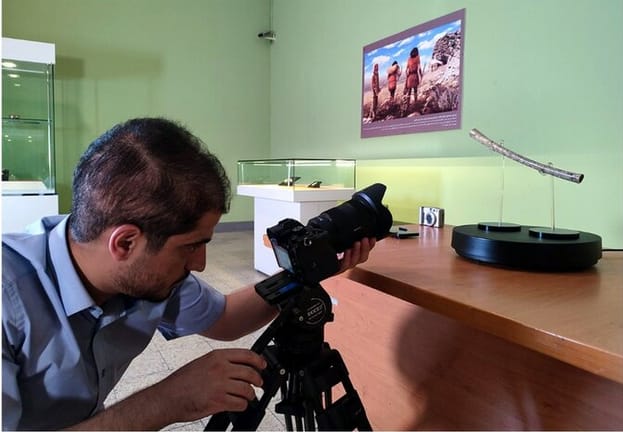
The National Museum of Iran has launched an exciting initiative in collaboration with the Public Relations Department of the Ministry of Cultural Heritage, Tourism and Handicrafts to bring its priceless historical treasures to a wider audience. Through a new series of short documentary videos, the museum is showcasing key artifacts—among them, a remarkable 8,000-year-old bone flute that could be one of the oldest known musical instruments in the world.
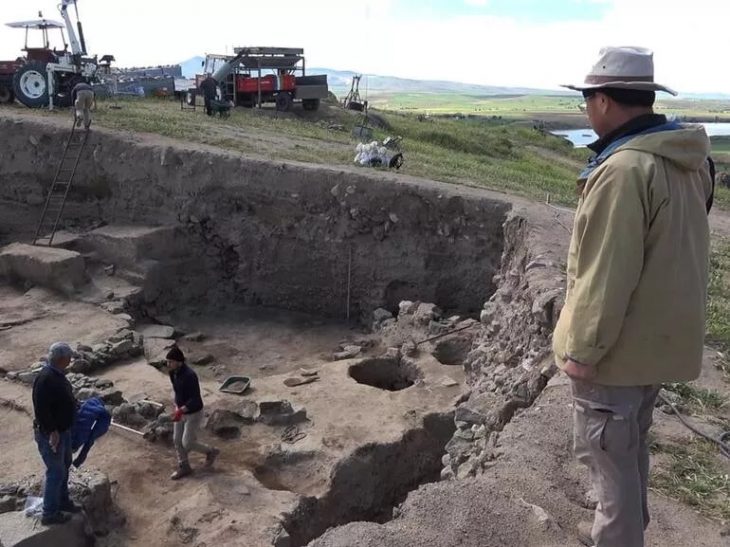
This prehistoric flute was unearthed during archaeological excavations in the 1970s at the Sang-e Chakhmaq mounds, located near Shahrud, a historic city in northeastern Iran. Shahrud lies in Semnan Province and is known for its diverse landscapes, ancient sites, and connection to the Silk Road. The discovery site, Sang-e Chakhmaq (meaning “flint mound”), is one of Iran’s most significant Neolithic settlements.
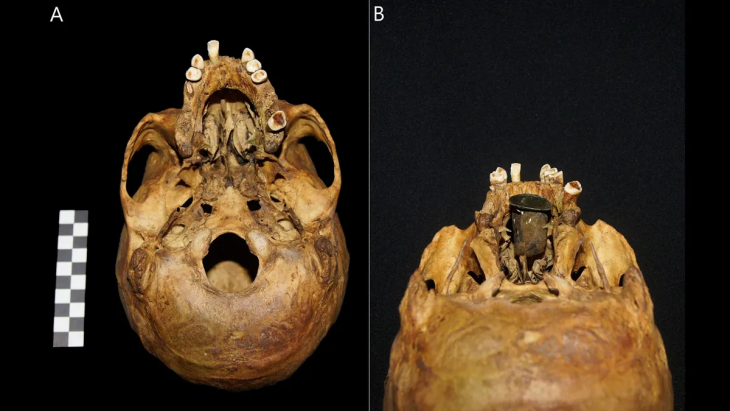
A Closer Look at the 8,000-Year-Old Flute
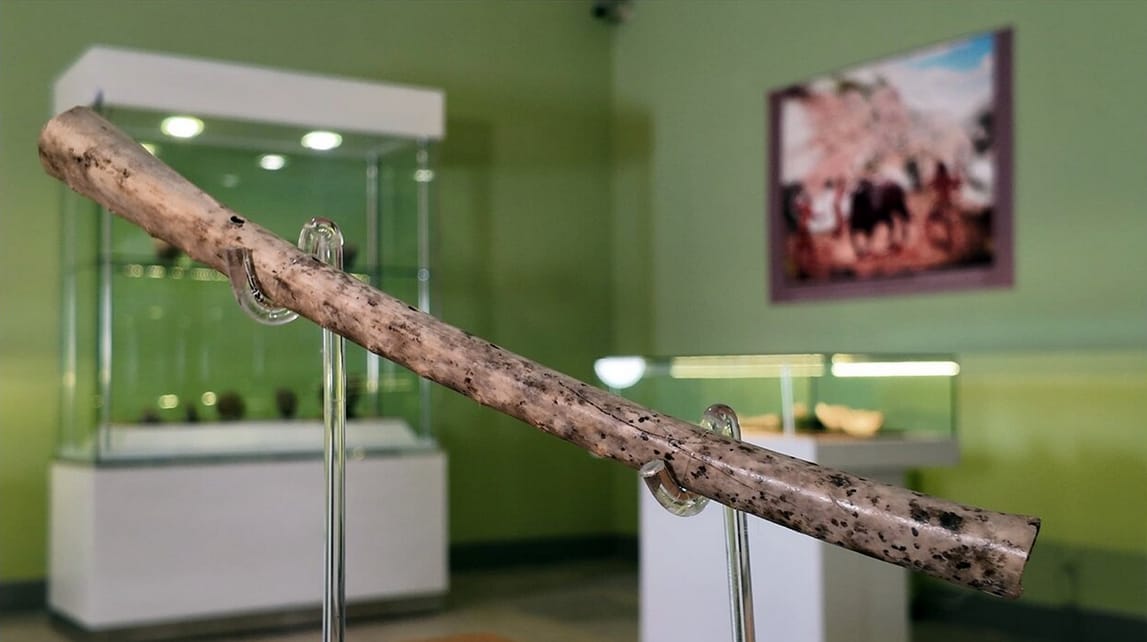
According to Dr. Fereidoun Biglari, deputy director of the National Museum of Iran, who spoke to the Tehran Times, the flute is made from the bone of a large migratory bird. It features four main finger holes and an additional hole near its end—testament to the complex craftsmanship of early humans. Stone tools were used to shape the long bone, and visible cutting marks on the surface offer rare insight into the instrument’s manufacturing process.
Efforts are currently underway to reconstruct the ancient flute using similar materials. With the help of a professional musician, the museum aims to recreate the sounds once produced by this remarkable artifact—potentially allowing us to hear the echoes of music from the Neolithic era.

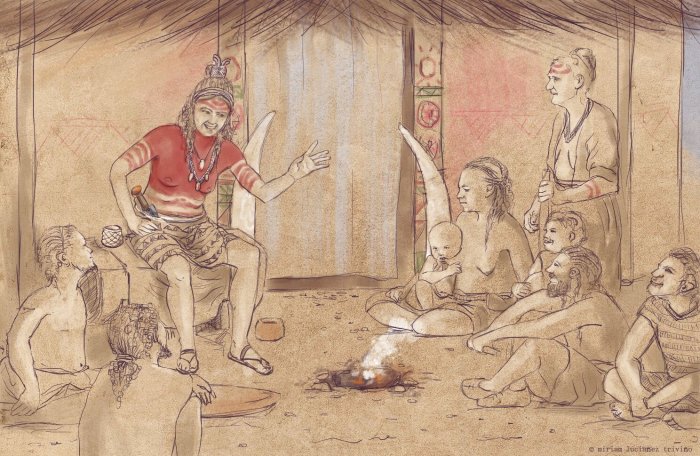
The Role of Music in Ancient Iran
