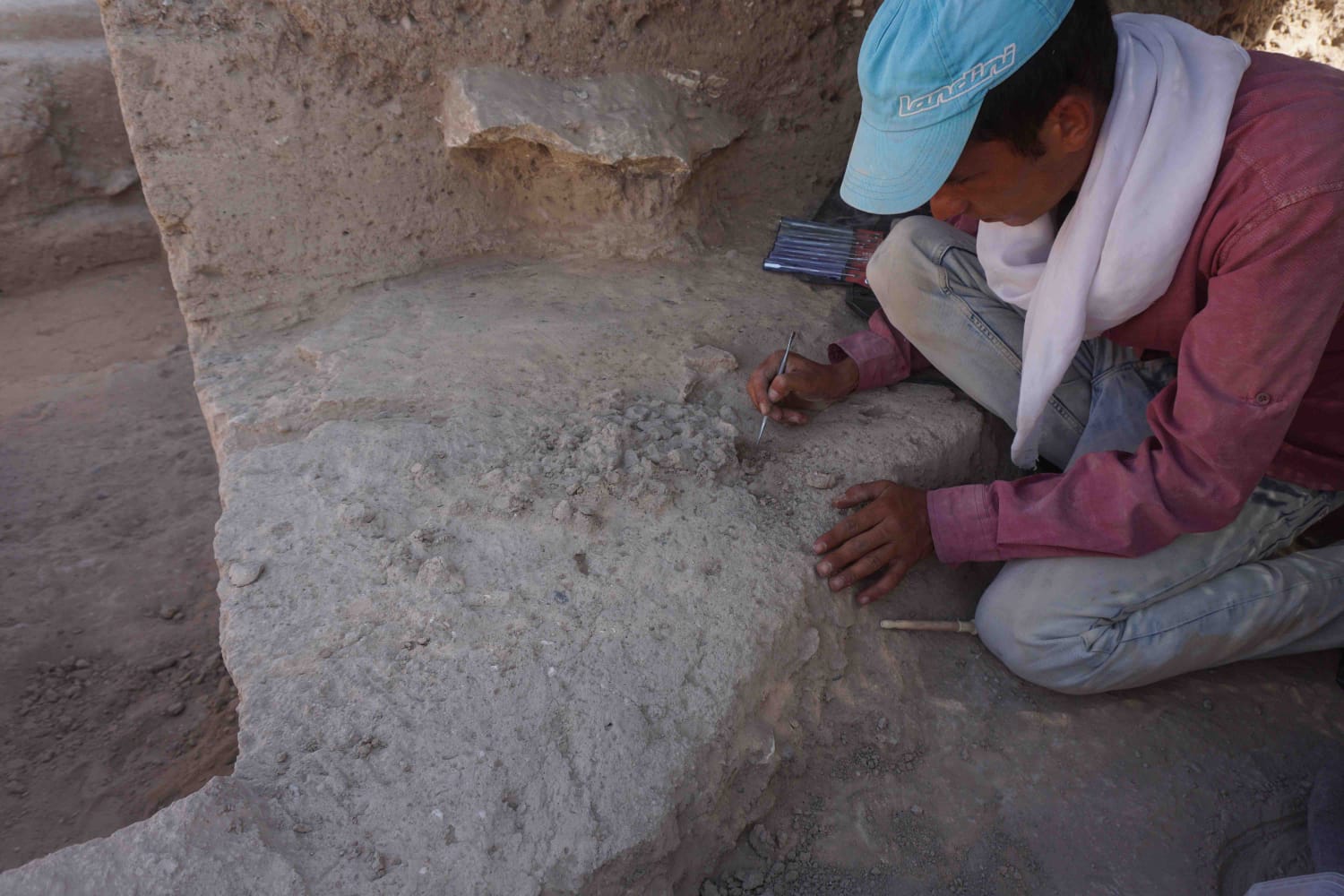
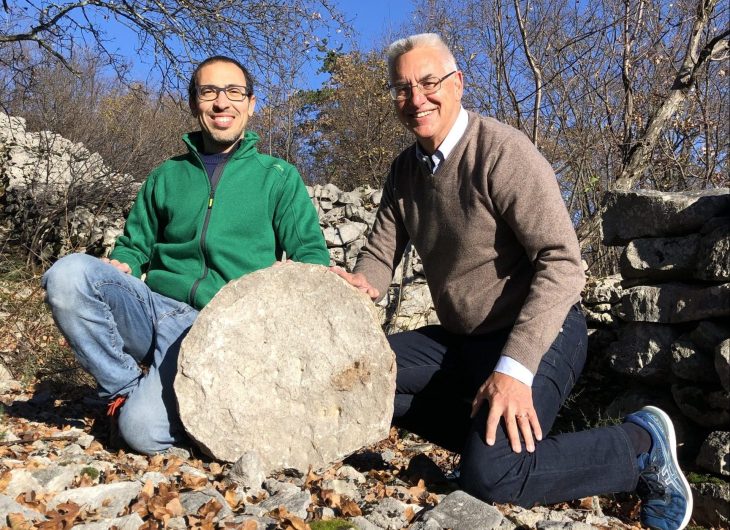
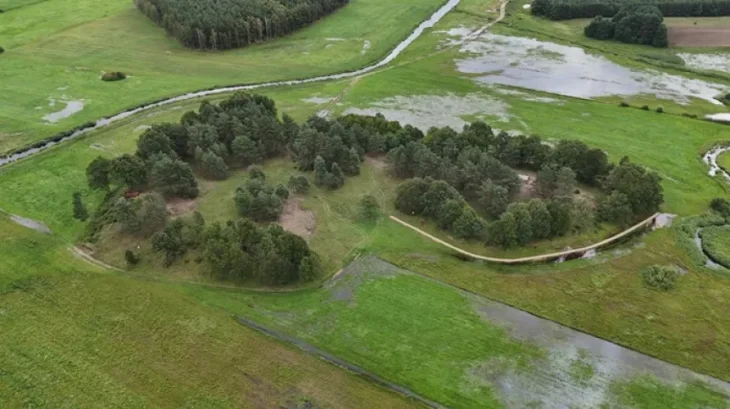
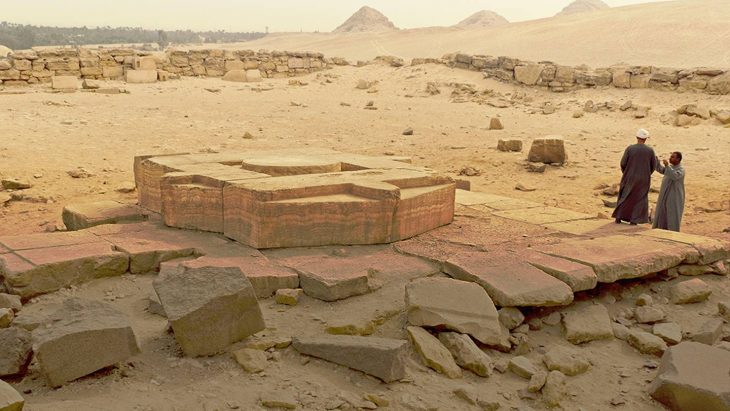
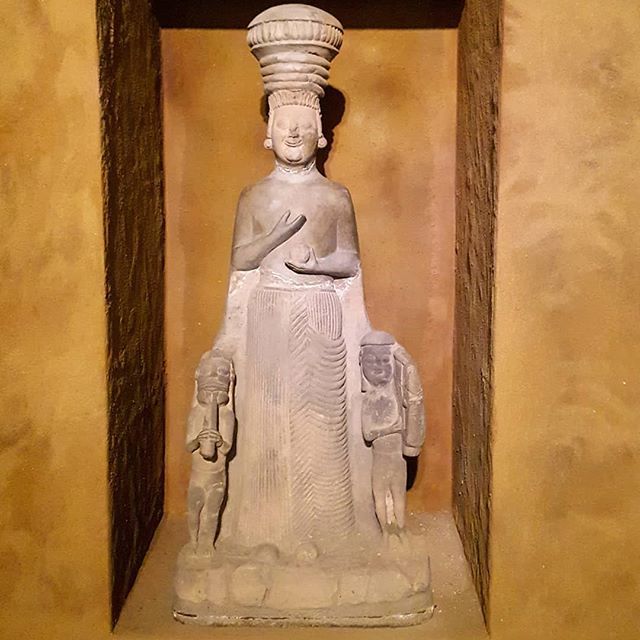
