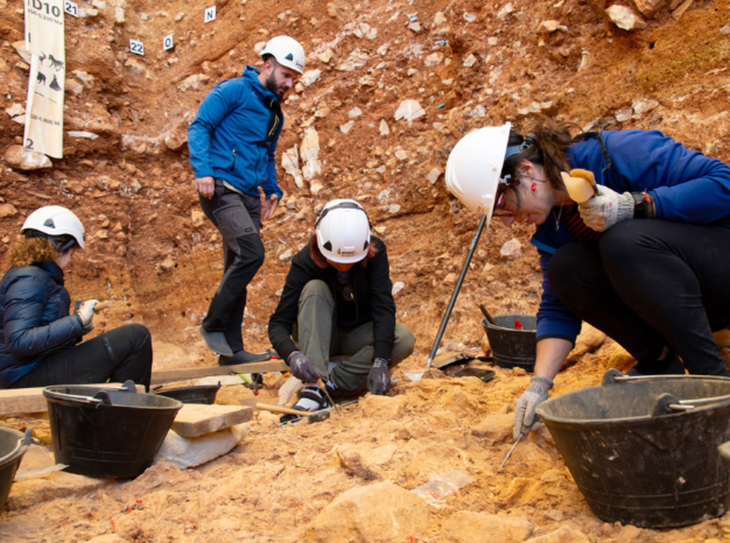
Archaeologists excavating in Jerusalem have uncovered a network of mysterious channels dating back to the days of King Joash and Amaziah, some 2,800 years old.
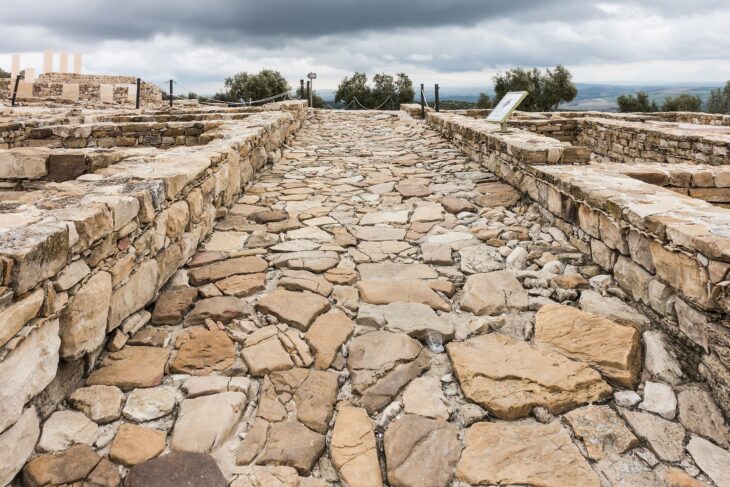
The installations are the first of their kind ever discovered in Israel, the IAA said in an announcement Wednesday. The national park in which the structures were found contains the City of David archaeological site—considered by most scholars to be the location of the original settlement at Jerusalem.
