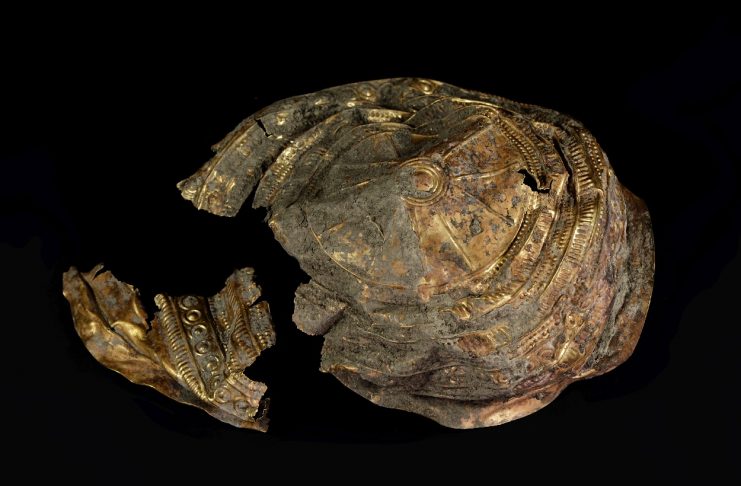
A golden sun bowl and several hundred bronze objects were discovered during archaeological excavations in a prehistoric settlement in today’s Ebreichsdorf in Austria.
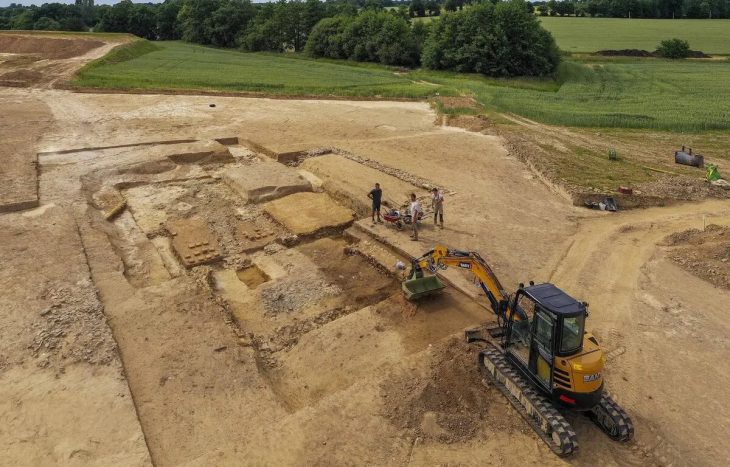
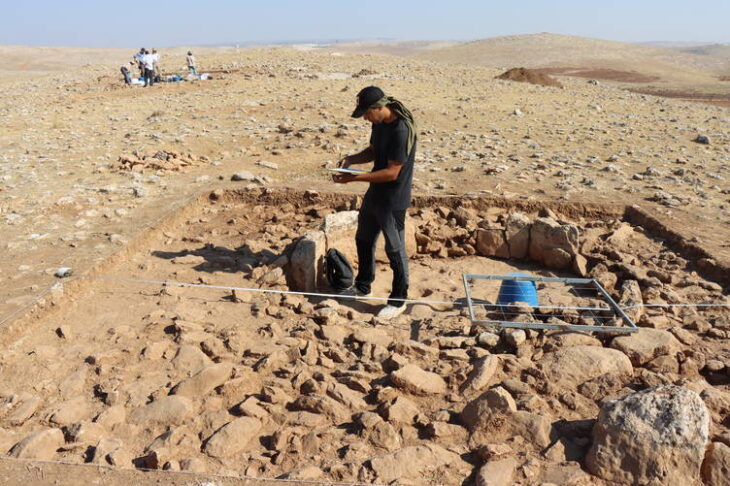
Since September 2019, archaeologists have been excavating at Ebreichsdorf, where they discovered an ancient settlement dating from 1300-1000 BC, which experts have linked to the urn field culture (related to the cremation type of funeral rites).
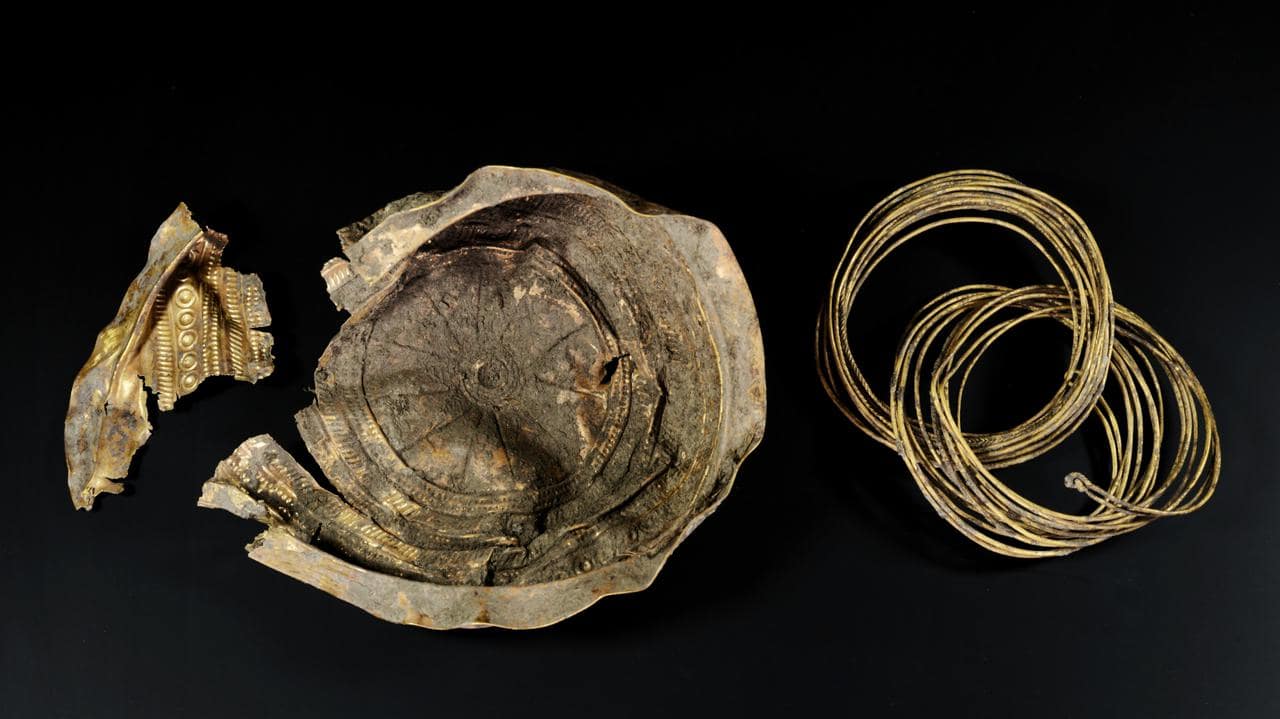
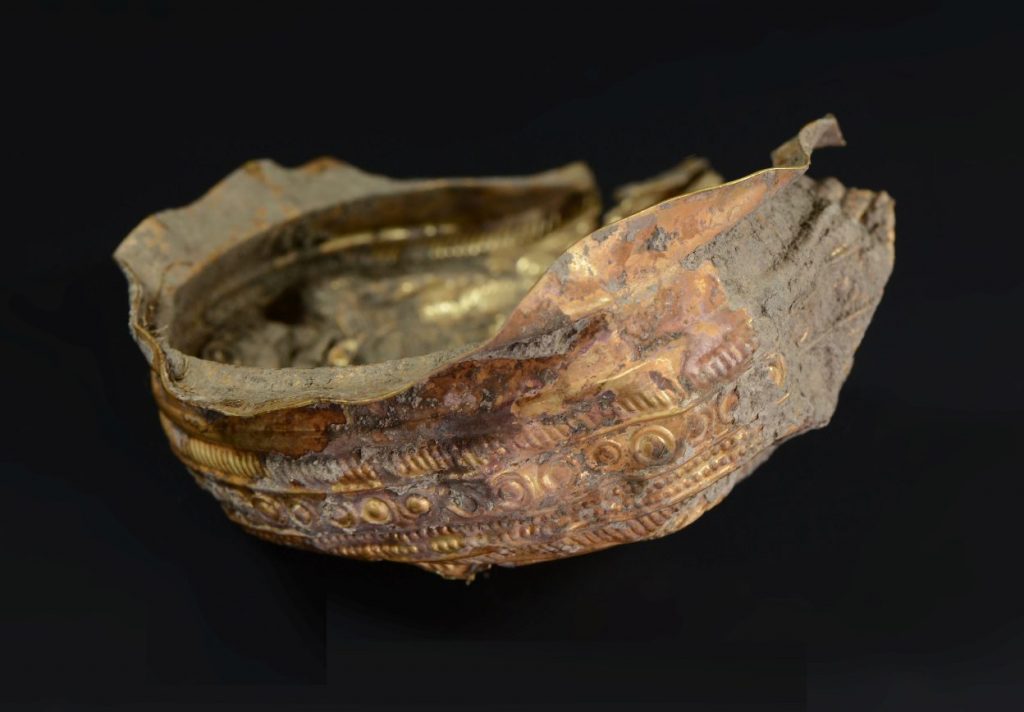
The bowl was discovered next to the wall of one of the settlement’s prehistoric homes. The former craftsman even put an image of the sun’s rays to the bowl, which is adorned with a sun pattern. It has a diameter of 20 centimeters and a height of five centimeters. It is constructed of very thin sheet metal. 90% of it is gold, with the rest being silver and copper. Researchers are now trying to figure out where the basic ingredients used to smelt it came from.
Inside the bowl was coiled golden wire wrapped in organic material clumps that had been stitched with gold thread. The cloth might have been decorative scarves worn during religious rites to honor the sun, according to the research team.
– This is the discovery of life for me – said the head of the excavations in Ebreichsdorf, Polish archaeologist Dr. Michał Sip from the Novetus company, commenting on the discovery of a golden treasure from thousands of years ago. – I have worked on several continents, including Egypt and Guatemala, but so far I have not been able to find anything similar – he added.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The bowl is the first of its kind found in Austria and the second to the east of the Alpine line. That single vessels of this type have so far been discovered in Spain, France, and Switzerland.
– Much more is known from the area of northern Germany, Scandinavia and Denmark – because they were produced there – said the archaeologist Dr. Michał Sip. According to his estimates, more than thirty such bowls are known throughout Europe.
These are not the only remarkable finds in a prehistoric settlement. Up to 500 bronze artifacts, including pins, daggers, and knives, as well as different ceramic clay containers, shells, and animal bones, have been unearthed near the village since excavations began in 2019.

The settlement unearthed in the region of today’s Ebreichsdorf was occupied by an archaeologist-defined society known as the ash field culture about 1300-1000 BC (this name is related to the cremation type of the funeral rite). It belonged to the Middle and Late Bronze Ages. The population had a sedentary existence and was involved in agriculture and animal husbandry, especially sheep.
This culture is also recognized for its remnants in modern Polish territories, and its unique, local variation is known as the Lusatian culture.
The bowl will be placed on display at the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, with excavations of the settlement site to continue for the next six months.
Cover Photo: Andreas Rausch