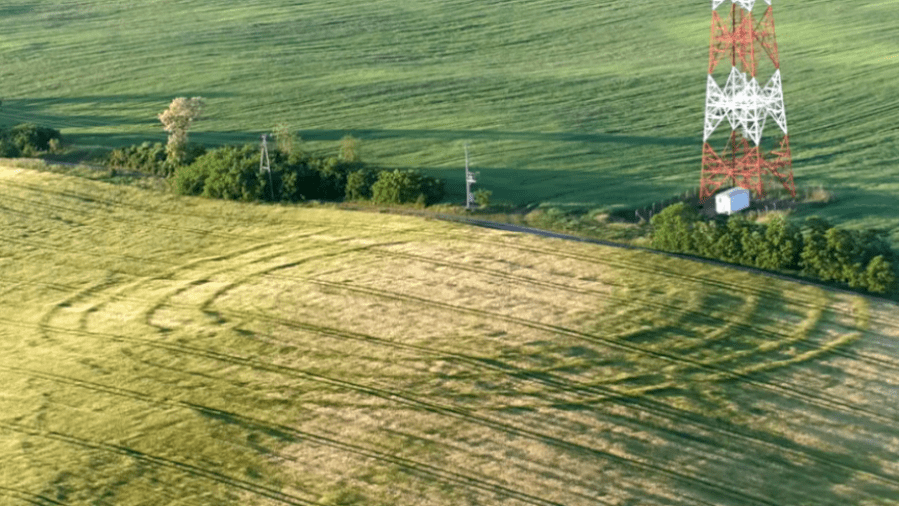
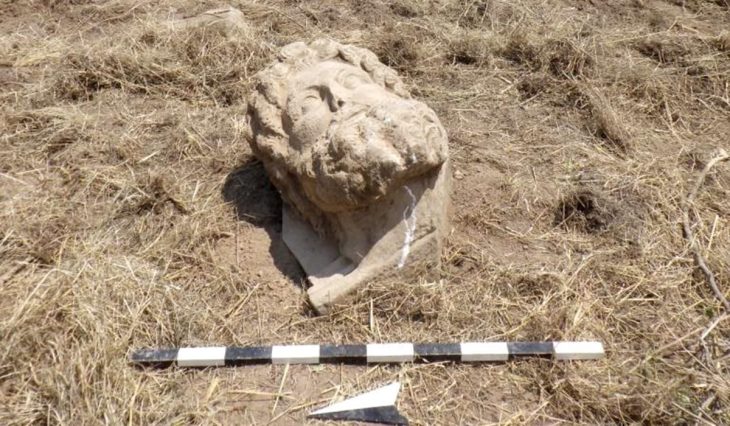
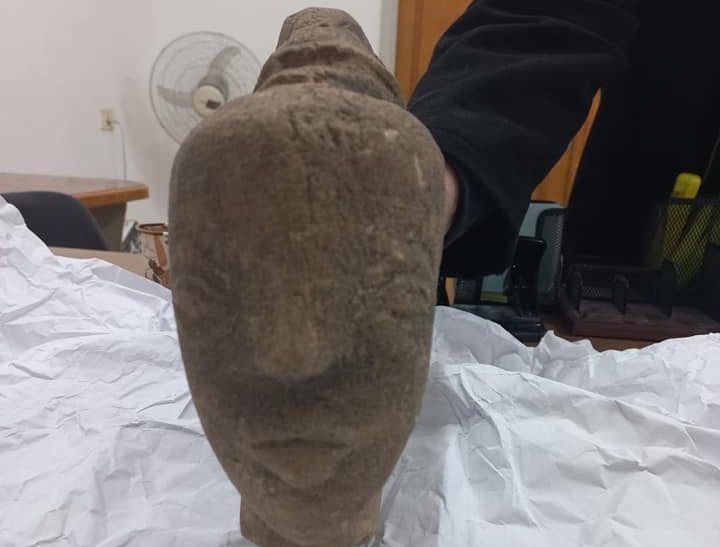
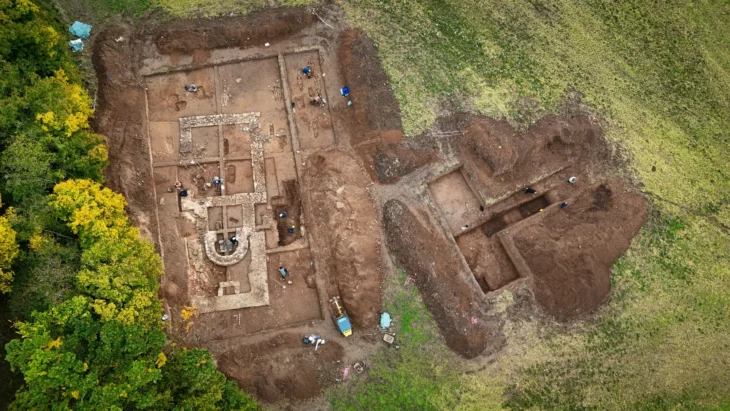
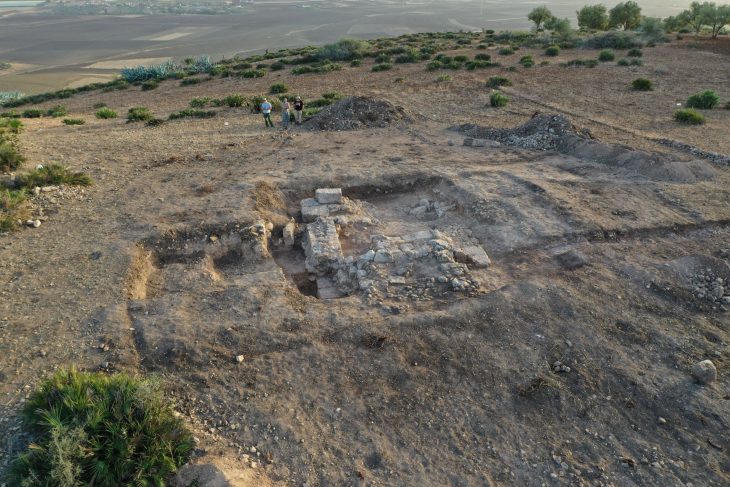
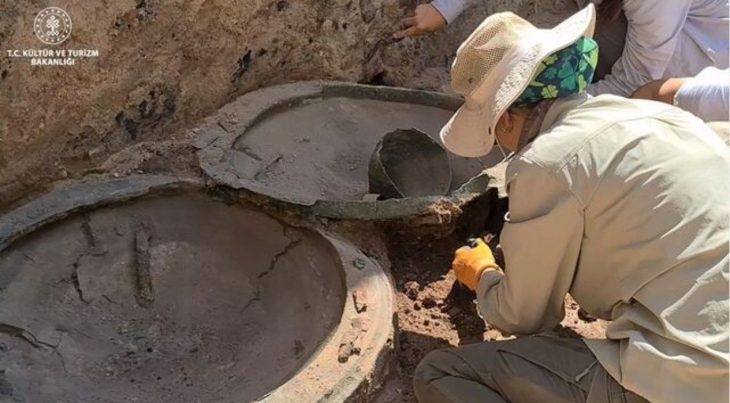
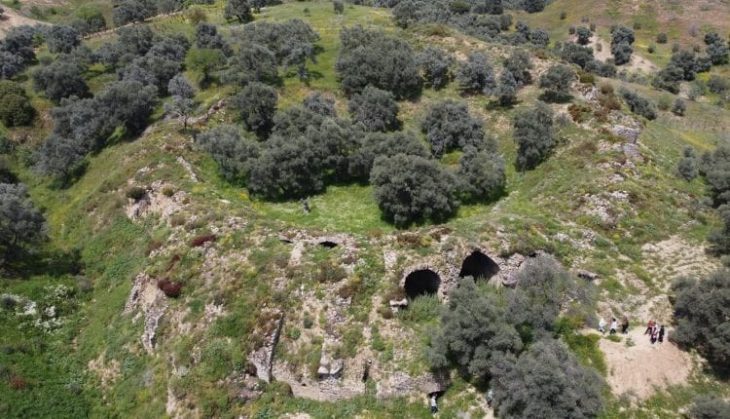
An archaeological excavation at Nowe Objezierze in north-western Poland has uncovered a rondel dating to around 4800 BC, offering new insights into the ceremonial and social practices of Neolithic societies.
The discovery, led by Dr. Lech Czerniak of the University of Gdańsk, has conducted a detailed analysis of a rondel, a monumental ceremonial structure. This discovery, the result of years of excavation and advanced analysis methods, has revealed previously unknown aspects of the ceremonial centers’ construction, use, and ritual significance.
Rondels are distinctive ceremonial centers that first appeared in Danubian Neolithic societies circa 4800 BCE. They are circular constructions with concentric ditches and wooden palisades. They were well-known in areas ranging from the Vistula and Rhine rivers to the middle Danube. It is believed that these buildings served as gathering places for group rites that frequently coincided with astronomical occasions like the winter solstice. Their use lasted for roughly 300 years before progressively decreasing around 4500 BCE as a result of changing environmental and social factors.
