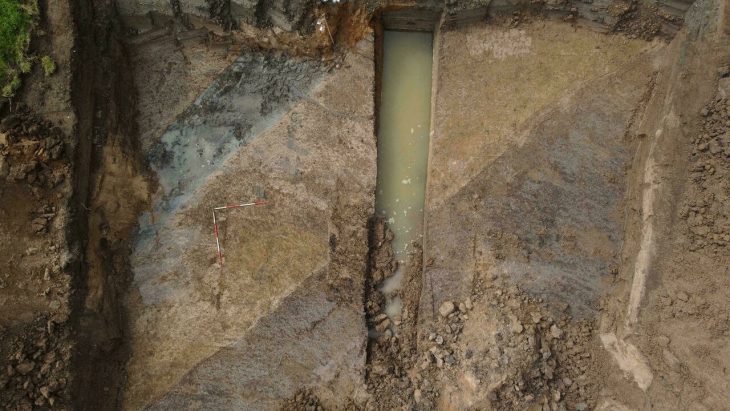
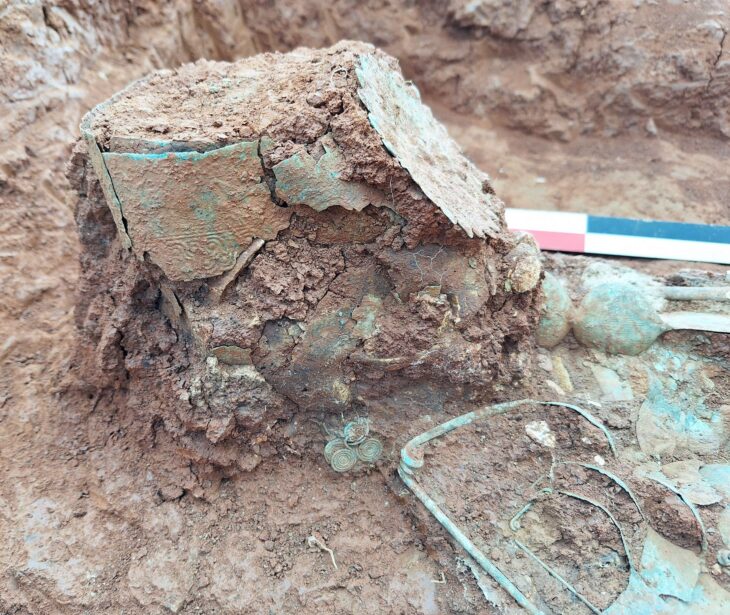
Chinese archaeologists recently discovered a large group of terracotta figurines from a tomb in a group dating to the Northern Wei Dynasty (386-534) in Datong, Shanxi province.
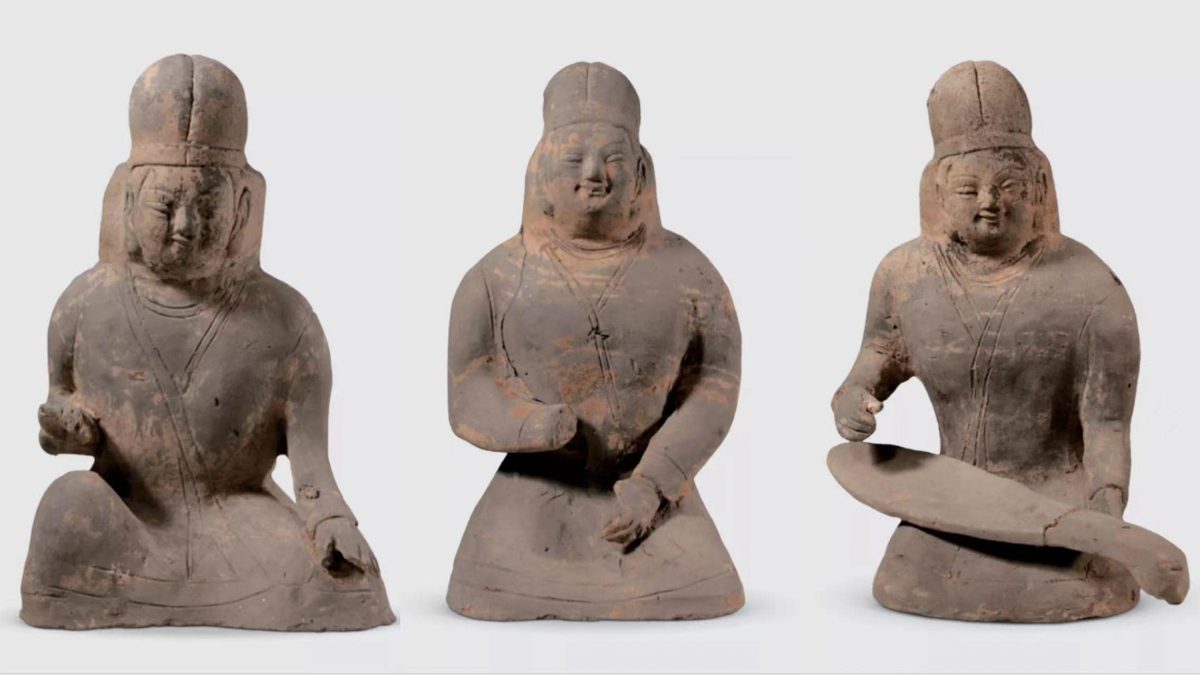
Numerous burial items, primarily earthenware figurines, were found in tomb 113 and contained dozens of burial objects, the majority of which were earthenware figurines. The figurines are led by pottery horsemen. Behind them is a full entourage of laborers, animals, objects of daily life, bullock carts, and 10 Hu figurines, musicians, acrobats, and dancers posted in dynamic forms.
According to experts, the recent archaeological find offers fresh data for the study of the dynasty’s social life, ethnic dress, and funeral customs.
