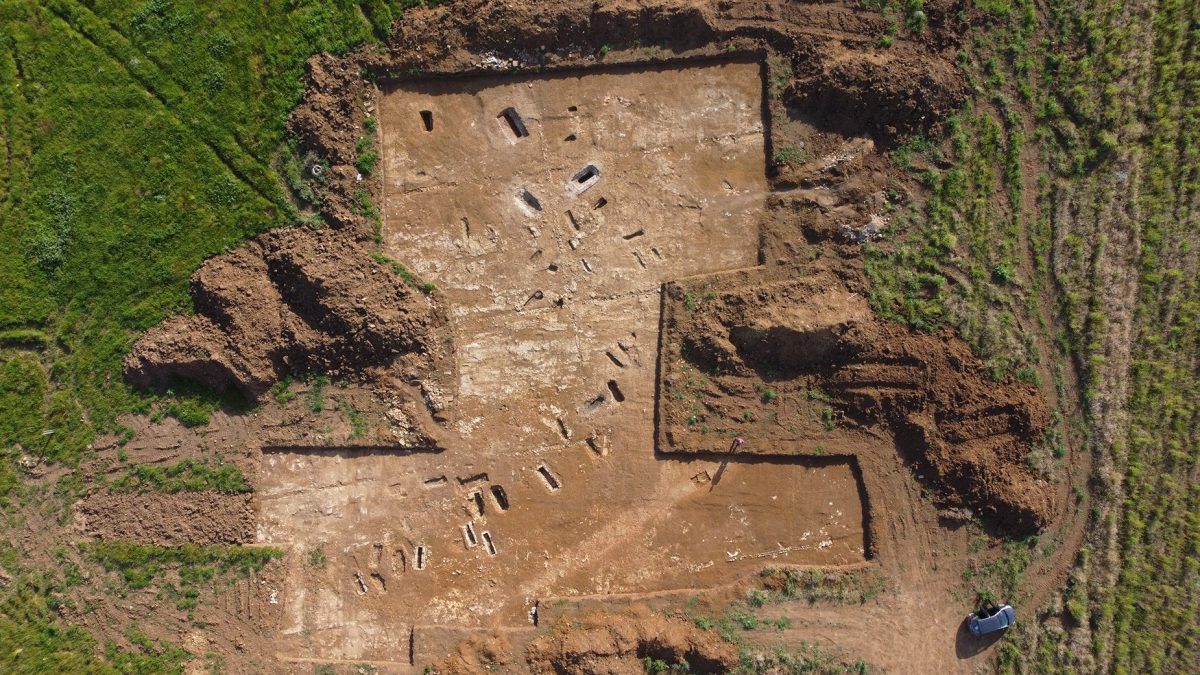
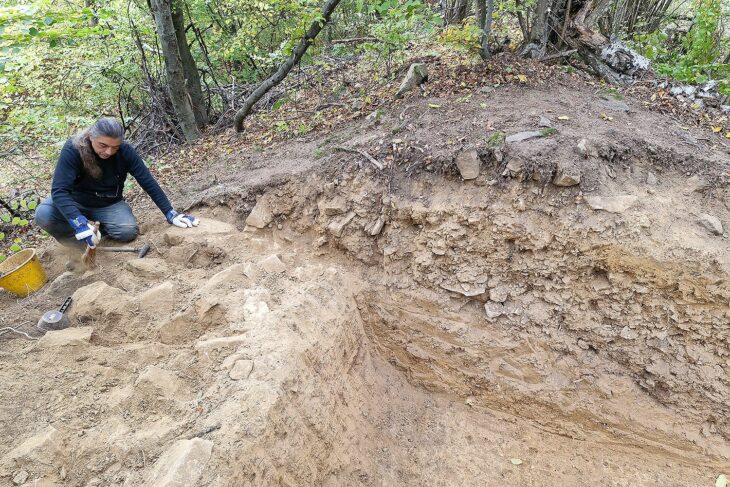
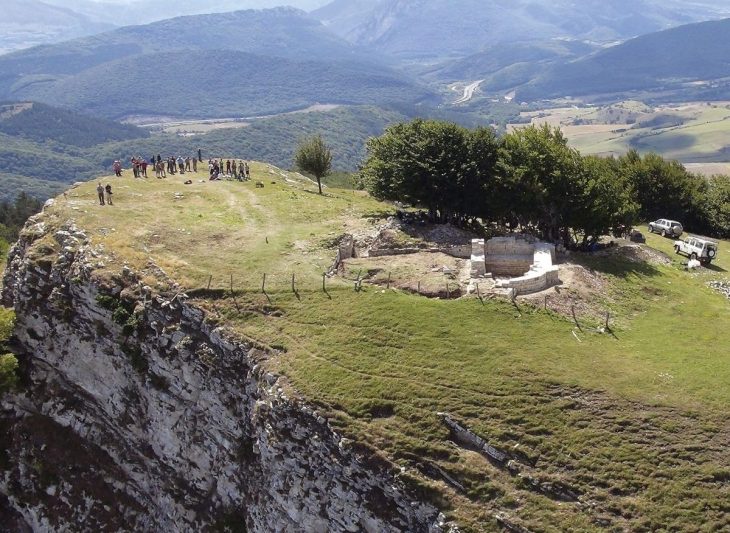
Archaeologists involved in a two-year-long excavation project at the site of a planned solar energy plant ancient city of Tarquinia, north of Rome, have unearthed an ancient Roman necropolis containing 67 skeletons buried in 57 ornate tombs.
