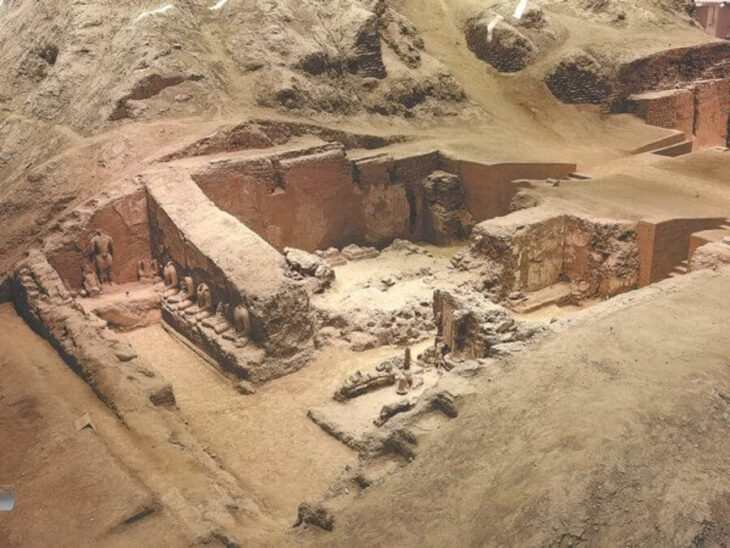
Researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery at the site of the Yamashiro Kokubunji temple, revealing what is believed to be one of the largest ancient cafeterias from the Nara Period (710-784). The Kyoto prefectural board of education announced the findings on February 4, shedding light on the historical significance of this site.
Originally constructed as a food preparation and dining area for monks, the ruins are located at the site of the Yamashiro Kokubunji temple, which was established under the orders of Emperor Shomu (701-756). This temple was part of a broader initiative to promote Buddhism across Japan, with the emperor commissioning the construction of several Kokubunji provincial temples.
The Yamashiro Kokubunji temple itself was built as a reconstruction of the imperial palace after the Kuni-kyo capital, established by Shomu, was relocated. The temple grounds are expansive, covering approximately 275 meters from east to west and 330 meters from north to south. Previous archaeological efforts have uncovered various structures, including a hall and a pagoda, but the latest findings are particularly noteworthy.
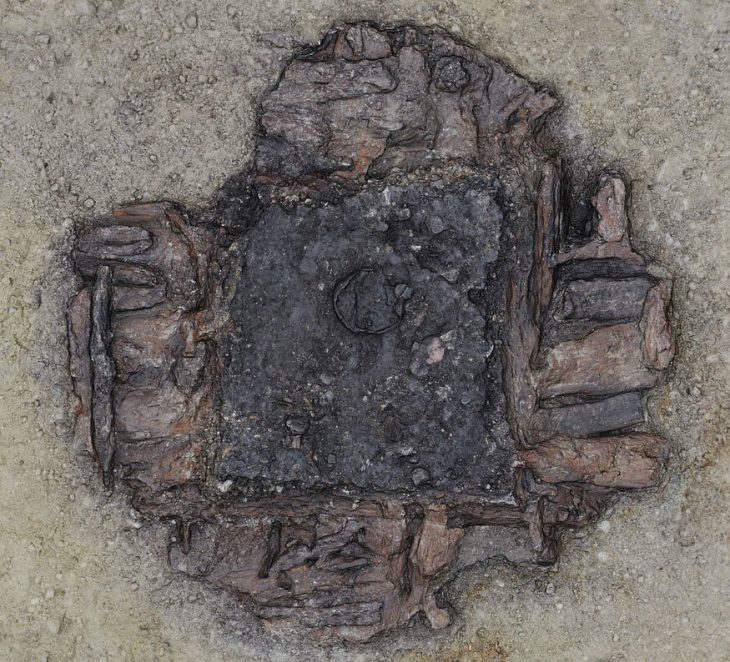
In this recent study, researchers discovered large foundation stones, each about 70 centimeters in size, along with the holes left behind when these stones were removed, located in the northeastern section of the temple grounds. These findings suggest the existence of a substantial building measuring 38.1 meters from east to west and 10.8 meters from north to south.
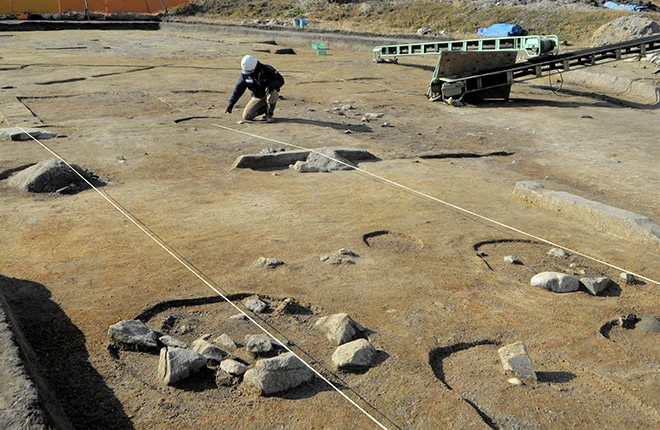

Additionally, earlier excavations revealed a hallway extending from the south of the newly discovered site, leading researchers to believe that the cafeteria was connected to other structures within the temple complex. This architectural layout aligns with similar findings at the Todaiji and Saidaiji temples in Nara, which also featured cafeterias and connecting structures oriented in a north-south direction.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Mahito Uehara, a professor emeritus of archaeology at Kyoto University with expertise in ancient temples, indicated that the latest ruins are likely remnants of buildings that served as a kitchen or storage area. He emphasized the importance of this find, noting that it is the first instance in Japan where the cafeteria layout of a Kokubunji temple can be reconstructed.
The historical context of the site adds further intrigue. The Kuni Palace, built by Emperor Shomu, was intended to serve as his capital during a tumultuous time marked by epidemics and warfare. After relocating from Heijokyo (Nara) to what is now Mikanohara, Kamo-cho, in 740, the new capital was abandoned just four years later. Following this, the site of the main palace hall was repurposed as the Yamashiro Kokubun-ji temple, which utilized the former palace hall as its main hall.
Today, the remnants of the Yamashiro Kokubun-ji still display the stone foundations of both the main hall and the pagoda, which is believed to have originally stood seven levels tall based on the size of the foundation stones. This discovery not only enriches our understanding of the temple’s historical significance but also highlights the architectural advancements of the Nara Period.
Cover Image Credit: Yamashiro Kokubunji temple. Naracity