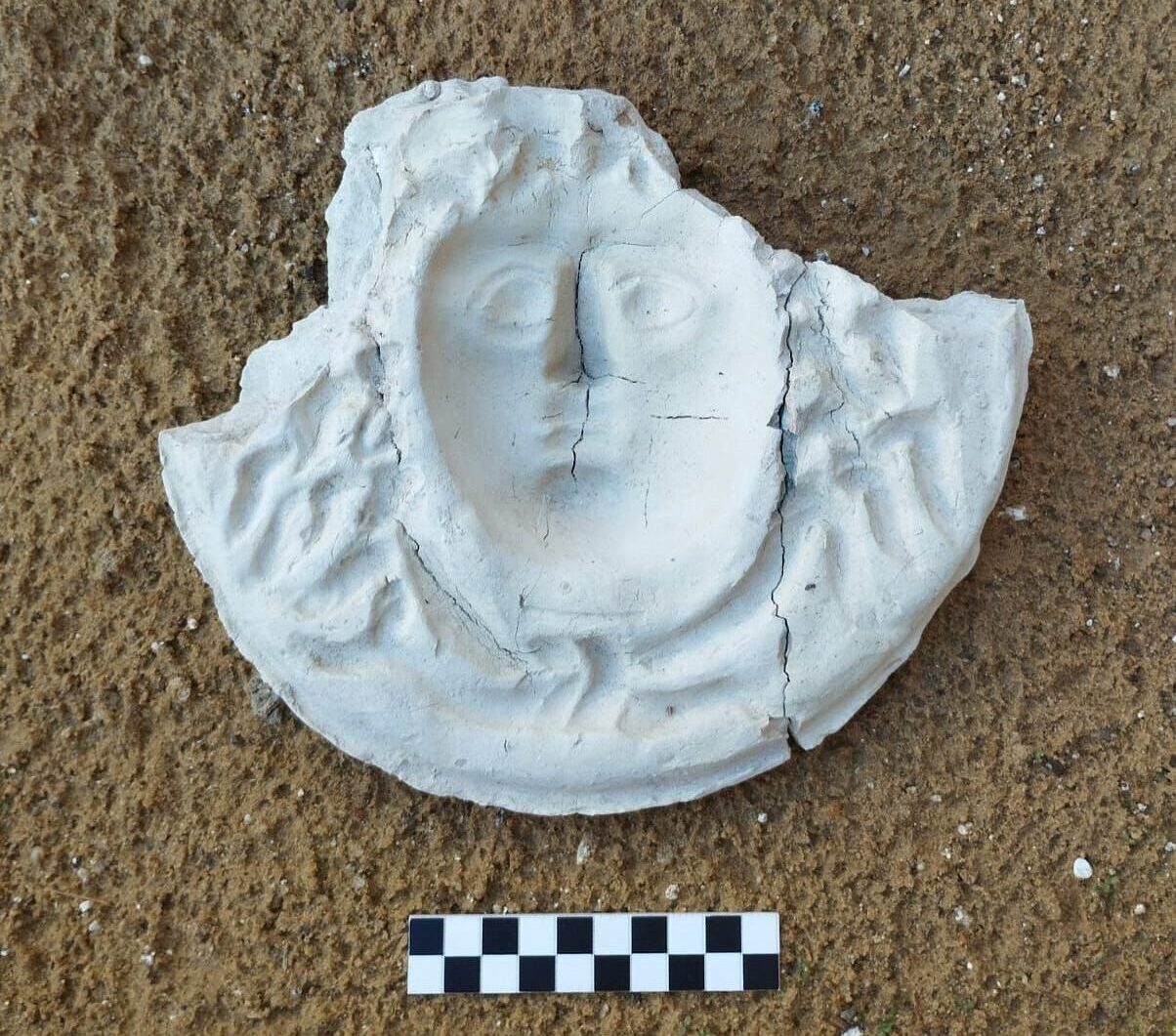
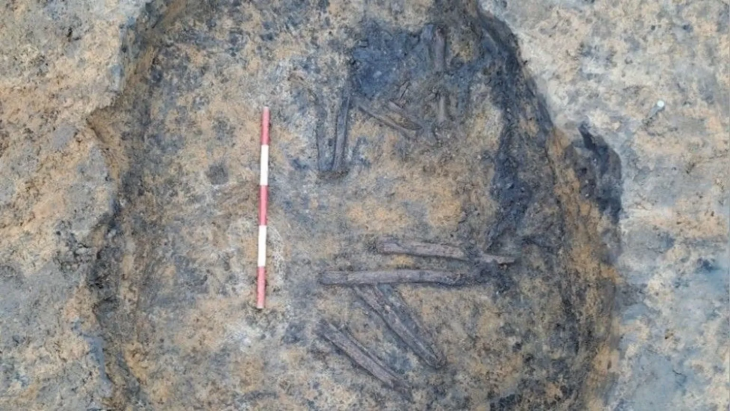
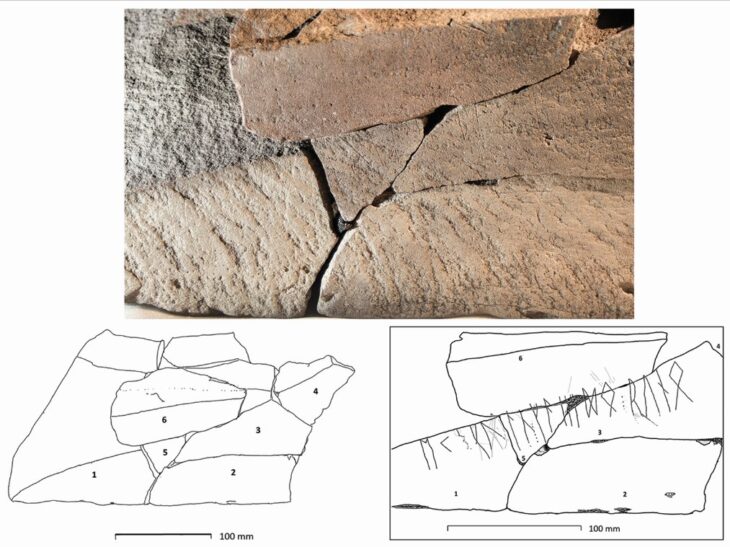
At the Finziade archaeological site in the Sicilian town of Licata, archaeologists have discovered a mask mold that could represent Medusa from Greek mythology.
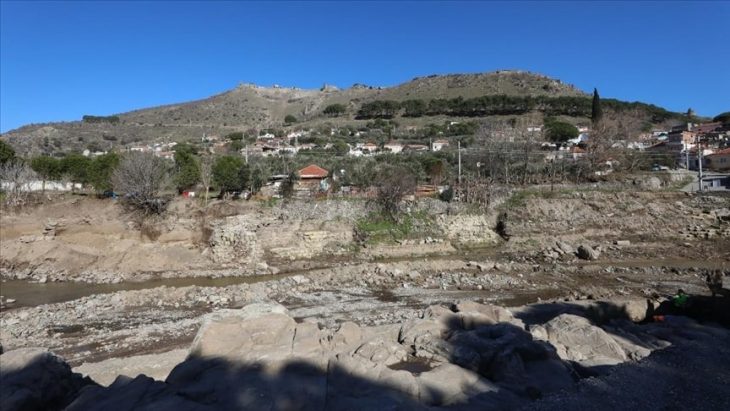
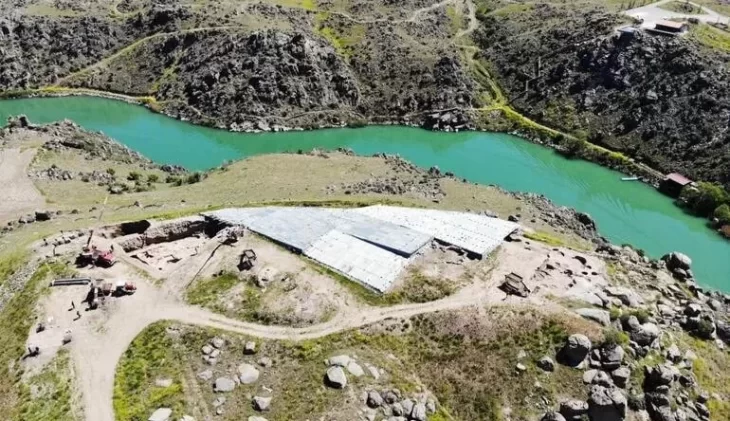
The site of ancient Finziade lies near the centre of the modern city of Licata in the province of Agrigento on the southern coast of Sicily. A hill system morphologically characterizes the area arranged E-W for about 8 km: the so-called ‘Mountain of Licata’, marked on its eastern side by Mount S. Angelo and to the north by an alluvial plain bordered by other hill systems. The excellent location allows you to check the harbors to the south and go up the Salso River, the ancient southern Himera, and the Sicilian hinterland.
