History is littered with artifacts that were later discovered to be forgeries, but the opposite can also occur. A new analysis of ancient Roman coins that had previously been dismissed as forgeries has revealed that they appear to be authentic, revealing a previously unknown Roman emperor.
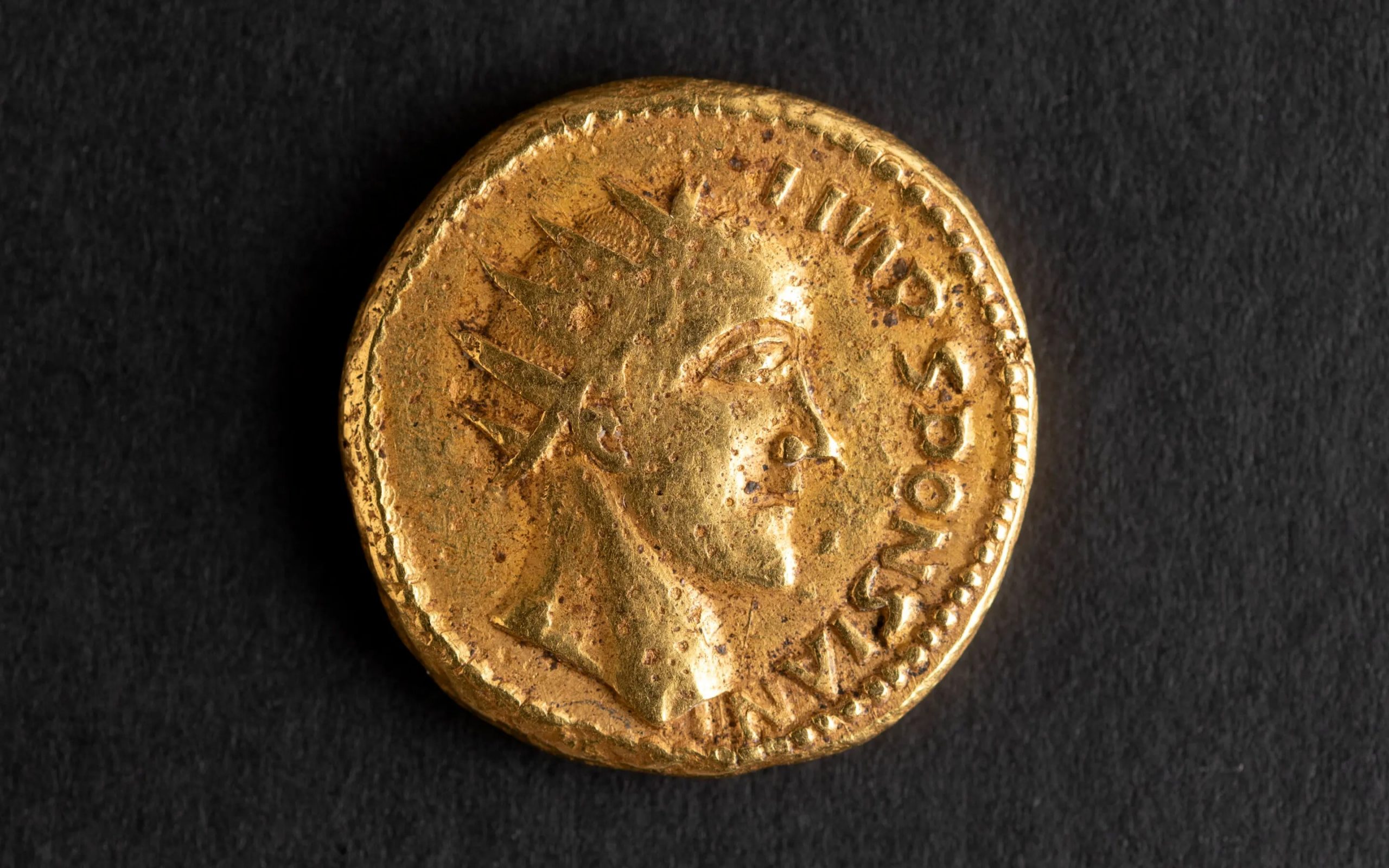
Coins that serve as the sole remaining proof of the existence of the fictitious Roman emperor Sponsian have been discovered to be genuine 3rd-century issues.