Early testing suggests the tombs and their occupants date back to the second through fourth centuries AD.
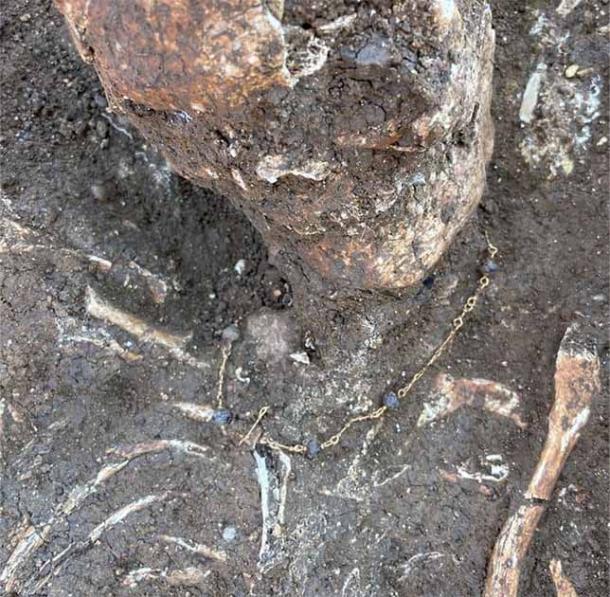
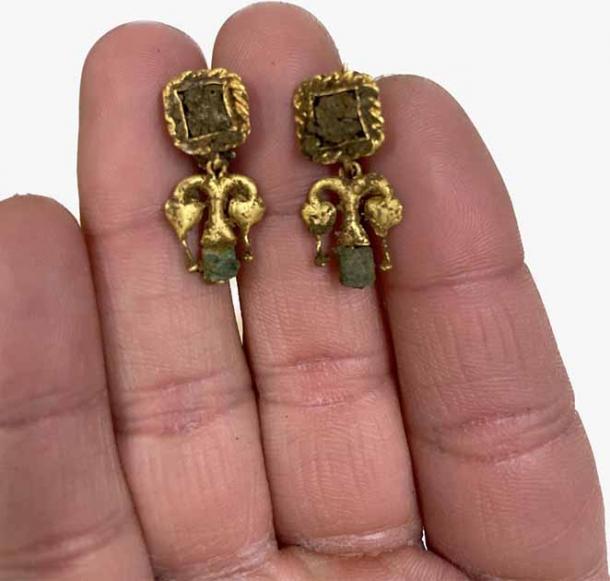
This cemetery was undoubtedly reserved for wealthy and powerful Roman elites. The well-preserved skeletons were dressed in gold jewelry and fancy leather footwear, and their tombs appear to have been designed to resemble the architecture of their earthly homes (smaller in scale).