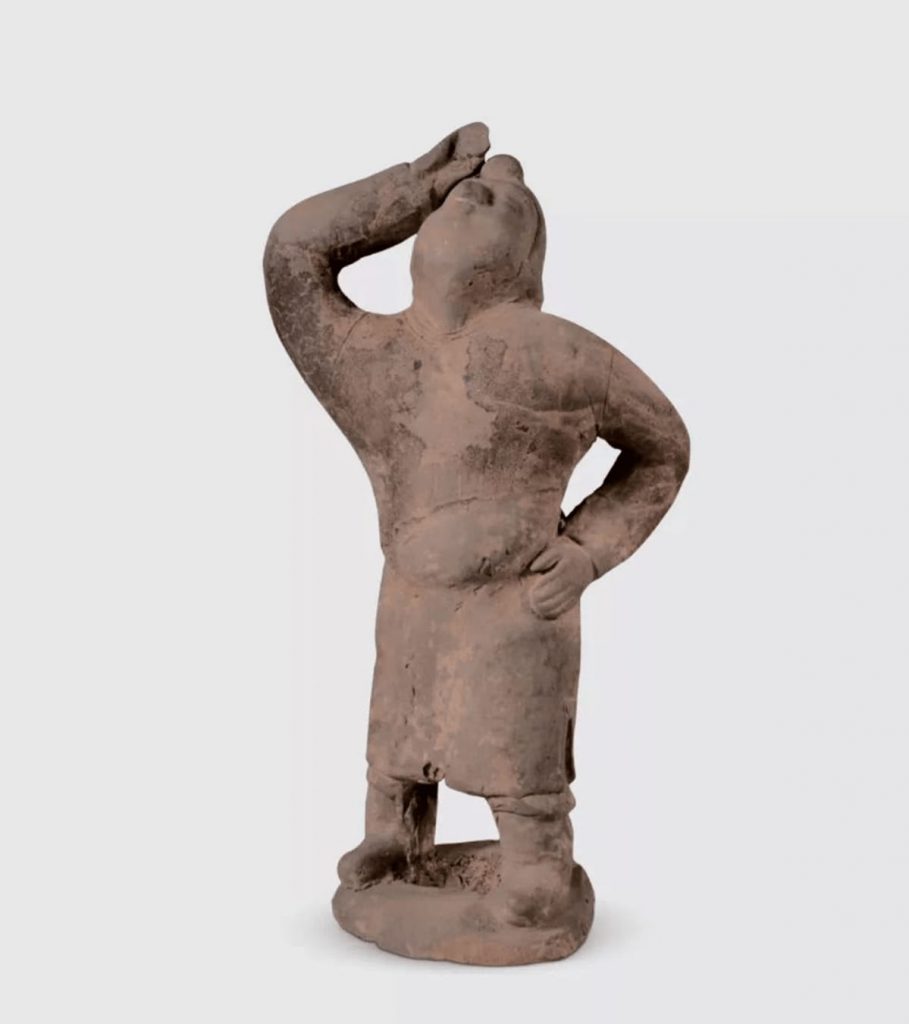

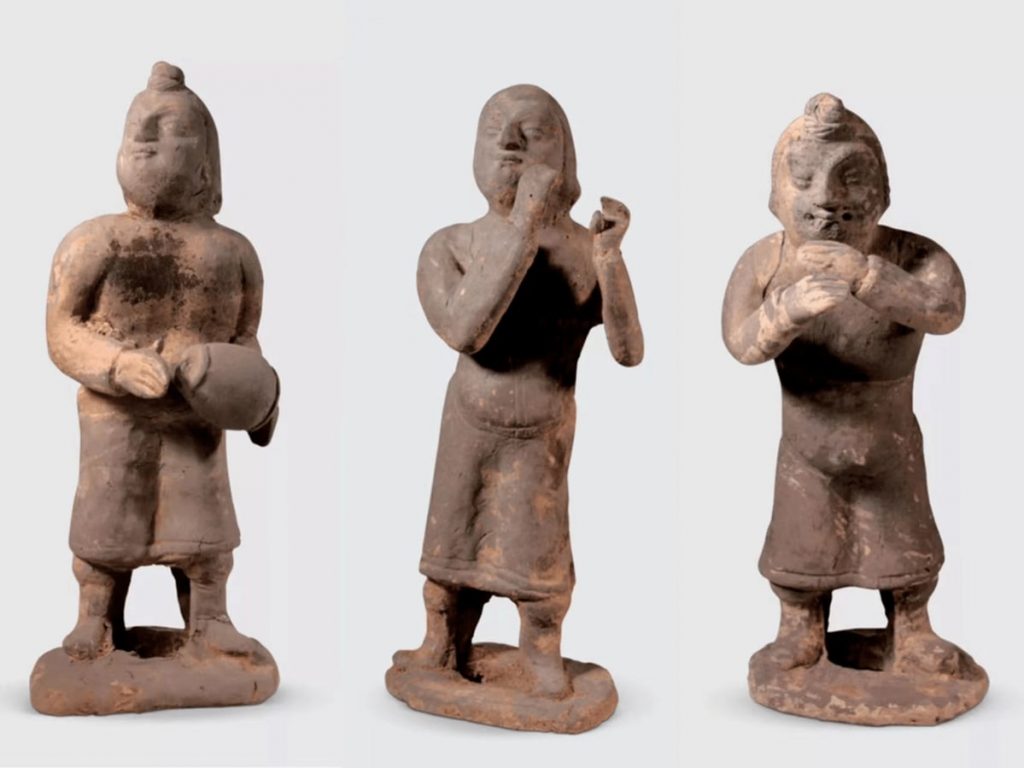
In a typical Northern Wei Hu character, the player’s eyes are deep and wide, and the nose is short and high. They wear robes with round necks and narrow sleeves. The underside of the robe has slits to reveal the performers’ boots. The ensemble of three musicians is particularly striking. They were all seated, wearing tall bell hats with a cruciform ridge on the front and back. The hat is tied around the back of the head, and a little skirt covers the back of the neck underneath the hat’s tie.
The relics indicate that the tomb owners belonged to the upper class. Female musicians’ costumes demonstrate the period’s integration of national culture and costume development.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

From 398 to 494, Pingcheng (modern-day Datong) was the capital of the Northern Wei Dynasty. Drought, repeated famines, and incursions from the proto-Mongolic Rouran Khaganate to the north compelled Emperor Xiaowen to relocate the capital to Luoyang in 494 A.D., despite his court’s protests. Unlike Pingcheng, which was in the nomadic steppe, Luoyang had been the capital for several ruling dynasties dating back millennia, and the Yellow River basin area was extensively settled and cultivated. It remained a regional administrative center until the 520s, but its population and prosperity plummeted as a result of the relocation.