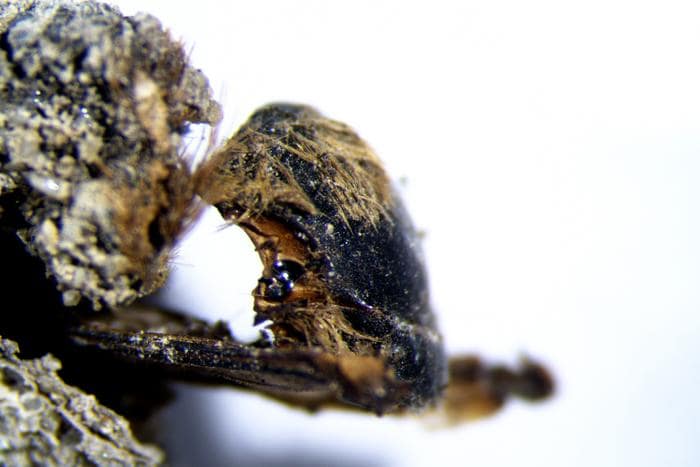
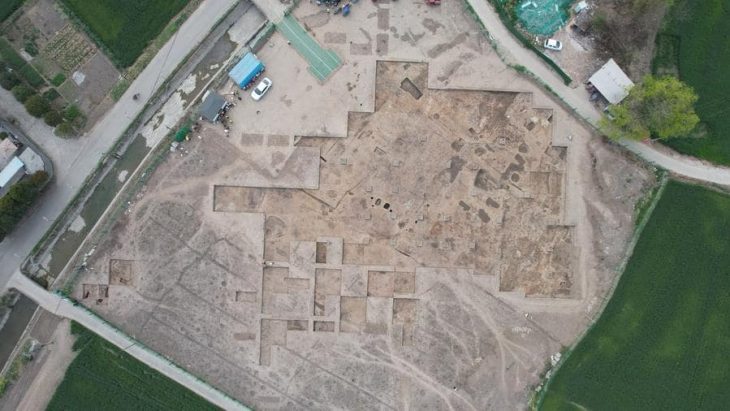
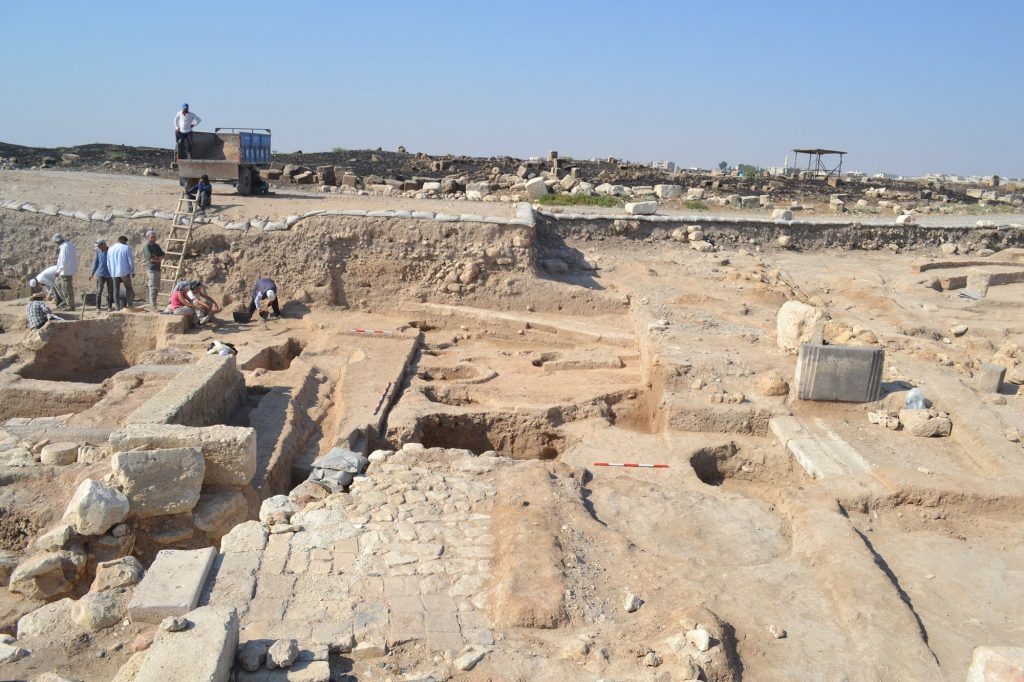
During the excavations carried out in southeastern Turkey’s Gaziantep’s Karkamış (Carchemish) Ancient City, seals and prints determined to belong to a female administrator named Matiya were found 3,000 years ago during the called “Late Bronze Age”.