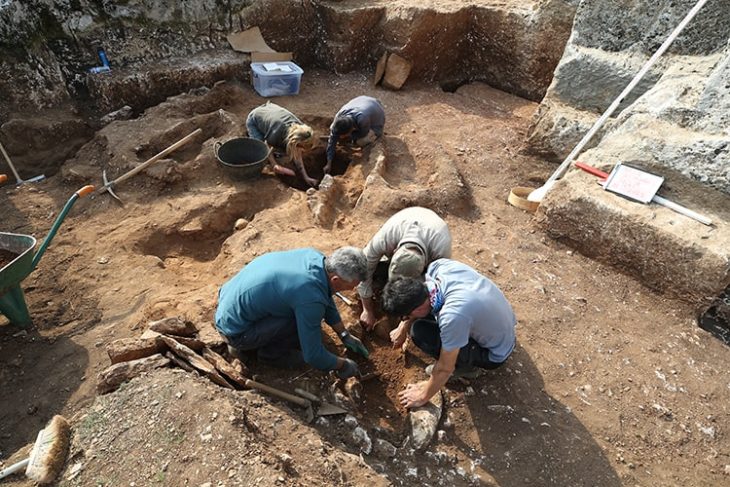
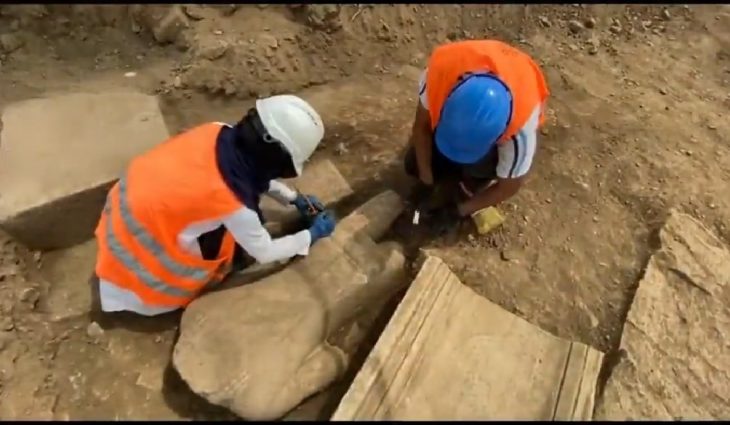
This discovery was made during excavations in the so-called “House 18,” a late Republican-era structure that was probably transformed into an artisanal workshop that produced masks in its last years of use, which was around the beginning of the first century BCE.
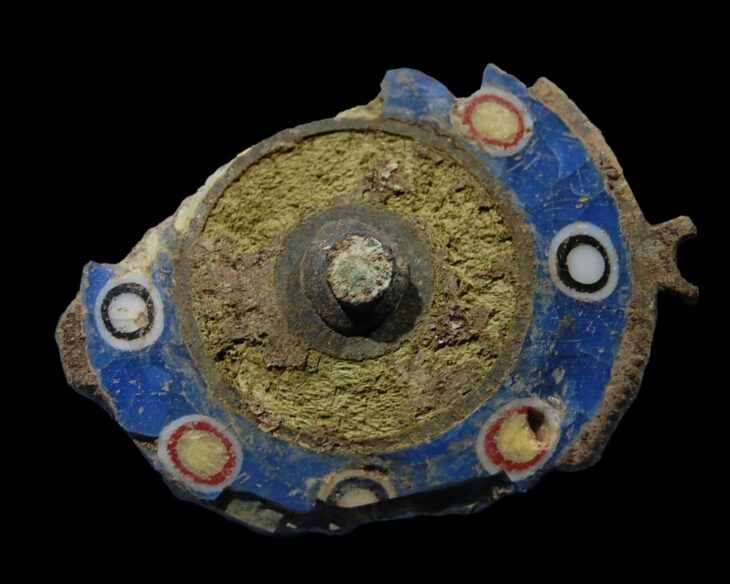
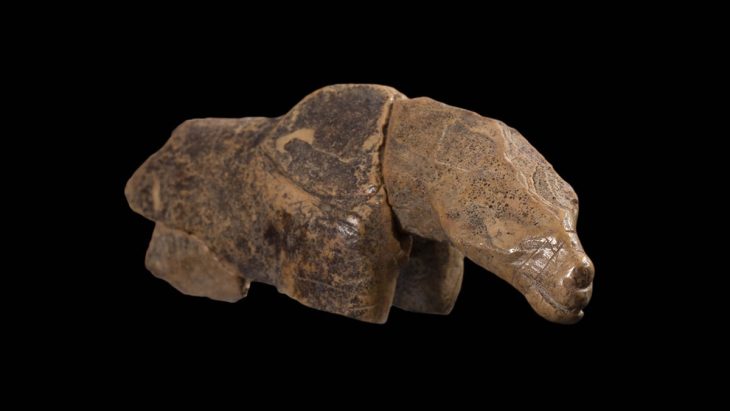
The discovery is part of a broader context, as additional remains linked to this artisanal activity have been uncovered at the same site. Evidence indicates that mask production was a vital component of the local economy and cultural expressions in ancient Finziade, underscoring the significance of symbolism and craftsmanship in Roman Sicily.