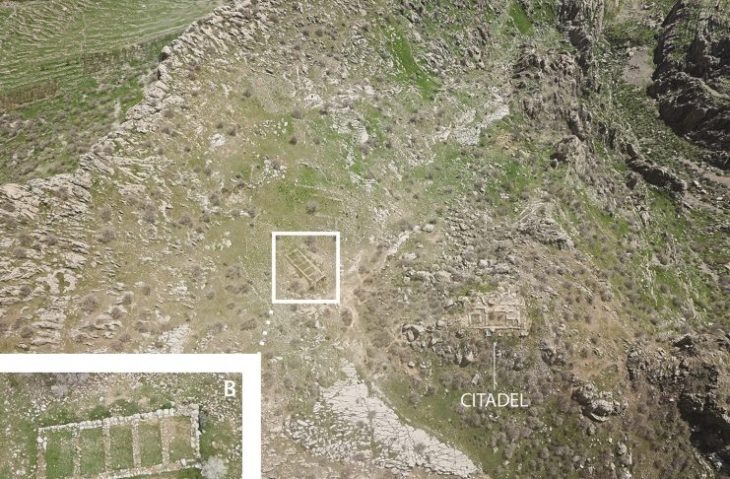
The size and intricacy of the rondel at Nowe Objezierze set it apart. It has a diameter of 112 meters and is encircled by three trench systems and four concentric ditches that were used as foundations for wooden buildings. Researchers used the chaîne opératoire method to reconstruct its construction, revealing a meticulous process that involved extensive planning, technical expertise, and social collaboration.
The evidence suggests that the construction of the roundel was a large-scale community project, involving hundreds of people over several years. Initial rituals to mobilize the community may have been part of the process, which started with marking the central circle and preparing the land. Over the trenches, wooden structures were constructed to withstand environmental conditions; these structures were probably reinforced with clay and reed roofs.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
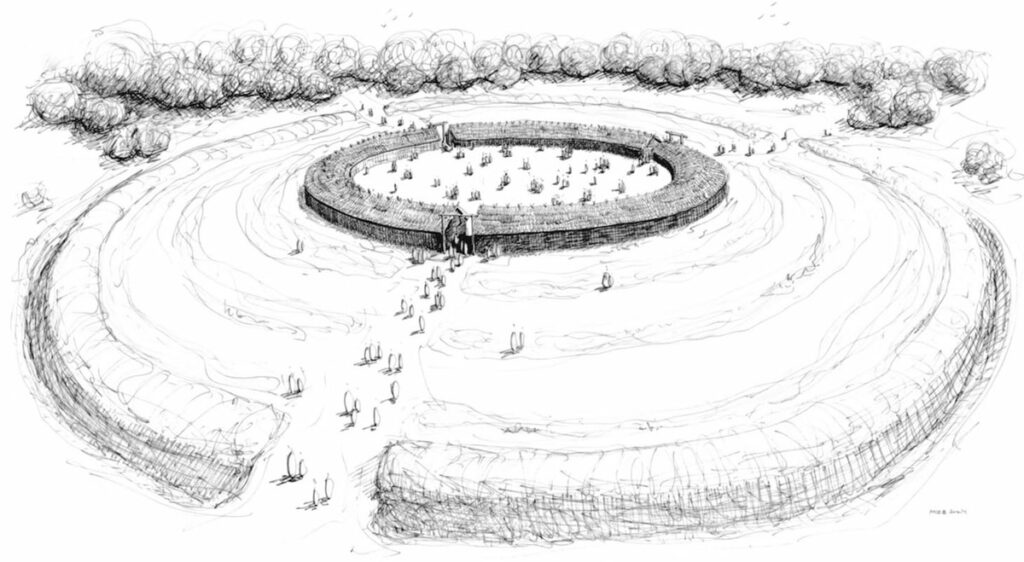
One of the most intriguing findings is the presence of a ritual cycle in the construction and use of the rondel. The ditches were not left open forever; following their ceremonial use, they were filled in and reopened for subsequent activity phases. This procedure points that the ceremonies dealt with the rondel’s inauguration as well as its upkeep and renewal, incorporating these events into the community’s ceremonial calendar.
The orientation of the rondel’s entrances also reveals information about the builders’ astronomical expertise. It is clear from the entrances’ alignment with particular cardinal points that the builders were interested in timing ceremonies with solar occurrences, like the winter solstice.
