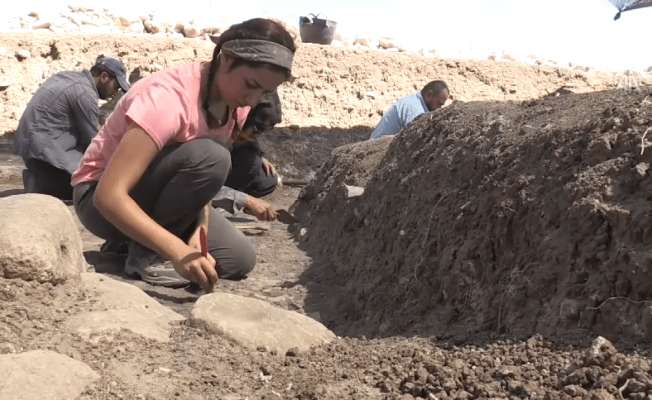
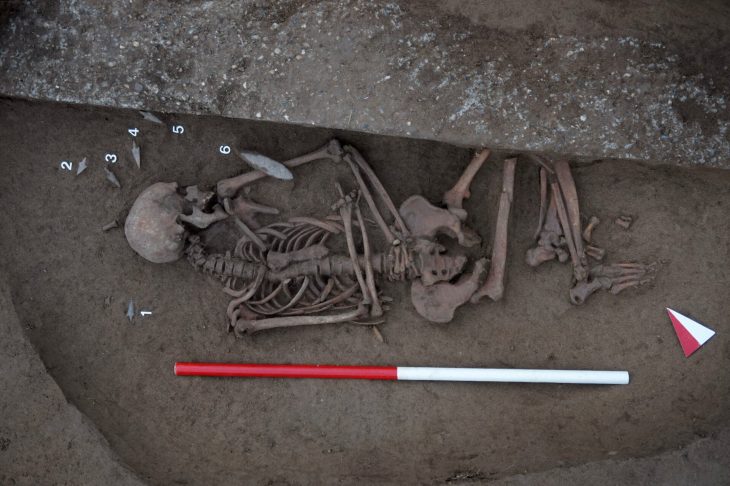
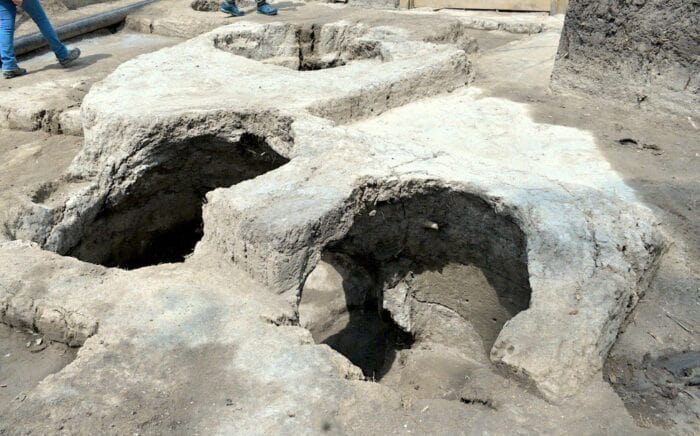
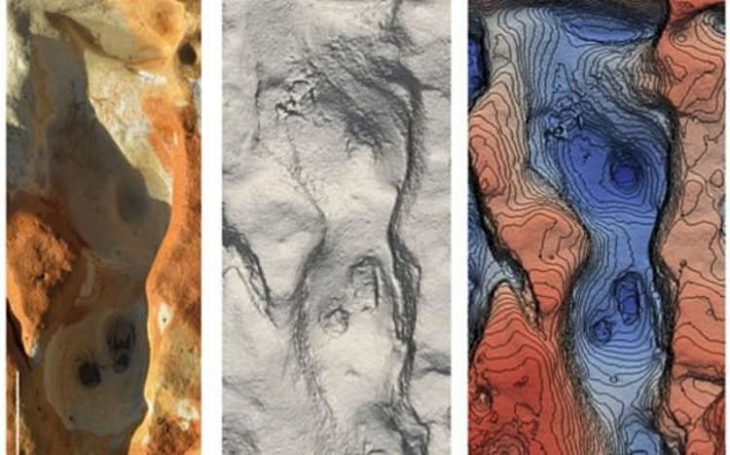
During the excavations in Domuztepe mound, it was revealed that an architectural structure thought to be 7-8 thousand years old had more than one storey and a balcony.