The seal impressions, which were determined to belong to a female administrator named “Matiya”, revealed the fact that women could also take part in the state administration in Mesopotamia in 1225 BC.
Carchemish, a strategically important place due to being on the Syrian trade routes, was a valuable kingdom for the Hittites, Mitanni, and Hurrians. The Kingdom of Carchemish, which was joined to the Hittite lands by Suppiluliuma I, has always been a vassal of the Hittite kingdom.
Karkamis was the most important administrative center in the region of the Hittite Empire, which ruled over Anatolia and Mesopotamia for centuries.
Istanbul University Hittitology Department Lecturer Assoc. Dr. With the assistance of Hasan Peker, excavations continue under the direction of Professor Nikolo Marchetti from the University of Bologna, Italy.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
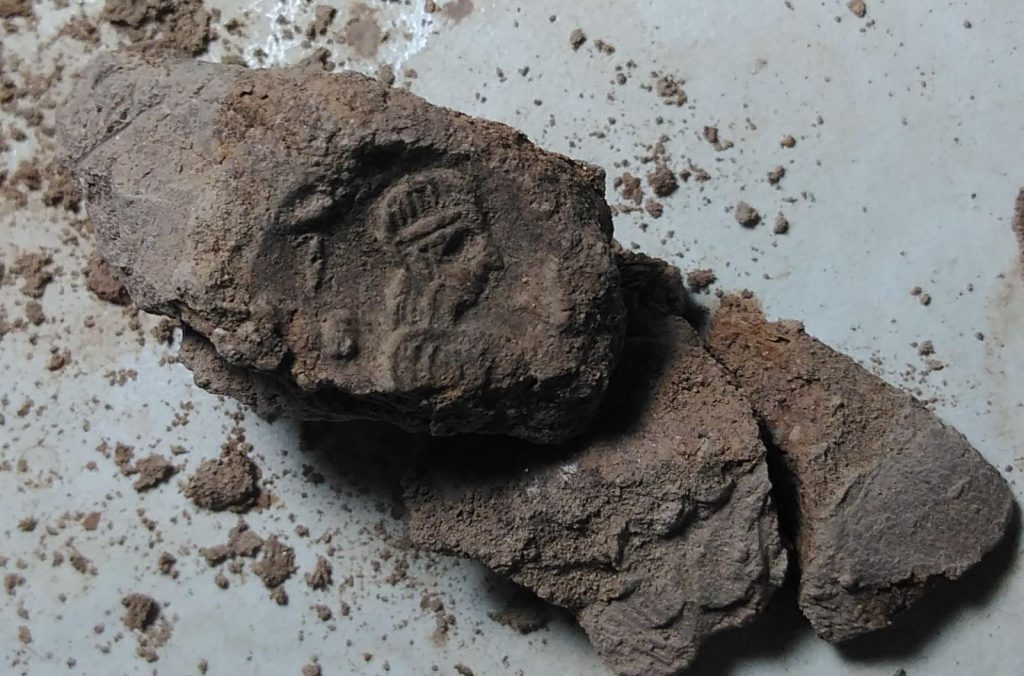

The findings were among dozens of clay seals belonging to the highest officials in a hierarchical order unearthed by an excavation team headed by Nicolo Marchetti, an archaeology professor at the University of Bologna in Italy, according to a statement by the Gaziantep metropolitan municipality.
It was determined that two-thirds of the Anatolian hieroglyphic seal impressions belonged to Matiya from the period defined as the “Late Bronze Age.”
The new discoveries are expected to shed light on the role of women in state governance during the Hittite Empire.

