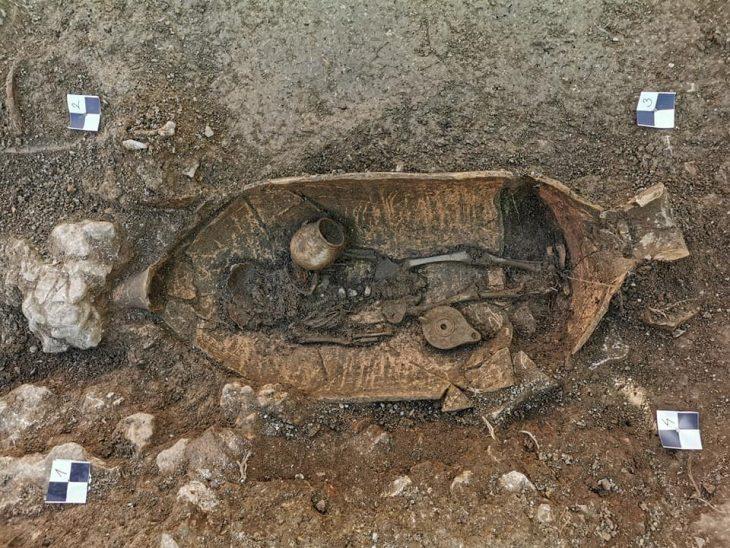
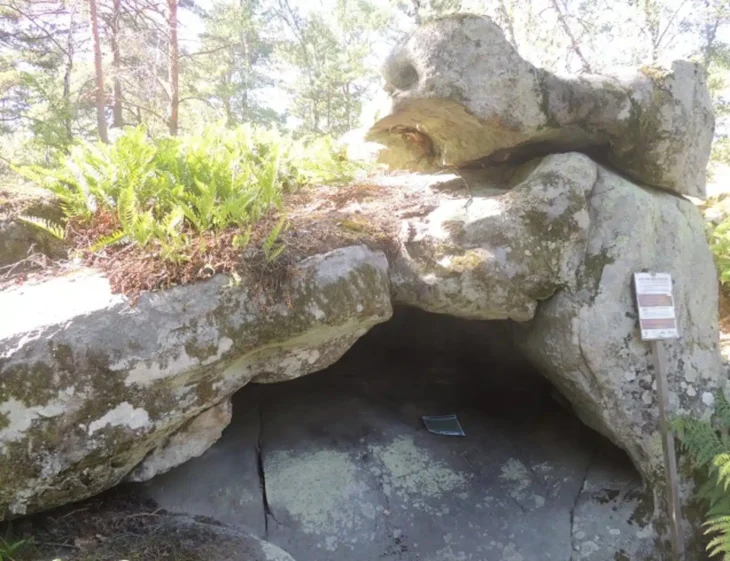
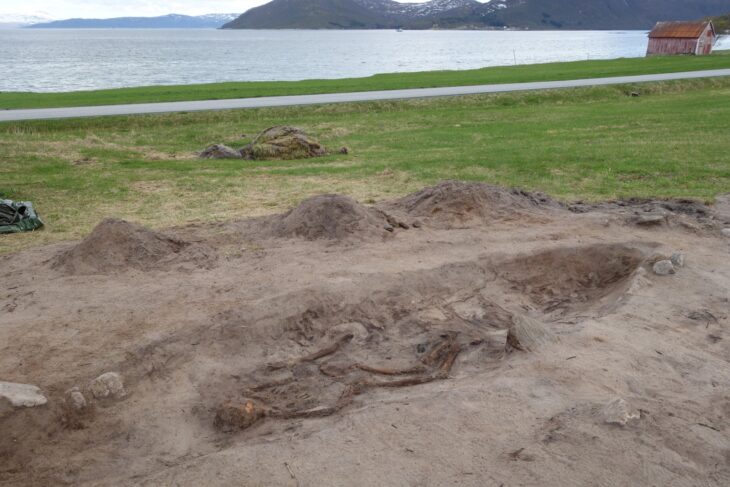
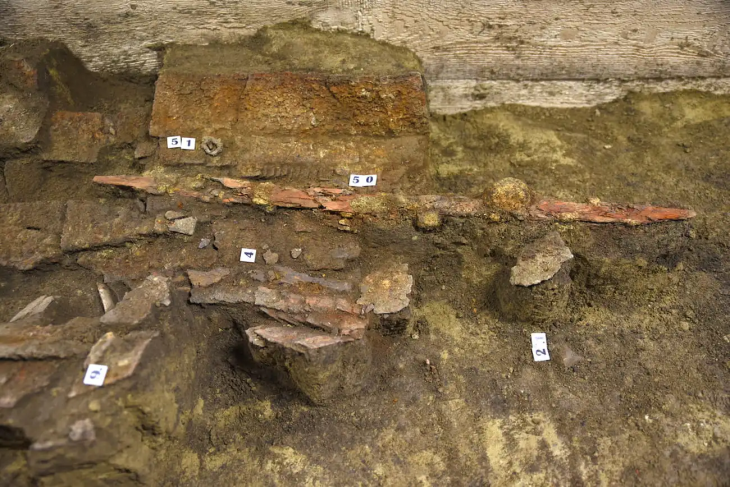
The fossilized Neanderthal skeleton, discovered in a cave system in the Rhône Valley of France, represents a previously unidentified lineage that split from other Neanderthals around 100,000 years ago. The researchers named the mysterious Neanderthal “Thorin” after a character from the universe of J. R. R. Tolkien.
