The Iraqi State Board of Antiquities and Heritage (SBAH) announced that 478 artifacts were uncovered during an excavation expedition in the historic province of Babylon.
The Director of the Excavations Department accompanied the Missions Follow-up Committee to site 19/3 in Sector 38 of Al-Fayyadiya district to examine the work of the archaeological mission in the Babil governorate, according to a statement released by SBAH.
Under the direction of archaeologist Quhtan Abbas Hassan Aboud, the mission has uncovered information that provides fresh insights into ancient Mesopotamian life and culture.
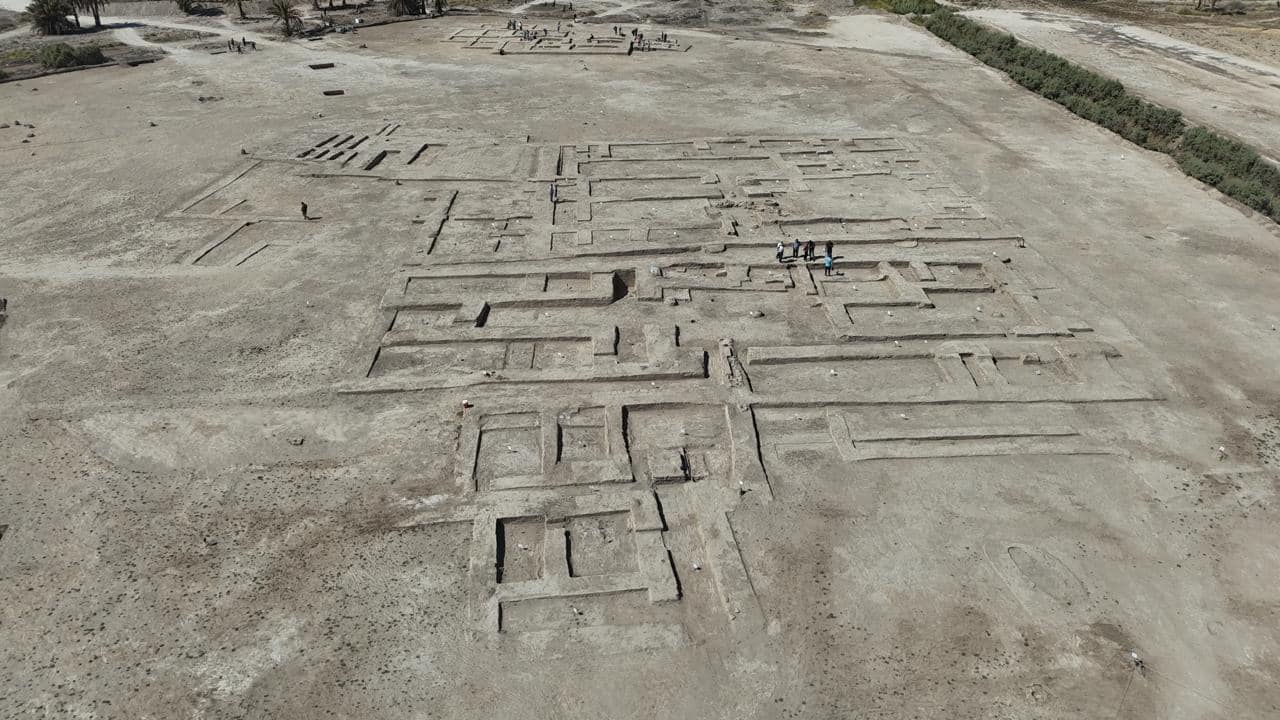
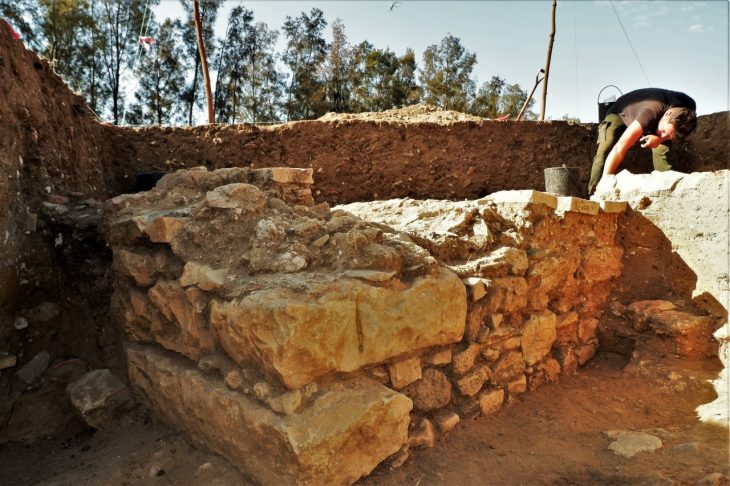