This year’s part of the excavation works, which continues within the borders of Kelibişler District, under the coordination of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism and under the direction of Hacettepe University Faculty of Letters Archeology Department Associate Professor Halil Tekin, has been completed.
AssociateProfessor Halil Tekin told Anadolu Agency (AA) that they had reached valuable findings during this year’s excavations.
Stating that an architectural structure, which is considered to be 7-8 thousand years old among the finds, has more than one floor and has a balcony, Tekin said that the balcony feature of the building is a situation seen for the first time in prehistoric Anatolian architecture.
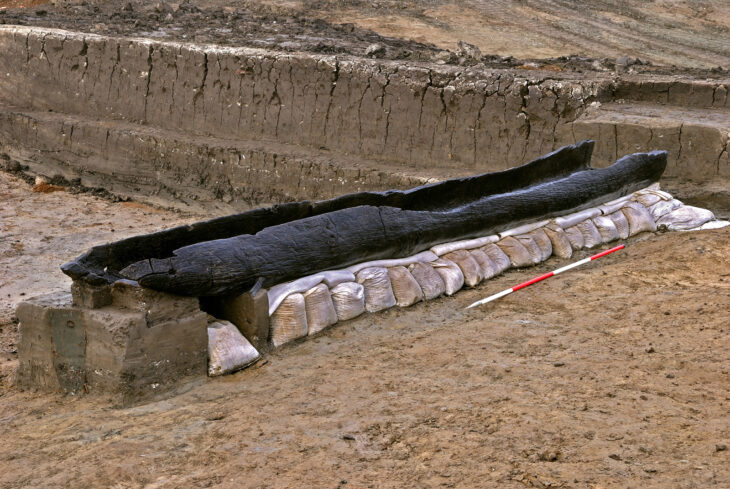
Tekin stated that they only reached the stone foundations of the buildings in the excavation area and that they could obtain information about the upper parts of the buildings thanks to the motifs on the pottery, and noted that they determined that the buildings in the region had stone foundations, wooden and multi-story structures.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
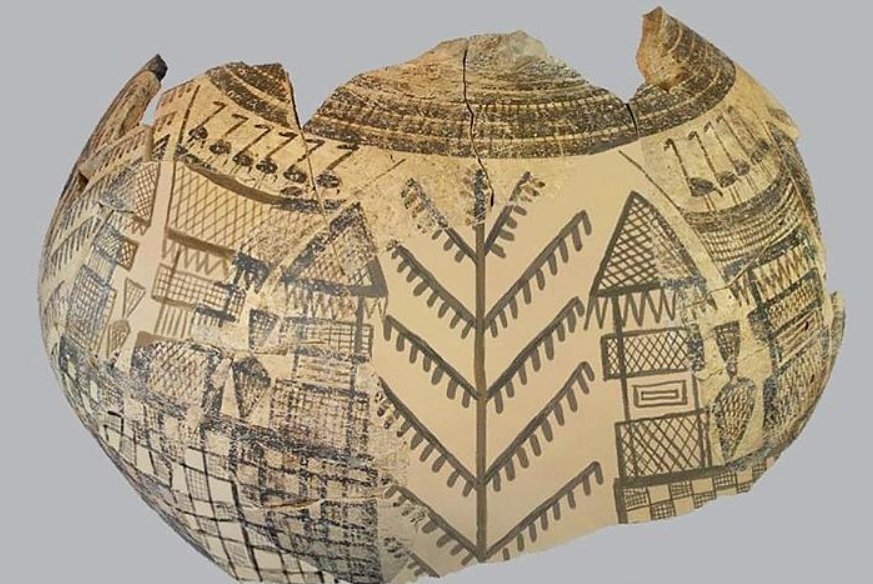

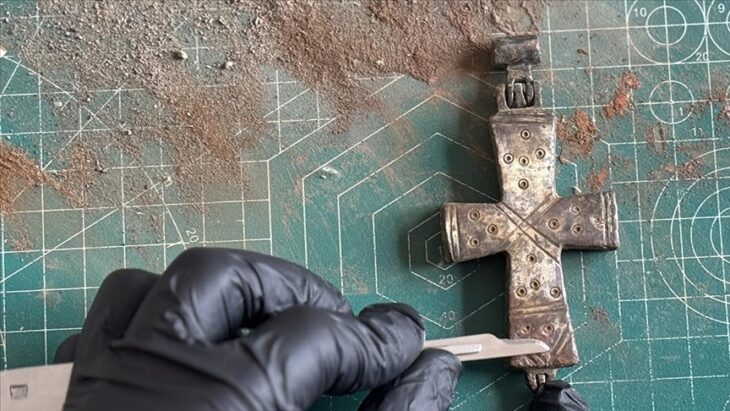
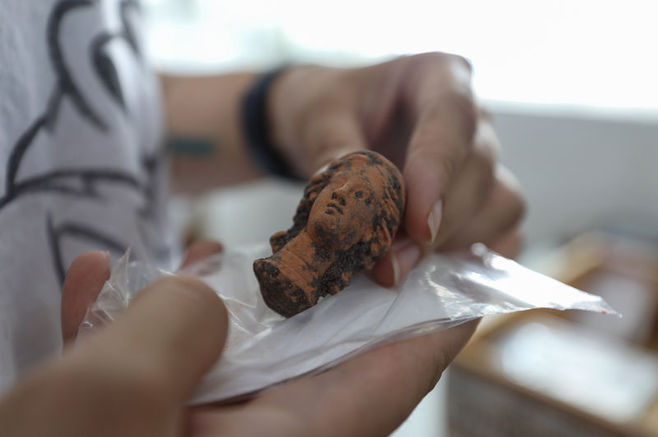
Tekin said that Göbeklitepe reflects with the relief technique on its steles, Çatalhöyük with its wall paints, and Domuztepe with its paint decorations on pottery the stone age art.
He pointed out that concrete data on the aftermath of Göbeklitepe were obtained in Domuztepe and that these regions were the leading representatives of visual art in the world neolithic.