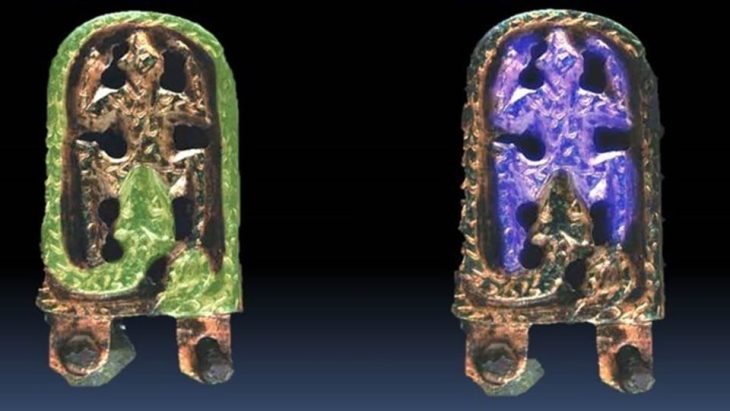
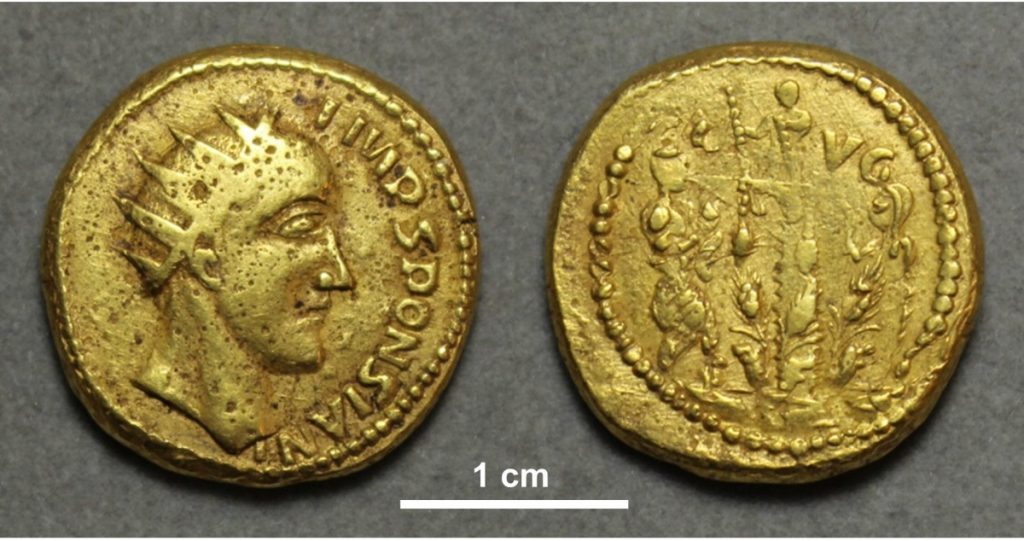
The coins in question were discovered in 1713 in Transylvania and bear a portrait of a man’s face with the inscription “Sponsian.” That name does not correspond to any known Roman emperor or other historical figures, and this, combined with the crude craftsmanship and mismatched design features, has led historians to dismiss the coins as poorly made forgeries since the mid-nineteenth century.
Carl Gustav Heraeus (1671-1725), Inspector of Medals for the Imperial Collection in Vienna, was the first to document the coins in March 1713. He recorded the acquisition of eight coins found in Transylvania. Another 15 coins that match Heraeus’ description came to light starting in 1730, and scholars believe they were part of a wider assemblage that was sold to a number of different collections over the years, including The Hunterian museum at the University of Glasgow.
Among the four coins from the wider assemblage now in the collection of The Hunterian is one featuring the unknown “emperor” Sponsian. It is designed in the style of coins from the mid-third century, but the design on the reverse is a copy of a Republican-era silver coin from the 1st century B.C. That reverse design would have been close to 400 years old when the Sponsian coin was made. That and other atypical features of the wider assemblage coins have led scholars to peg them as fakes, perhaps the work of a talented forger working in early 18th century Vienna who duped Heraeus.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Now researchers at University College London and the University of Glasgow have investigated the strange coins’ origins more closely.
The team examined one under powerful microscopes in visible and ultraviolet light, and with scanning electron microscopy and spectroscopy, and compared them to other coins confirmed to be genuine.
This comprehensive analysis revealed that the coin’s surface bore patches of minerals that were cemented in place by silica – evidence of a natural process that occurs when something is buried for a long time. On top of that is a layer of oxidation products, which occur only after something has been re-exposed to air. The coin itself also showed microscopic scratch marks, the kind of wear-and-tear expected from having been in active circulation at some point.
All of these indicators point to the coins being genuine, dating back nearly 1,800 years. Based on their findings, the team devised a hypothesis about who this Sponsian was, how his face ended up on coins, and why we’d never heard of him.
Considering the historical record alongside the new evidence from the coins, the researchers suggest that Sponsian was an army commander in the Roman Province of Dacia during a period of military strife in the 260s CE.
As a result, Sponsian’s name may not have been influential enough on a large enough scale to survive written history. It could also explain the crudeness of the coins.
“Scientific analysis of these ultra-rare coins rescues the emperor Sponsian from obscurity,” said Professor Paul Pearson, lead author of the study. “Our evidence suggests he ruled Roman Dacia, an isolated gold mining outpost, at a time when the empire was beset by civil wars and the borderlands were overrun by plundering invaders.”
The research was published in the journal PLOS ONE.