During the visit, the head of the committee received a detailed explanation from the mission leader regarding the findings of the excavation. The Al-Fayadiya district’s 19/3 excavation site is separated into two sectors, A and B. There are two layers of archaeological stratification in Sector A, which is 6 dunums (roughly 6,000 square meters) in size.
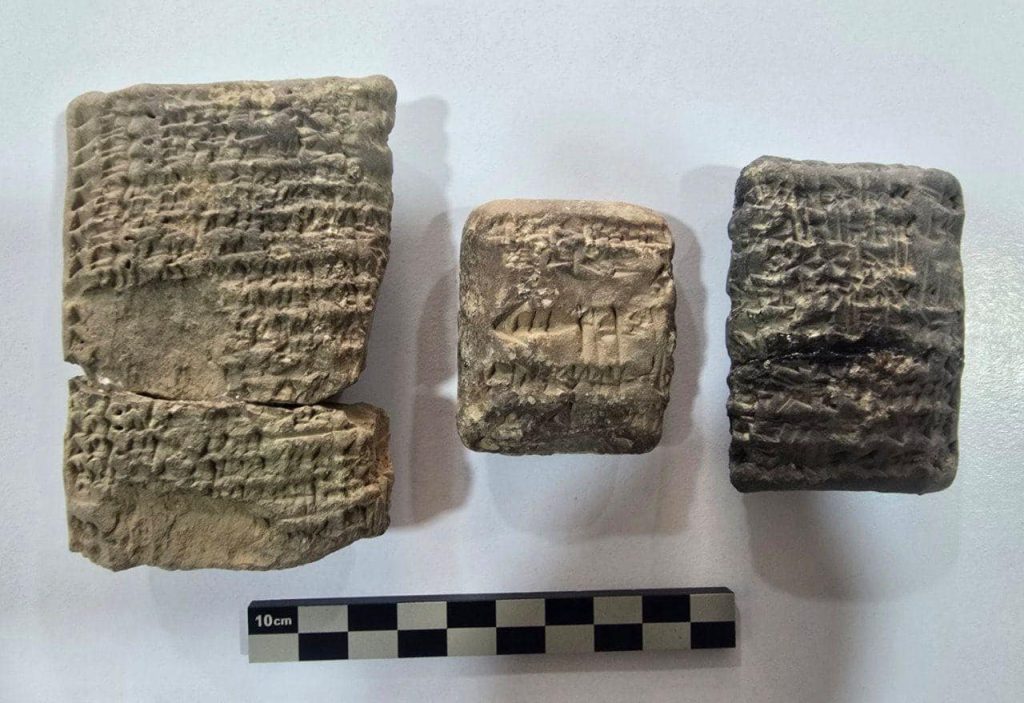

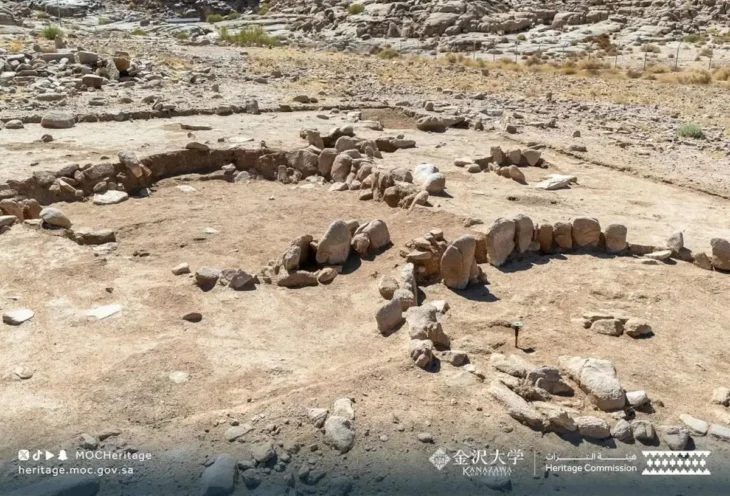
However, the structural discoveries in Sector B, which spans a wider area of 9 dunums (roughly 9,000 square meters), have been even more abundant. Two distinct residential units with rooms of varying sizes that may have served different purposes in the daily lives of the prehistoric occupants have been discovered in this zone.