A previously unknown subterranean tract nearly half a mile long of an Augustan-era aqueduct has been rediscovered in Naples, southern Italy.
The Spelo-archaeologists of the Cocceivs Association found a hitherto unknown stretch of the ancient Augustan aqueduct in Campania, thanks to the authorization of the Extraordinary Commissioner for the reclamation of Bagnoli and with the collaboration of Invitalia.
The Aqua Augusta was built between 30 and 20 B.C by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, best friend and son-in-law of Augustus when he held the high rank of curator aquarium, the magistrate in charge of the supply, management, and maintenance of Rome’s aqueducts.
The water came from the town of Serino in the Campanian Apennines, which was known for the purity of its springs. The aqueduct was more than 90 miles long and had ten branches, seven of which led to urban centers and three of which carried water to wealthy villas. For more than 400 years, it was the longest Roman aqueduct until the construction of the 265-mile-long Aqueduct of Constantinople.
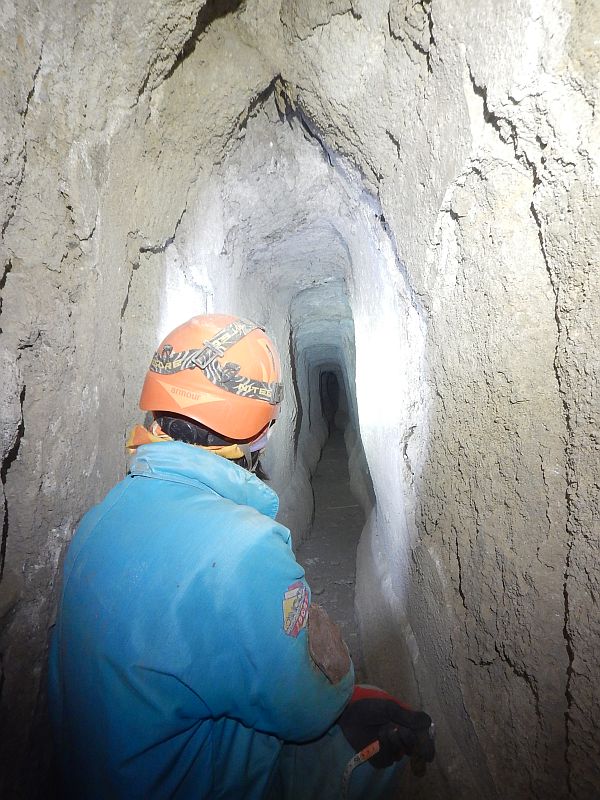

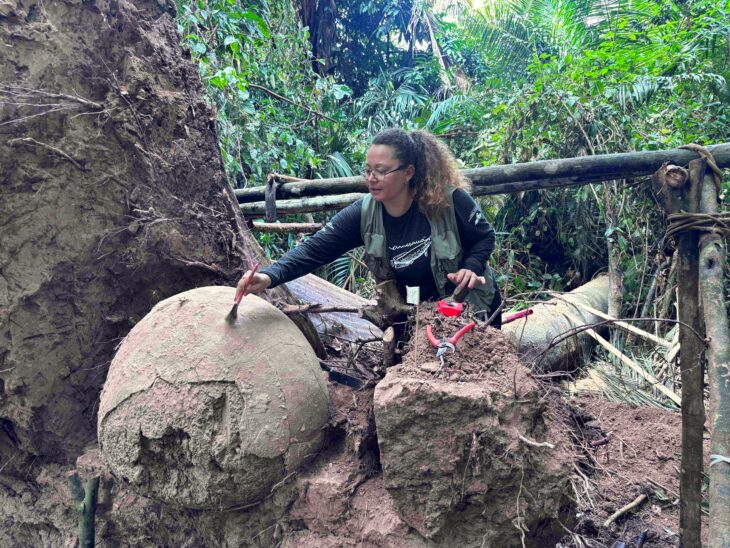
However, the intricate Aqua Augusta has received very little attention from researchers, making it the least well-researched aqueduct in the Roman world. New discoveries earlier this month by the Cocceius Association, a nonprofit group that engages in speleo-archaeological work, are bringing this fascinating aqueduct to light.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
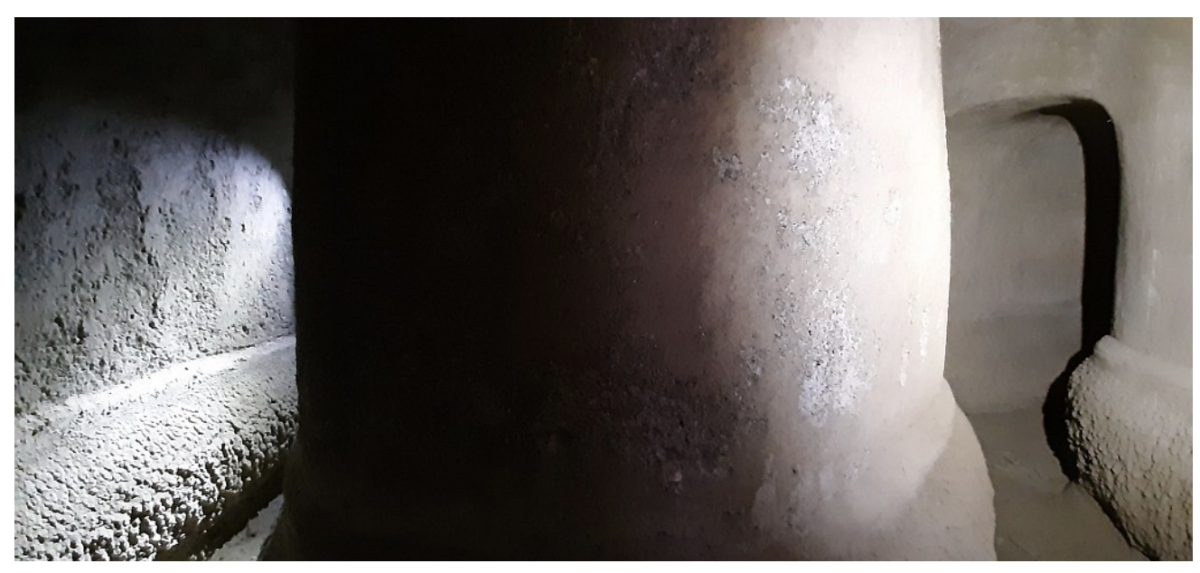
Association members discovered a branch of the aqueduct that carried drinking water to the hill of Posillipo and the crescent-shaped island of Nisida thanks to reports from locals who used to explore the tunnels as children. So far, approximately 2,100 feet (650 meters) of the well-preserved aqueduct have been discovered, making it the Aqua Augusta’s longest known segment.
Most of the route consists of a hole between 52 cm and 70 cm wide, with a 64 cm high hydraulic plaster coating at the base of the piers, which is in turn covered by a thick limestone deposit. It is a winding, turning path, the result of errors and/or necessary derailments encountered by Agrippa’s builders.
There are some obstacles and tight spots, but the entire length is accessible. This is the first long uninterrupted stretch of a Roman aqueduct in excellent condition that can be studied in great detail.