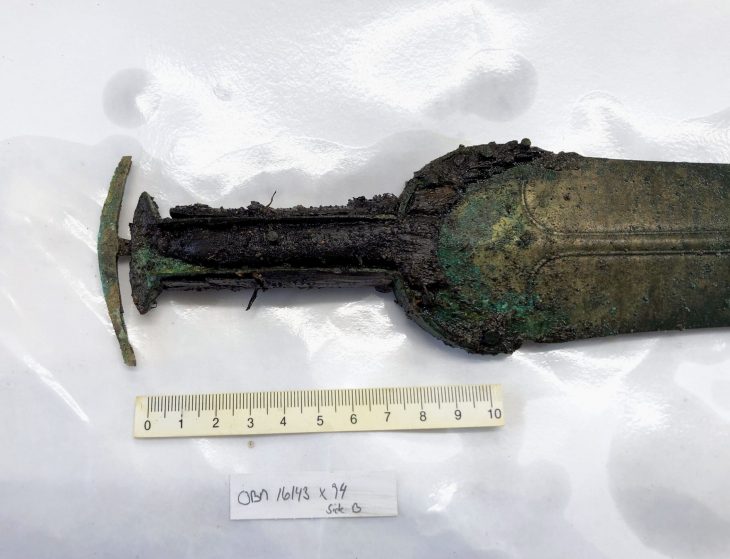
A bulla, an amulet worn like a locket, containing seal impressions belonging to Piradu, one of the important merchants of the Middle Assyrian Kingdom, was also found during the excavations, said the statement.
“The identity of Piradu will contribute to the analysis of Hittite-Assyrian relations which deteriorated towards the collapse of the Hittite State and the chronology of some events of the period.
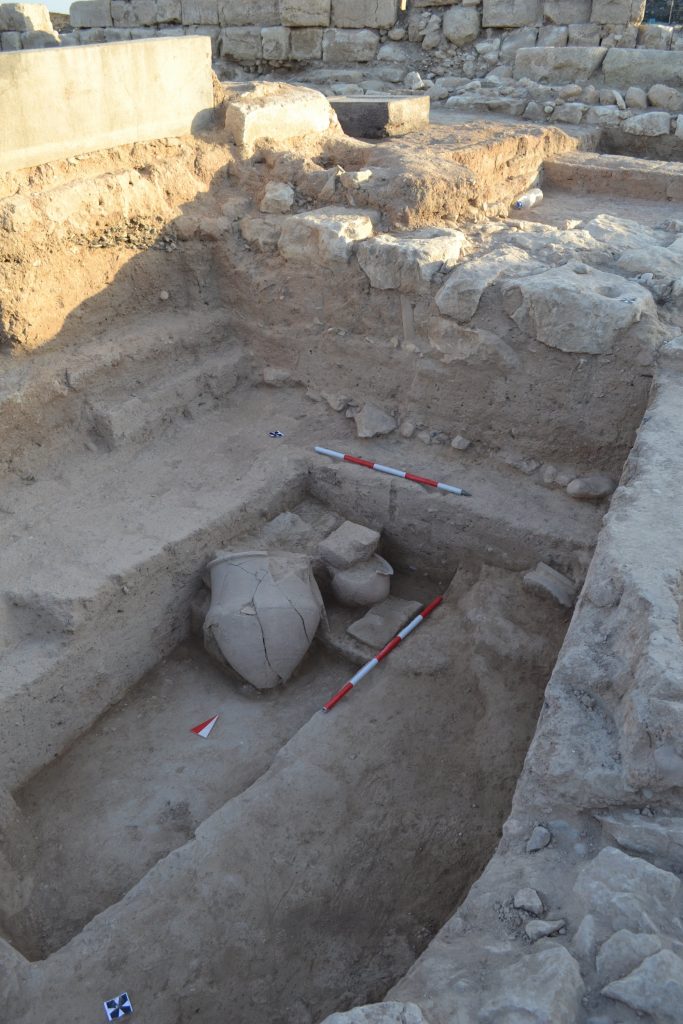

“In addition to these findings, in the Iron Age Cemetery just below the modern cemetery area, salvage excavations were carried out in order to prevent damage to the ancient tombs. Within two years, findings pointing to the cultural and traditional understandings of the 7th and 8th centuries BC were found,” it added.
Among these was a calcite tomb stele, or carved piece of stone, of a man named Sanai from King Kamani’s reign in the first half of the 8th century BC.
Gaziantep municipality also built an excavation house for newly unearthed archeological finds.