Dr. Biglari suggests that bone flutes like the one found at Sang-e Chakhmaq may have served multiple purposes in early human societies. They could have been used in spiritual rituals, community ceremonies, or even for practical tasks like herding animals or sending signals across long distances. These flutes reflect the early development of music as a social and cultural expression, highlighting the importance of sound and rhythm in prehistoric life.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Significance of Sang-e Chakhmaq
Sang-e Chakhmaq is a vital archaeological site that includes two major mounds: Eastern and Western. The ancient flute was found in the eastern mound, which shows evidence of ceramic production and early urban life. In contrast, the western mound holds older, aceramic Neolithic layers with mud-brick structures, fire pits, and flint tools.
This site spans a continuous cultural sequence from the 7th to early 5th millennium BCE, documenting the transition from pre-pottery Neolithic lifestyles to early Chalcolithic societies. The ceramics found here share stylistic elements with those of Turkmenistan’s Djeitun Culture and Iran’s Sialk I and II phases. Artifacts include early copper items, figurines, and architectural innovations that signal a major societal evolution.

A Crossroads of Early Civilization
As one of the few fully excavated Neolithic sites in northeastern Iran, Sang-e Chakhmaq is crucial for understanding the origins of agriculture, pottery, and metallurgy in the region. Its strategic location reveals cultural connections to both Central Asia and the Iranian plateau, suggesting it may have served as a major hub in the spread of early human innovations.
Today, several artifacts from the site—including the bone flute—are preserved in the Neolithic Gallery of the Iran Bastan Museum, part of the National Museum of Iran in Tehran. In recent months, the museum has begun sharing educational content and video features via social platforms like Instagram and Aparat, helping the public engage with Iran’s rich cultural heritage in new and dynamic ways.
Cover Image Credit: Tehran Times