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
According to Soheil Al-Tamimi, Director of the Department of Excavations, who was present during the visit of the Mission Monitoring Commission, the first layer corresponds to the Sasanian period. However, this layer has suffered considerable damage due to erosion and human intervention over the centuries.
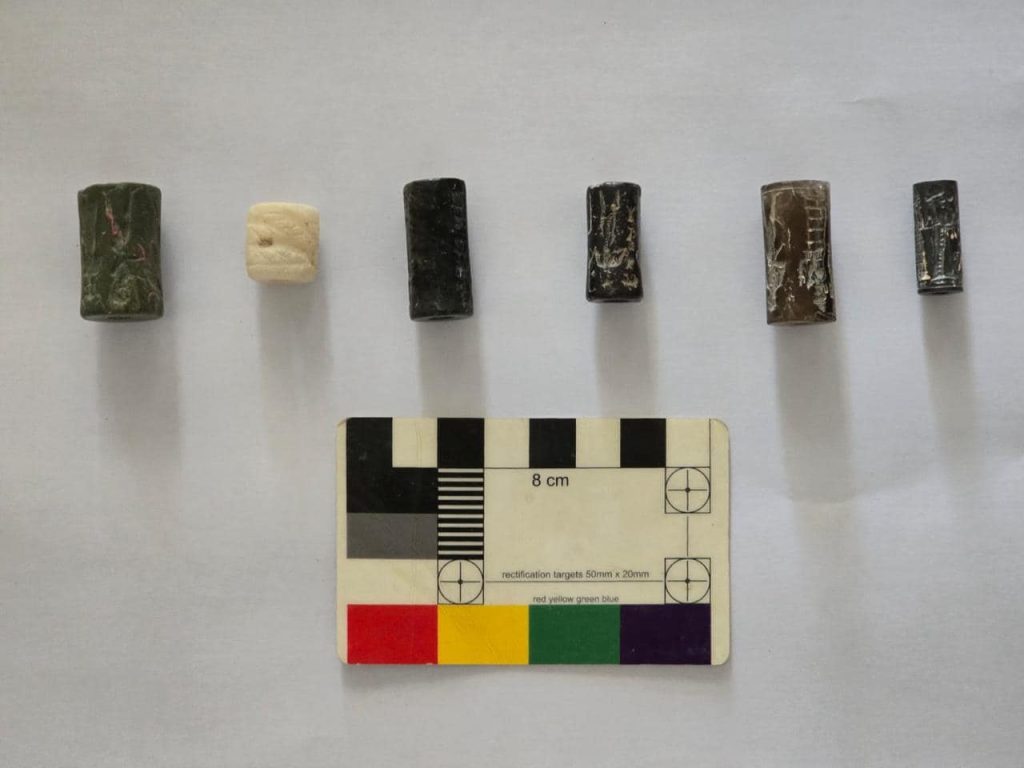

The second layer dates to the ancient Babylonian period, and the better-preserved, which has sparked special interest among researchers who hope to uncover more about the characteristics of urban life during that era.