House 18, situated within the archaeological zone of Finziade, serves as a compelling illustration of how residential spaces were adapted for commercial or industrial purposes during periods of social and economic transformation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
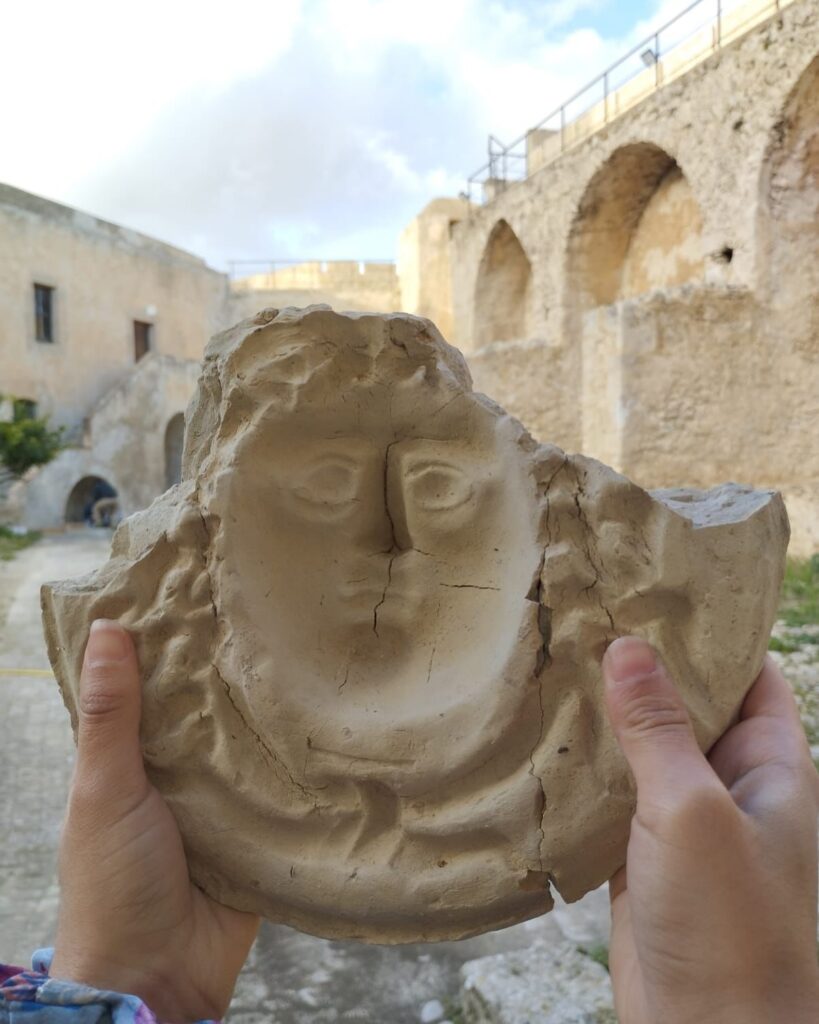

Archaeologists have found multiple mask molds in the same context, confirming the significance of this activity in the region.
One of the most remarkable artifacts is a mold that likely depicts Medusa, a figure steeped in rich symbolism. In Greek mythology, Medusa was one of the three Gorgons, embodying both peril and protection. Her image was commonly featured in decorative and architectural elements, as an amulet believed to repel evil.
The excavations, underway since last year, are supported by the Archaeological Park of the Valley of the Temples of Agrigento directed by Roberto Sciarratta in agreement with the CNR of Catania and are part of the “Finziade project” program, directed by archaeologists Alessio Toscano Raffa for the CNR-Ispc Catania, and Maria Concetta Parello, with the logistical coordination of Rosario Callea, of the Park of the Valley of the Temples.
Parco Archeologico e Paesaggistico della Valle dei Templi
Cover Image Credit: Finziade Project / Parco Archeologico e Paesaggistico della Valle dei Templi