“We found several skeletons still wearing their expensive stockings and shoes,” lead excavation archaeologist Emanuele Giannini, who works for the private archaeological firm Eos Arc, told CNN. “All these riches, and the fact that the bones show no sign of stress or physical labor, [leads us to believe] these weren’t local farmers, but upper-crust members of Roman families coming from cities.”

Although the region is known for such finds, the discovery, which took place on a 52-acre plot of land near the ancient city of Tarquinia, north of Rome, surprised the authorities. They simply had no idea that a cemetery reserved for aristocrats would have been located where it was, given the lack of any historical reference.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
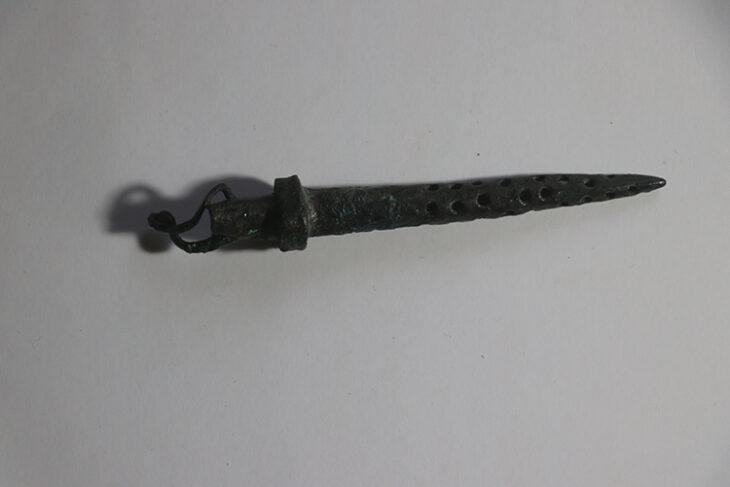
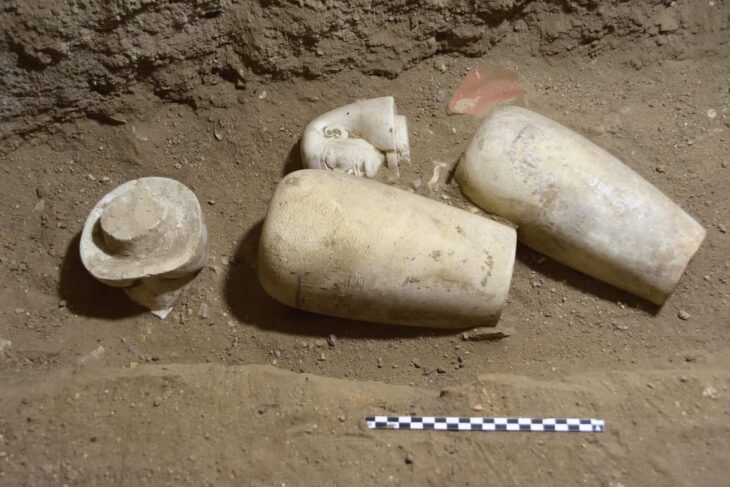
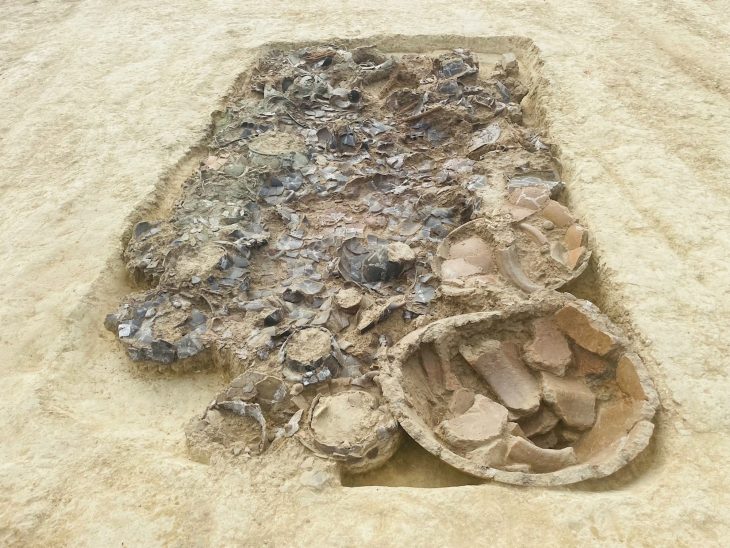
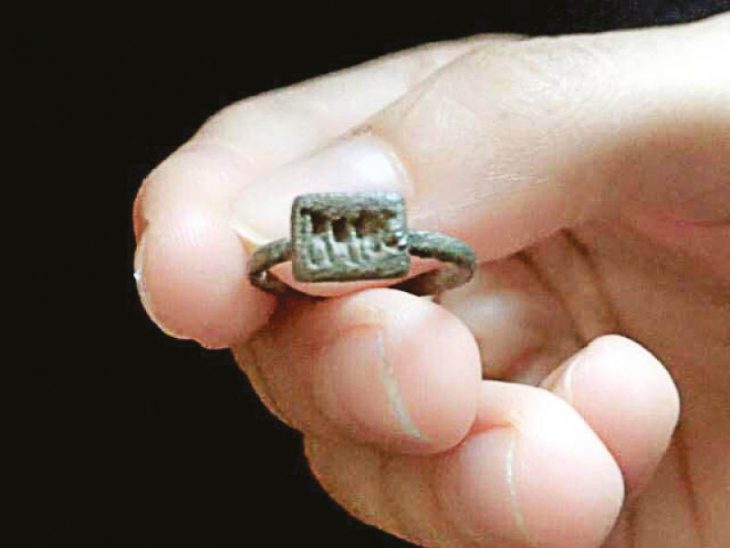
The collection of luxurious goods buried with the deceased individuals was extremely impressive. Among the highlights were silver rings with amber and engraved initials, amulets containing precious stones, many pieces of terracotta pottery, Roman coins of different values, shiny glass objects, and even some still-preserved items of clothing.