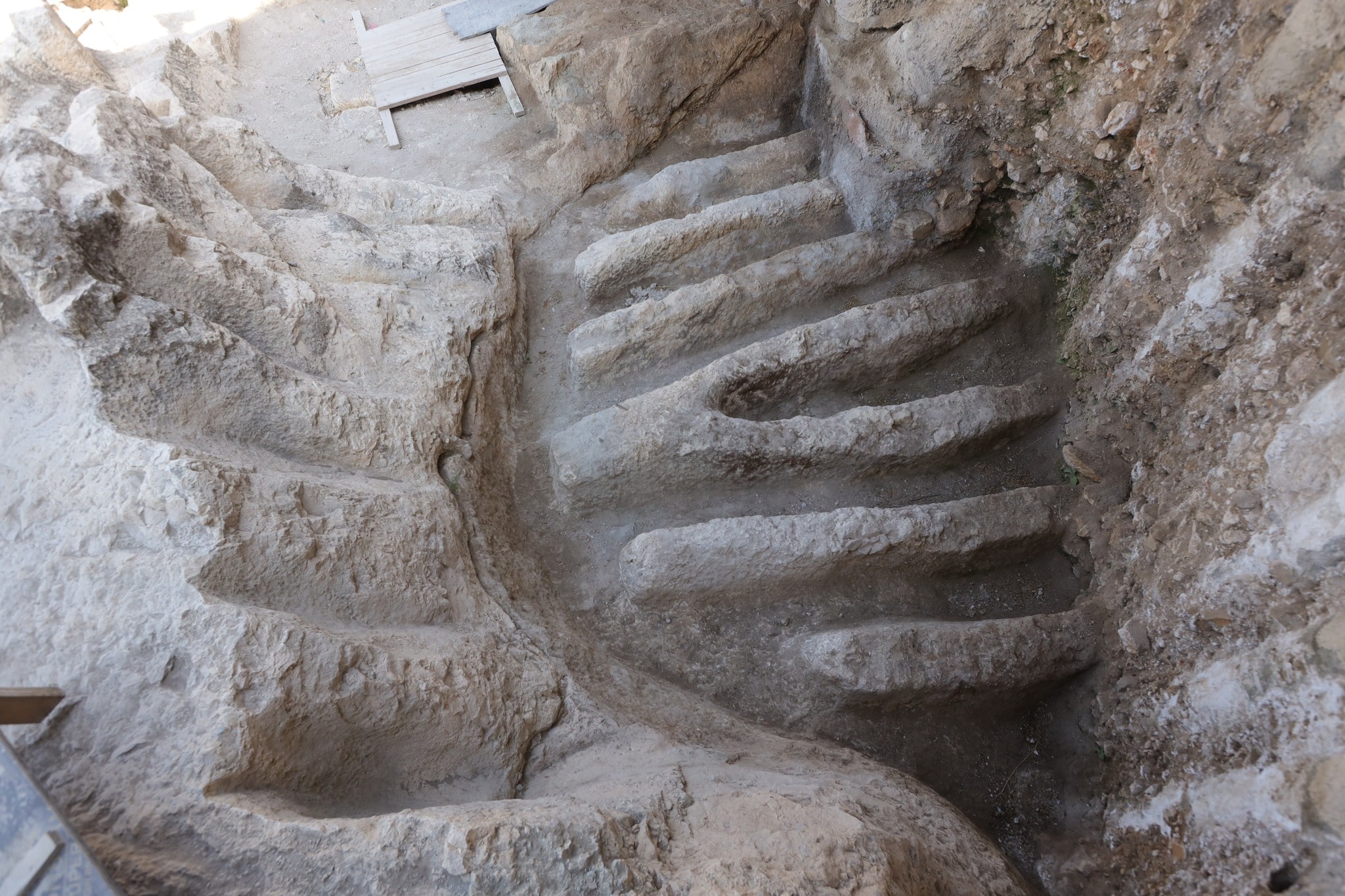
The grooves, cut into the bedrock, were likely used to soak some kind of product, though it is unclear what exactly the ancient Jerusalemites were making there, the Israel Antiquities Authority and Tel Aviv University said in a statement Wednesday.
Forensic testing of the ducts found no blood, suggesting that they were not used for animal slaughter. The ducts also do not appear to have been designed to carry a large volume of water.