Domuztepe will be animated in 3D
The settlement, which was found during the excavations of the Domuztepe Mound in the Türkoğlu district of Kahramanmaraş and is thought to belong to 7-8 thousand years ago, will be animated in three dimensions.

Emphasizing that they started to work on the 3-dimensional revitalization of the region, Tekin said, “We have embarked on a big project with the approval of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism. With the financial support of Türkoğlu Municipality, we will make copies of these structures so that they can be perceived in 3D, when visitors come, they can clearly perceive what kind of architecture was in Domuztepe 7-8 thousand years ago,” he said.
Türkoğlu Mayor Osman Okumuş said that rescue excavations of Domuztepe and Gavur Lake Swamp were carried out in the district, and new finds come to light in the regions every year.
Stating that the archeopark project, which was prepared to exhibit the finds and open them to world tourism, is coming to an end, Okumuş said:
“How they lived here 7-8 thousand years ago, will be animated in 3D and our children will go back thousands of years. At the same time, this was a region full of swamps and lakes at that time. Domuztepe is also in the Gavur Lake basin, which is on the world’s largest bird migration route. “We found elephant fossils during excavations sponsored by us this year. We are preparing a project that will be a first in the world with these elephant fossils,” he said.
Okumuş added that their support for the excavations will continue in the following periods as well.