A recent archaeological excavation in Mongolia’s Dornod Province revealed an elite tomb embedded in the walls of an abandoned fortress dating to the post-Kitan and pre-Mongolian periods.
As a component of the Mongolian-Israeli-American Archaeological Project, this discovery provides an intriguing look into the social structure, trade networks, and funerary customs of the era. It also has the potential to completely reshape our understanding of the political and cultural changes that occurred in the Mongolian steppe in the 12th and 13th centuries.
Once, the vast Kitan-Liao Empire (916–1125 CE) ruled over much of what is now central and eastern Mongolia. Following its fall, the Mongolian Empire and the legendary Chinggis Khan gained prominence by 1206 CE.
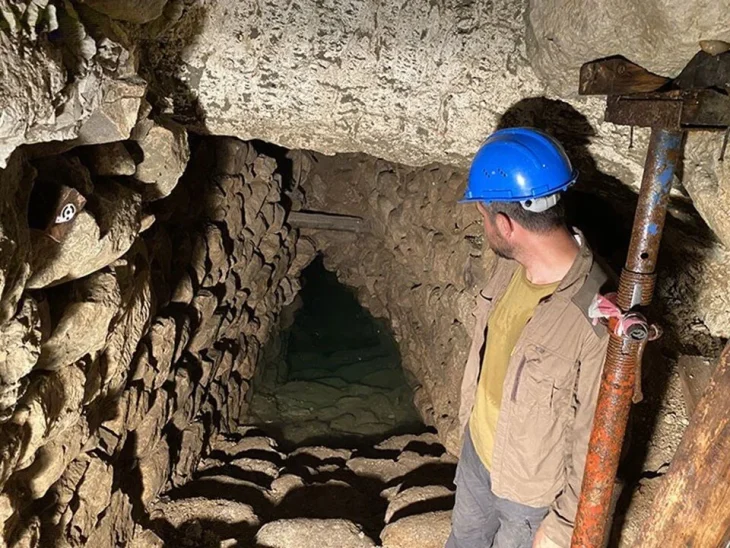
The Mongol-Israeli-American Archaeological Project has surveyed and excavated along Kitan frontier ‘long-walls’ in the northeast of Mongolia since 2018.
