New research blends cutting-edge artificial intelligence with advanced radiocarbon dating and offers a transformative perspective on the origins of the Dead Sea Scrolls.
A revolutionary study led by Professor Mladen Popović from the University of Groningen is challenging long-standing assumptions about the Dead Sea Scrolls’ age and authorship. Published in PLOS ONE, the research leverages cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) alongside enhanced radiocarbon dating methods to date these ancient manuscripts with unprecedented accuracy—some scrolls now appear to be up to 150 years older than earlier estimates.
The Dead Sea Scrolls, discovered in the Qumran caves between 1946 and 1947, represent the oldest surviving texts of the Hebrew Bible. Written primarily in Hebrew, with some passages in Aramaic and Greek, the scrolls encompass religious scriptures, legal texts, and ancient calendars, originally dated from the third century BCE to the second century CE.
Historically, scholars relied on paleography—analyzing handwriting styles—to estimate the scrolls’ age. Later, radiocarbon dating offered more precision. However, previous radiocarbon results were skewed due to a mid-20th-century preservation method that coated scrolls with castor oil. This new study revisited those samples, meticulously cleaning 30 fragments to remove contamination, with 27 yielding reliable radiocarbon results.
To push the boundaries of historical dating, the research team developed an AI model called Enoch, named after the ancient biblical figure associated with knowledge and wisdom. Trained on 62 high-resolution images from 24 scrolls, Enoch learned to identify subtle handwriting differences. When tested on 135 previously undated scrolls, Enoch’s estimates aligned with expert paleographers’ expectations 79% of the time.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“This AI technology is like opening a time machine to the ancient world,” said Prof. Popović. “It brings us closer than ever to the people who actually penned the earliest versions of the Bible.”
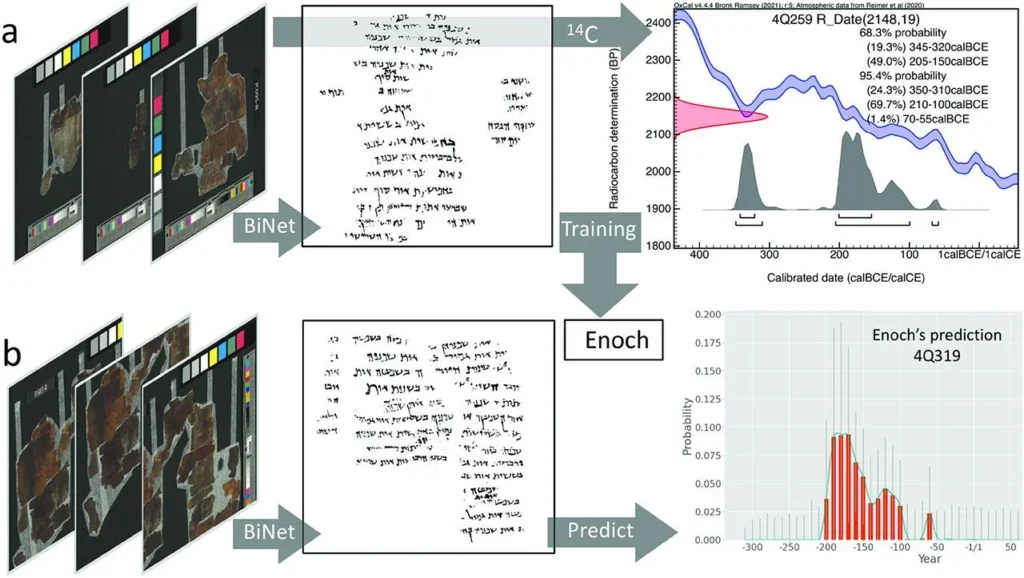
One striking example is scroll 4Q114, containing excerpts from the Book of Daniel. Earlier studies placed its origin in the late 2nd century BCE. Enoch, however, suggests a date between 230 BCE and 160 BCE—potentially aligning it with the lifetime of its purported author.
Moreover, the study highlights overlapping use of Hasmonean and Herodian script styles, indicating a broader time frame for their coexistence than previously believed. In another significant find, a fragment of Ecclesiastes was dated to the precise era traditionally associated with its authorship—possibly redefining timelines in Jewish intellectual history.
Beyond the Dead Sea Scrolls, the research team sees vast potential for Enoch’s application in dating other ancient manuscripts, offering a non-invasive alternative to traditional carbon dating.
This pioneering fusion of AI and archaeology not only transforms our understanding of biblical history but also opens new doors for exploring humanity’s literary and religious heritage with precision and care.
Popović M, Dhali MA, Schomaker L, van der Plicht J, Lund Rasmussen K, La Nasa J, et al. (2025) Dating ancient manuscripts using radiocarbon and AI-based writing style analysis. PLoS One 20(6): e0323185. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0323185
Cover Image Credit: Dead Sea Scroll 28a from Qumran Cave 1, complete, the Jordan Museum in Amman. Public domain