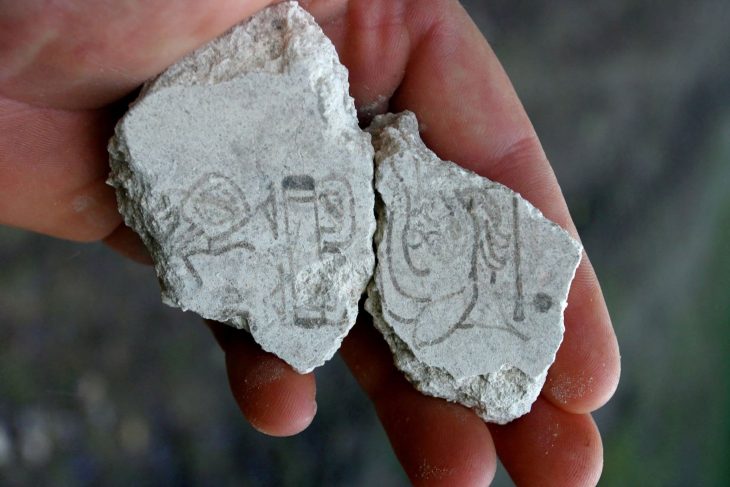
The researchers stress that the technical know-how required to construct the rondel was transmitted from one generation to the next, most likely through customs and educational ceremonies. Furthermore, the existence of ceramics typical of the Stichbandkeramik style (punctuated decorated pottery culture) implies that the builders were immigrants from areas such as northern Bohemia or Lower Silesia.
Animal remains and pottery discovered in the ditches indicate that the rondel was a site for social events, festivals, and perhaps sacrifices. These rituals created communal hierarchies, strengthened social cohesiveness, and perhaps settled territorial disputes.
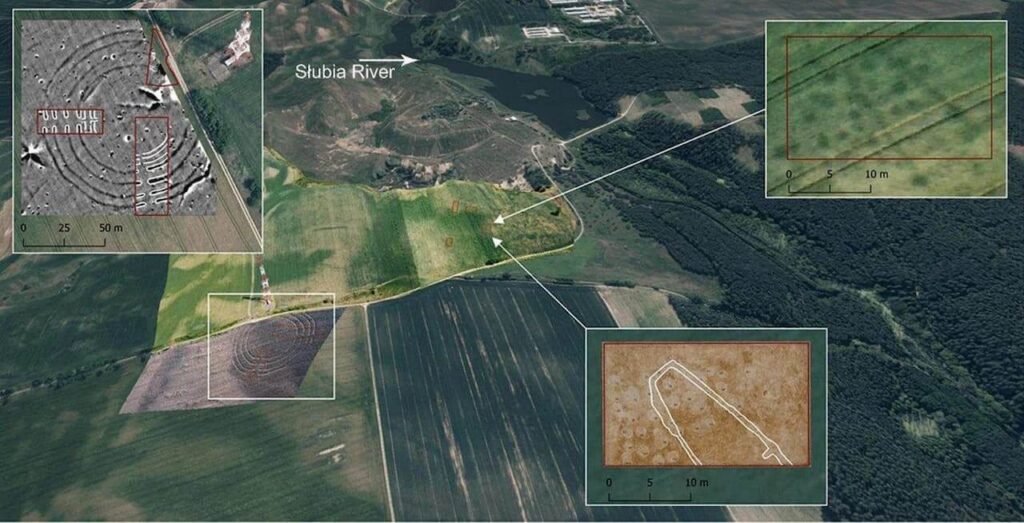
The evidence from Nowe Objezierze points to a more egalitarian society, despite the claims of some scholars that rondels were demonstrations of political power. Its collective construction and upkeep suggests a common goal, perhaps overseen by organizations similar to secret societies that preserved ritual knowledge.
Additionally, the study offers hints regarding the rondel’s decline. Around 4500 B.C., the structure was no longer in use due to changes in the social structure and environment of the area. A decrease in agricultural activity, as indicated by pollen analysis, points to a decline in the local population. An era in the history of Neolithic communities may have come to an end with this abandonment, which may have been caused by internal strife or migration.
Czerniak, L. Construction, Maintenance and Ritual Practices on the Neolithic Rondel at Nowe Objezierze (Northwestern Poland): The chaîne opératoire of Rondel’s Architecture. J Archaeol Method Theory 32, 7 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10816-024-09669-2
Cover Image Credit: The rondel at Nowe Objezierze is notable for its size and intricate design. Photo: X/@archaeologyEAA