This grave, whose analysis indicates that it probably predates the fortress’s use, offers valuable insights into the networks and organization of the local communities in the 12th century CE.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
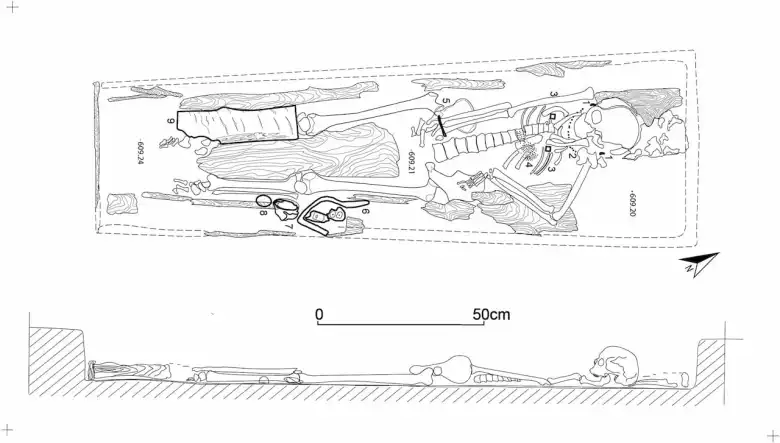
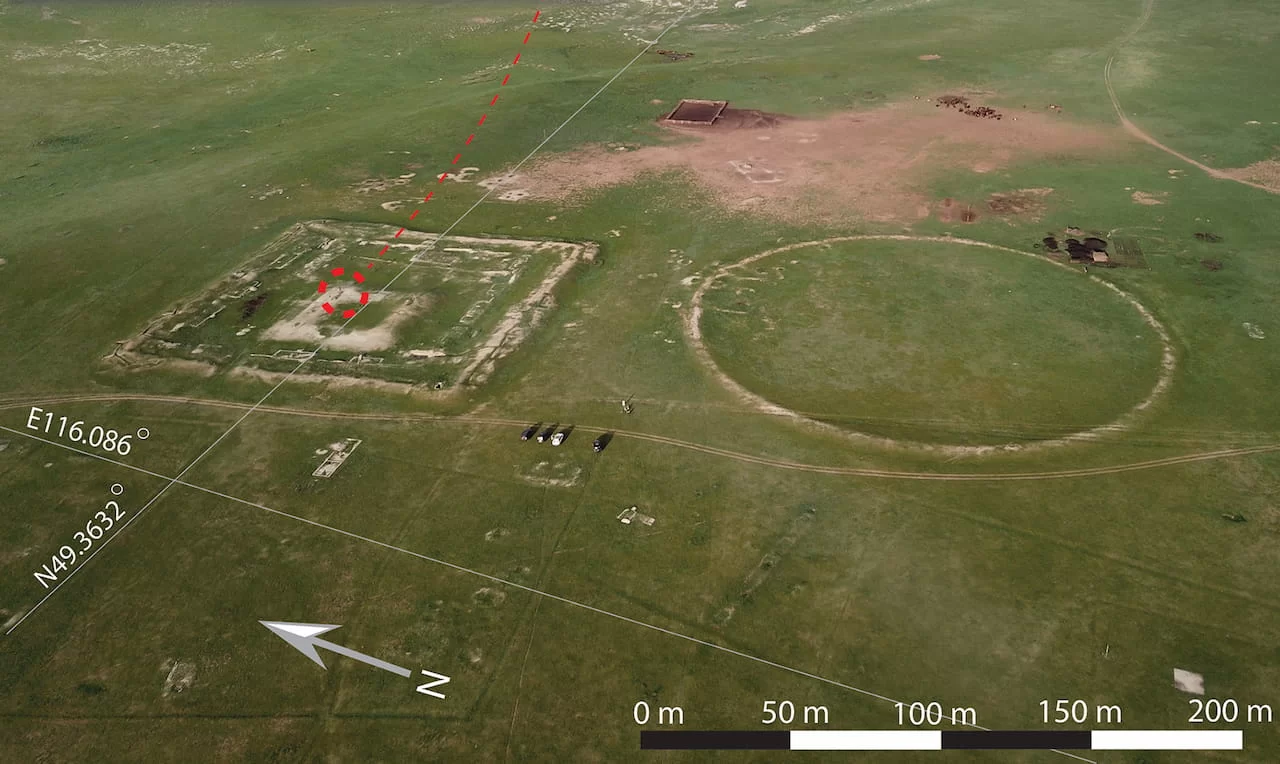
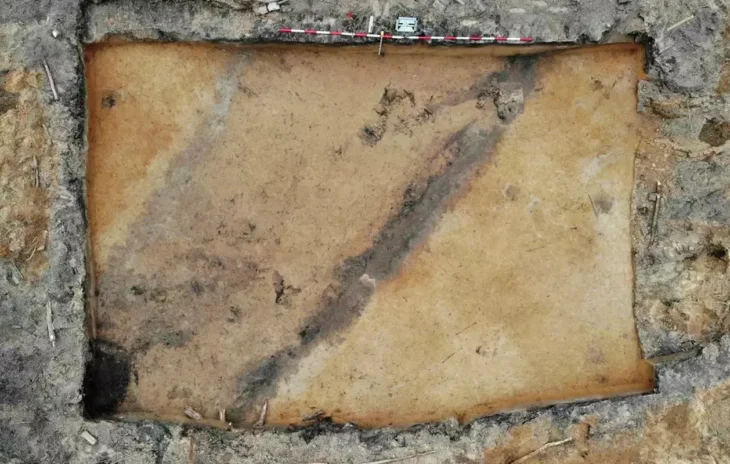
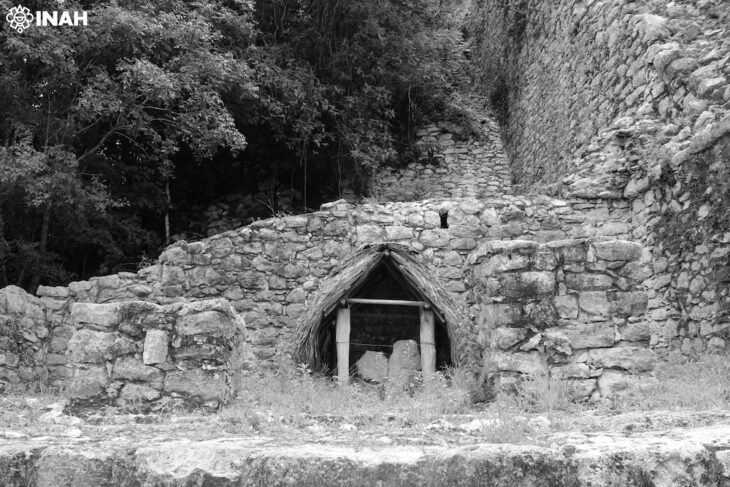
The discovery of this tomb was at a location within the ancient fortified complex of Khar Nuur known as “Cluster 27.” The complex is situated close to Mongolia’s northeastern border, a strategically significant area that was once a Khitan Empire stronghold and is well-known for its vast network of walls and fortifications. What makes this find particularly interesting is that the tomb appears to have been built after the fort was abandoned, implying that the space was reused during a period of political transition.