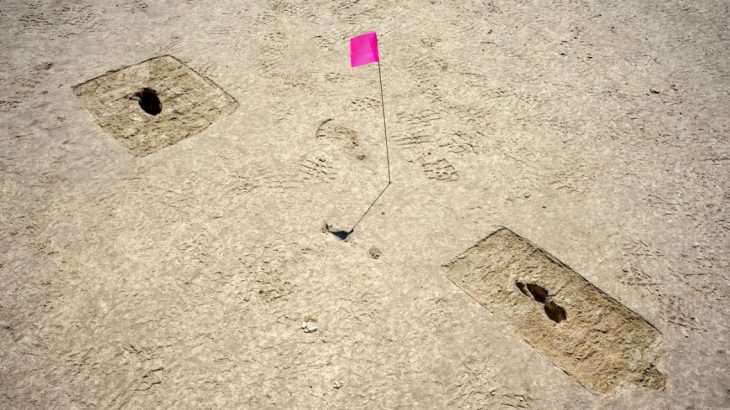
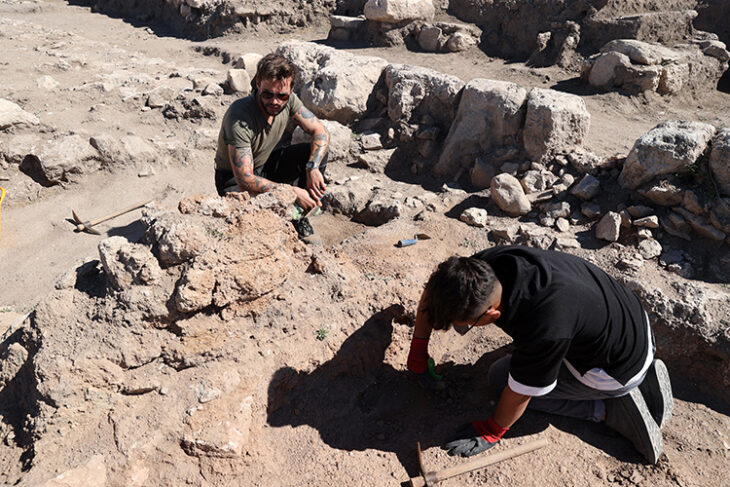
Thorin’s fossilized remains were first discovered in 2015 in Grotte Mandrin—a well-studied cave system that also housed early Homo sapiens—and he is still being slowly excavated. This latest work shows that the cavern also housed Neanderthals at a different time, around 40,000 to 45,000 years ago, towards the end of their existence as a species.
Based on Thorin’s location within the cave’s sediment, the team’s archeologists suspected that he lived around 40–45,000 years ago, making him a “late Neanderthal.” To determine his age and relationships with other Neanderthals, the team extracted DNA from his teeth and jaw and compared his full genome sequence to previously sequenced Neanderthal genomes.
Surprisingly, the initial genomic analysis suggested that Thorin was much older than the archeological age estimate because his genome was very distinct from other late Neanderthals and much more closely resembled the genomes of Neanderthals who lived more than 100,000 years ago.
By comparing his genome with those of other Neanderthals, researchers estimated Thorin lived around 105,000 years ago. However, archaeological evidence and analysis of the isotopes in his bones unequivocally showed that Thorin lived no more than 50,000 years ago.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
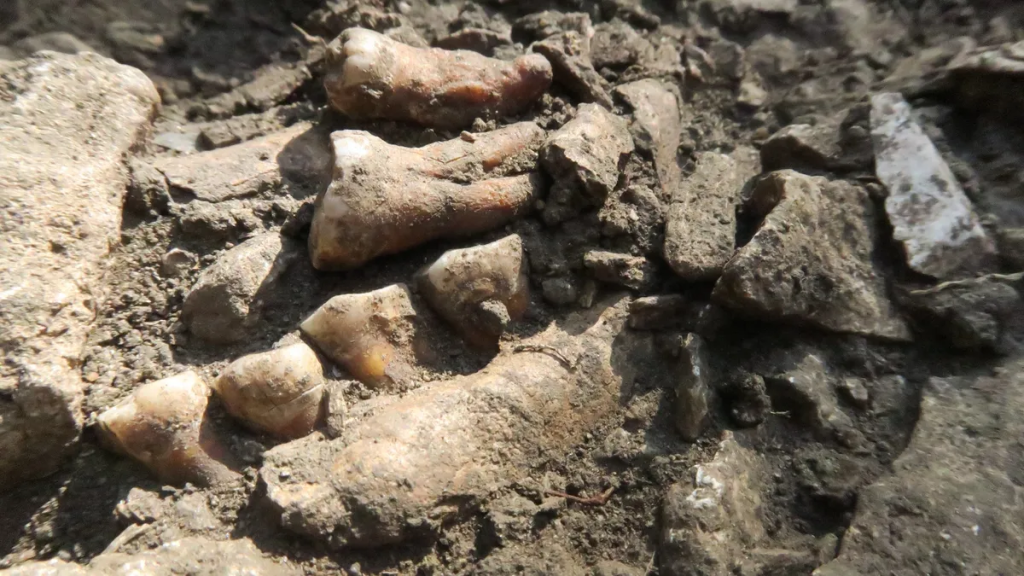

To solve this riddle, the researchers analyzed isotopes from Thorin’s bones and teeth to gain insight into what type of climate he lived in—late Neanderthals lived during the Ice Age, while early Neanderthals enjoyed a much warmer climate. The isotopic analysis showed that Thorin lived in a very cold climate, making him a late Neanderthal.
