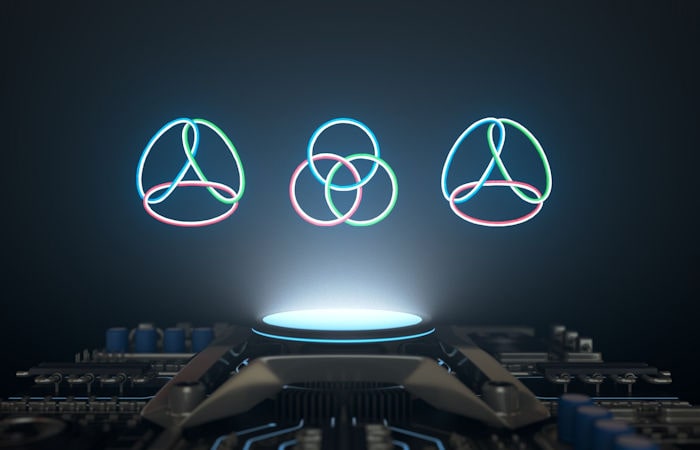
Scientists demonstrated how three vortices can be linked in such a way that they cannot be dismantled. Although this study focused on vortices in a special type of matter known as a Bose-Einstein condensate, the structure of the links resembles a pattern used by Vikings and other ancient civilizations. The findings have implications for quantum computing, particle physics, and other fields.
Postdoctoral researcher Toni Annala uses strings and water vortices to explain the phenomenon: ‘If you make a link structure out of, say, three unbroken strings in a circle, you can’t unravel it because the string can’t go through another string. If, on the other hand, the same circular structure is made in water, the water vortices can collide and merge if they are not protected.’
‘In a Bose-Einstein condensate, the link structure is somewhere between the two,’ says Annala, who began working on this in Professor Mikko Möttönen’s research group at Aalto University before moving back to the University of British Columbia and then to the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton. Roberto Zamora-Zamora, a postdoctoral researcher in Möttönen’s group, was also involved in the study.
The researchers mathematically demonstrated the existence of a structure of linked vortices that cannot break apart because of their fundamental properties. ‘The new element here is that we were able to mathematically construct three different flow vortices that were linked but could not pass through each other without topological consequences. If the vortices interpenetrate each other, a cord would form at the intersection, which binds the vortices together and consumes energy. This means that the structure cannot easily break down,’ says Möttönen.
From antiquity to cosmic strands
The structure is conceptually similar to the Borromean rings, a pattern of three interlinked circles which has been widely used in symbolism and as a coat of arms. A Viking symbol associated with Odin has three triangles interlocked in a similar way. If one of the circles or triangles is removed, the entire pattern dissolves because the remaining two are not directly connected. Each element thus links its two partners, stabilising the structure as a whole.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The mathematical analysis in this research shows how similarly robust structures could exist between knotted or linked vortices. Such structures might be observed in certain types of liquid crystals or condensed matter systems and could affect how those systems behave and develop.
‘To our surprise, these topologically protected links and knots had not been invented before. This is probably because the link structure requires vortices with three different types of flow, which is much more complex than the previously considered two-vortex systems,’ says Möttönen.
These findings may one day help make quantum computing more accurate. In topological quantum computing, the logical operations would be carried out by braiding different types of vortices around each other in various ways. ‘In normal liquids, knots unravel, but in quantum fields there can be knots with topological protection, as we are now discovering,’ says Möttönen.
Annala adds that ‘the same theoretical model can be used to describe structures in many different systems, such as cosmic strings in cosmology.’ The topological structures used in the study also correspond to the vacuum structures in quantum field theory. The results could therefore also have implications for particle physics.
Next, the researchers plan to theoretically demonstrate the existence of a knot in a Bose-Einstein condensate that would be topologically protected against dissolving in an experimentally feasible scenario. ‘The existence of topologically protected knots is one of the fundamental questions of nature. After a mathematical proof, we can move on to simulations and experimental research,’ says Möttönen.
Cover Photo: In Borromean rings, each circle holds the pattern together by passing through the other two circles. Photo: Alexandr Kakinen / Aalto University