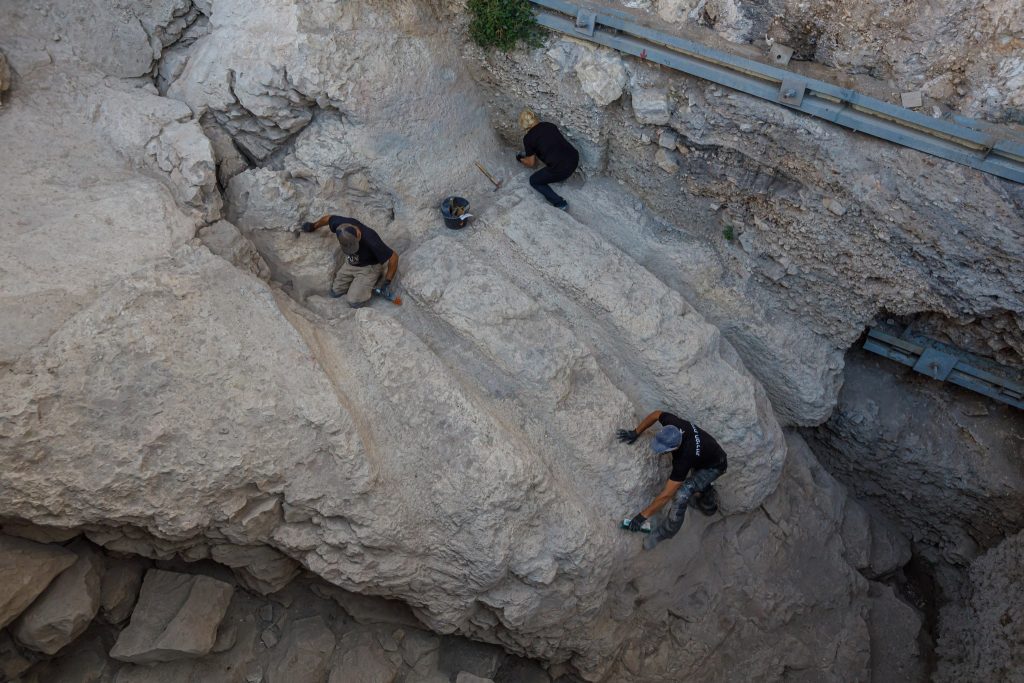

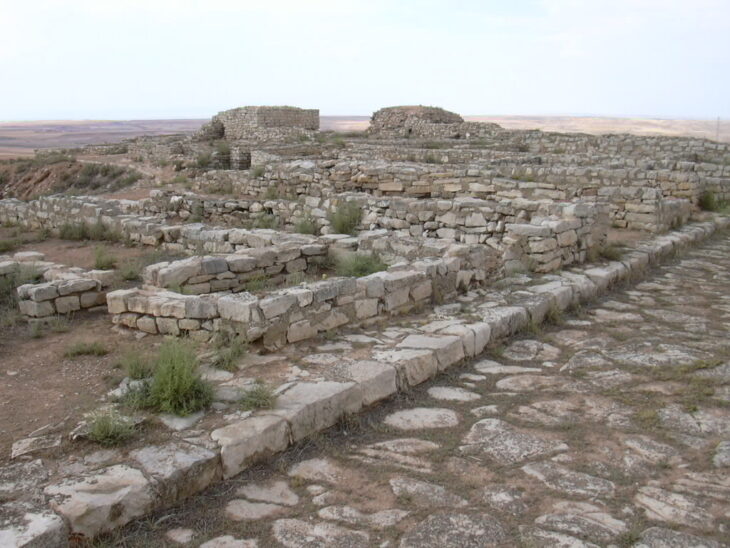
There is no known parallel for such a structure in Israel, so the researchers say they can only speculate on its purpose. Their central location indicates that the product was connected to the Palace or Temple economy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The structures were in use when the city’s First Temple was thought to have existed, researchers said.
Excavations conducted by the IAA and Tel Aviv University in the City of David National Park have so far uncovered two installations just over 30 feet (10 meters)apart, which may have been part of one large installation.
Despite some differences in the way the two channels were hewn and designed, it is clear that both are quite similar, the IAA said.
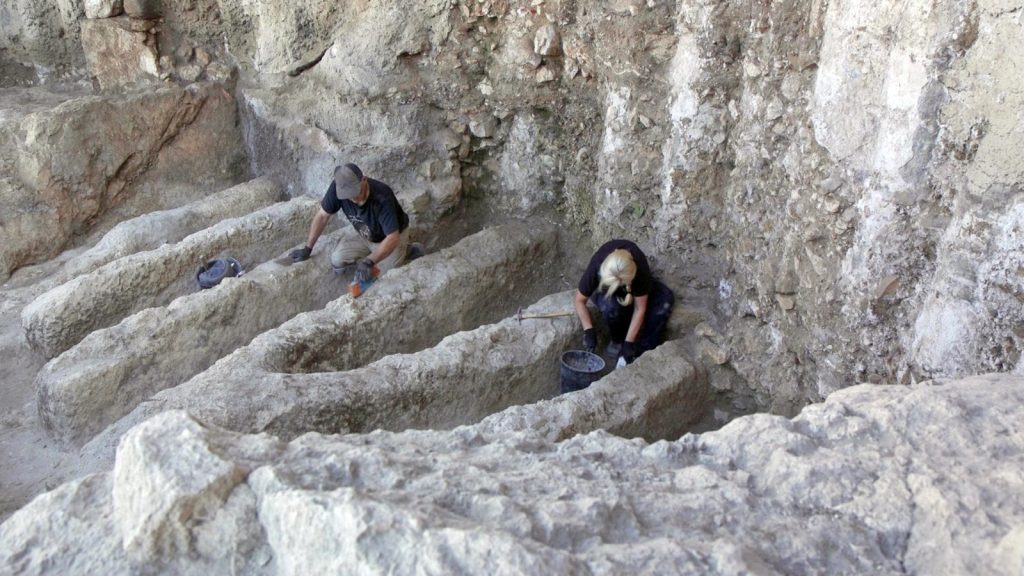

Channels are knee-deep and stand in two clusters, 10 meters apart. They are made of hewn rock and are about 30 centimeters wide and 50 centimeters high. They are not connected to any other water sources, and they do not appear to have been used for drainage or sewage disposal.