Archaeologists believe that the occupants wanted to recreate heavenly spaces similar to their earthly homes based on the diversity of funerary objects found near the remains and the luxurious designs and linings inside the tombs. Many tombs used to have elaborate cloth linings or were surrounded and covered by tiles or terracotta pieces that looked like little houses.
The skeletal remains were found very close to the surface of the earth, buried at a depth of approximately 20 inches (50 cm). Most of the discovered graves were communal graves, probably built for at least two people who shared the same family connection. Several skeletons were also found wrapped together.
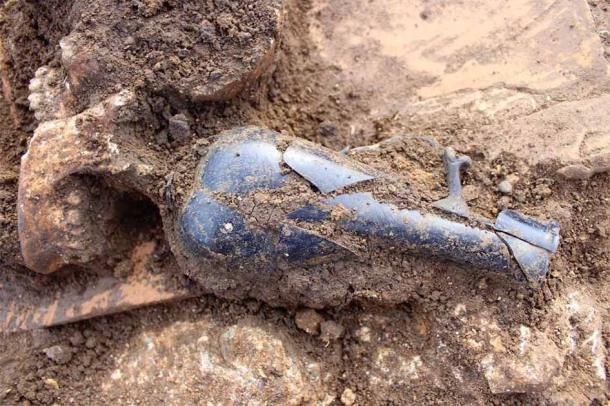

The site’s unique state of preservation has been attributed to the fact that “huge limestone blocks that stick out of the ground (made) plowing, seeding, and modern farming impossible in the area,” said Giannini. “It has remained untouched (for) centuries.”
Authorities are certain more hidden wonders will come to light as digs for the solar park move to another nearby site. The area where the necropolis has been discovered will not form part of the solar park and will be cordoned off for safety reasons, without public access.
Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti Paesaggio Etruria Meridionale