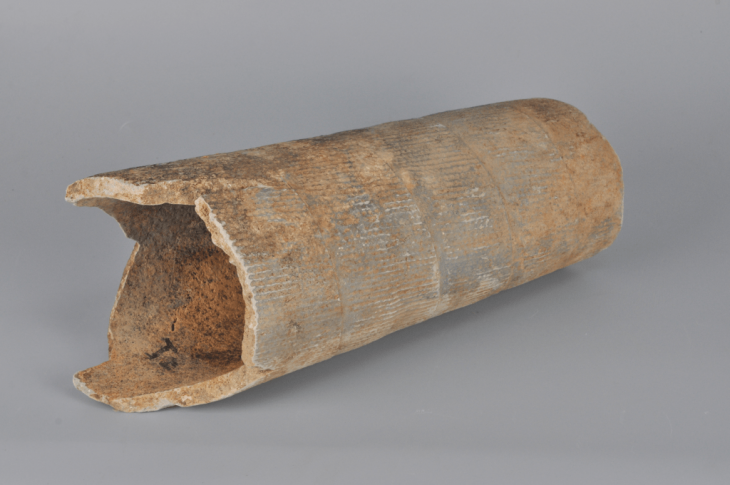
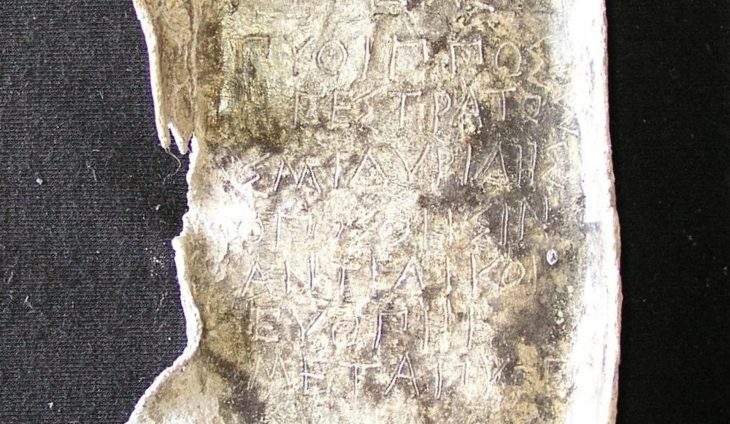
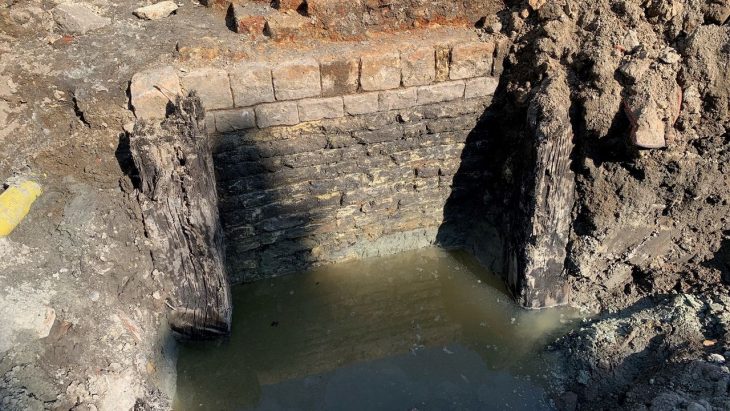
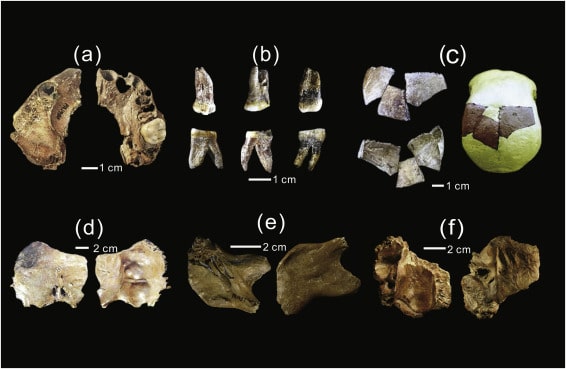
The excavation team found 478 diverse artifacts, including pottery jars, cuneiform texts, and cylindrical seals, according to the statement, which added that work is still ongoing to complete the scientific excavation work according to the specified period.