“The mystery only grew deeper when we found the second installation to the south,” Yuval Gadot of Tel Aviv University’s Archeology and Ancient Near Eastern Civilizations Department said in a statement.
“We looked at the installation and realized that we had stumbled on something unique, but since we had never seen a structure like this in Israel, we didn’t know how to interpret it,” Yiftah Shalev, a senior researcher at the IAA, said in a statement. “Even its date was unclear.”
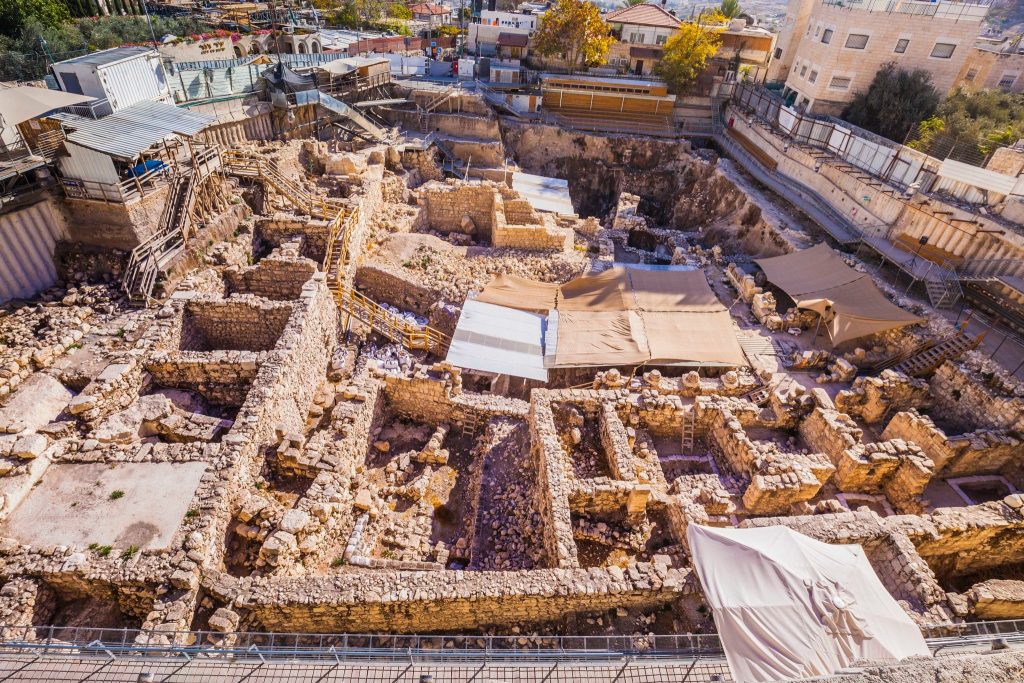

Researchers have managed to date when the installations fell out of use—at the end of the 9th century B.C. during the days of the biblical Judean kings Joash and Amaziah.
The area where the ducts are located was formerly occupied by a sizable industrial and residential complex. As a result, it is possible that the ducts were used for a variety of activities, such as the manufacture of textiles, the production of food, and religious rituals.
The discovery of the ducts is a mystery, but it is an important one. It provides new insights into the ancient city of Jerusalem and its people. The ducts are an unusual discovery that is assisting archaeologists in better understanding Jerusalem’s history.
Cover Photo: IAA/Facebook