“For a very long time we [geneticists] were convinced that Thorin really was an early Neanderthal, just because his genetic lineage was so distantly related to contemporary Neanderthals in the same region,” says team member Tharsika Vimala of the University of Copenhagen. “On the other side, the archaeologists were convinced that he was a late Neanderthal.”
“We worked for seven years to find out who was wrong—archeologists or genomicists,” says co-first author and discoverer of Thorin, Ludovic Slimak, CNRS researcher of Université Toulouse Paul Sabatier.
Compared to previously sequenced Neanderthal genomes, Thorin’s genome most closely resembled an individual excavated in Gibraltar, and Slimak speculates that Thorin’s population migrated to France from Gibraltar.
“This means there was an unknown Mediterranean population of Neanderthals whose population spanned from the most western tip of Europe all the way to the Rhône Valley in France,” says Slimak.
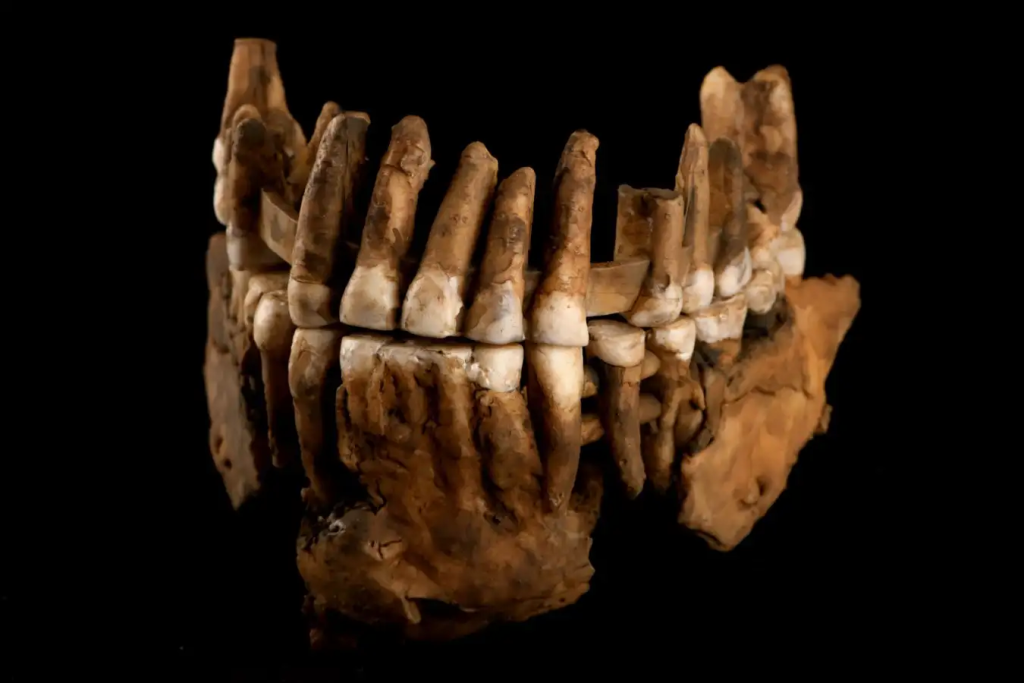
Knowing that Neanderthal communities were small and insular could be key to understanding their extinction because isolation is generally considered to be a disadvantage for population fitness.
“It’s always a good thing for a population to be in contact with other populations,” says Vimala. “When you are isolated for a long time, you limit the genetic variation that you have, which means you have less ability to adapt to changing climates and pathogens, and it also limits you socially because you’re not sharing knowledge or evolving as a population.”
However, to really understand how Neanderthal populations were structured and why they went extinct, the researchers say that more Neanderthal genomes need to be sequenced.
Cover Image: CC-0. https://pixabay.com/illustrations/neanderthals-stone-age-8783874/