The missions committee suggested that all excavation work be disclosed, that the work be photographed and drawn, and that the artifacts be recorded by the scientific contexts that SBAH adheres to.
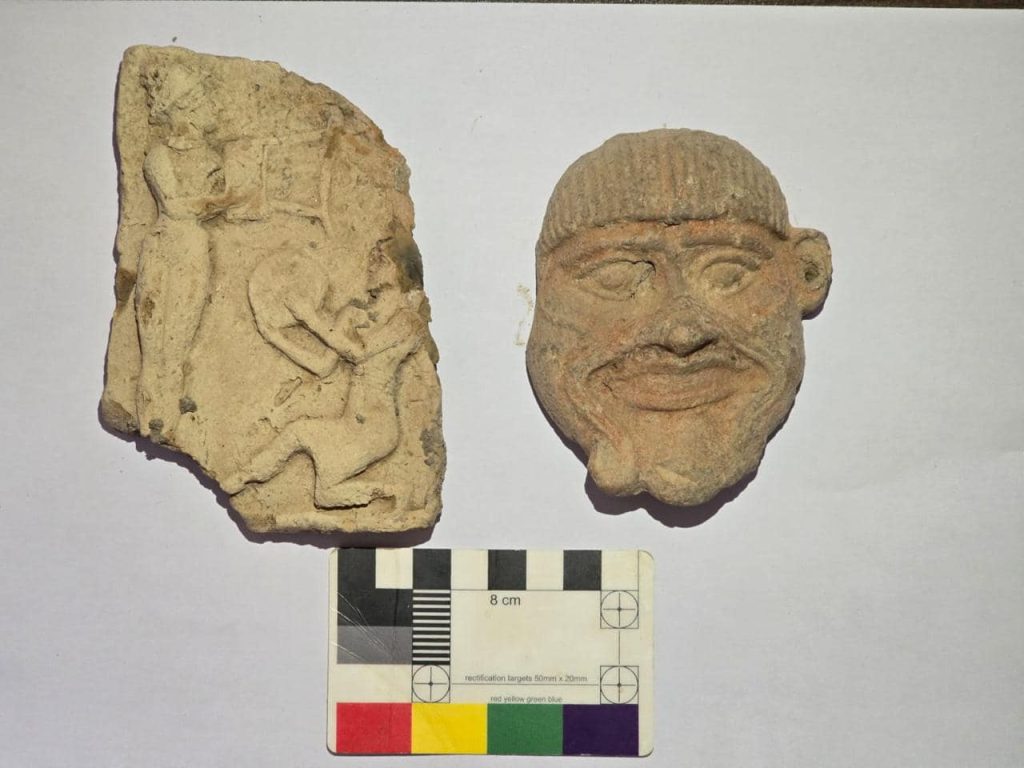

These findings promise to provide fresh insight into the material culture and urban growth of one of the most powerful civilizations in ancient history, in addition to marking a breakthrough in Babylonian archaeological studies.
Iraqi State Board of Antiquities and Heritage (SBAH)
Cover Image Credit: Iraqi State Board of Antiquities and Heritage (SBAH)