Situated roughly 1.4 km west of Lake Khar Nuur, the site is home to a sizable circular structure with a smaller rectangular enclosure inside. Archaeologists found a well-preserved tomb inside the enclosure’s outer wall that dates to between 1158 and 1214 AD. The skeleton of an adult woman, possibly between the ages of 40 and 60, wearing a yellow silk cloak and embellished with priceless items, was found inside a wooden coffin within the tomb.
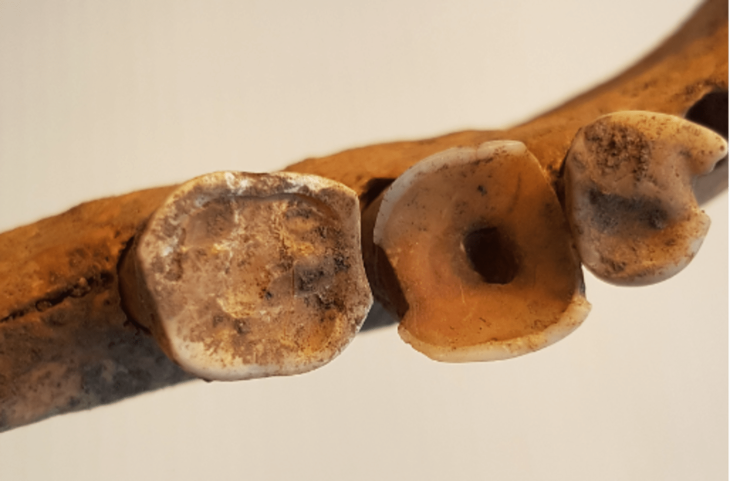
She likely belonged to the elite, as evidenced by the golden earrings, silver cup, bronze vessel, gold bracelet, and coral and glass beads found within her grave, among other grave goods.
How these objects may have facilitated her in the afterlife is unknown. Professor Shelach-Lavi, an archaeologist working on the project, explains, “We really do not know much about specific ideas. We know that the belief in the Sky (Tengri) already existed in Mongolia and that Shamanism was also practiced, but we cannot connect those broad ideas to the specific artifacts and practices seen in the grave.”
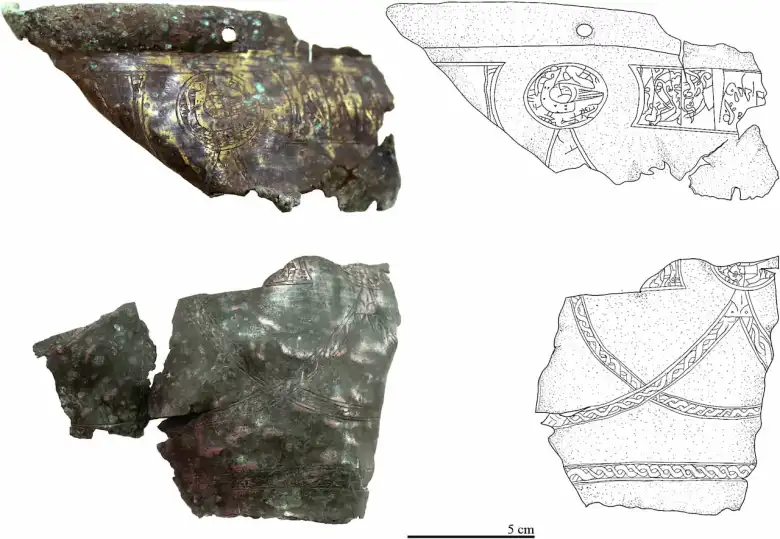

A small bronze cup with geometric figures and finely engraved lines is one of the most remarkable discoveries. It differs significantly from other medieval artifacts discovered in Mongolia, indicating that it may be a one-of-a-kind item or have some connection to an unidentified craft tradition. Furthermore, pieces of a leather-coated, bronze-framed wooden objects were discovered. Its purpose is unknown, but it may have been a quiver or a case for a bow and arrows, common objects interred with male elites during the Mongol imperial era.
An additional noteworthy relic is a silver cup that was originally roughly 17 cm in diameter but has been broken into 26 pieces. The cup, which has incised motifs and gilded strips, doesn’t seem to have a direct counterpart, though comparable objects have been discovered in tombs from the medieval Mongol era.
Many of the artifacts were not native to the area. For example, the silk was probably made in southern China, and the wood was probably taken from birch, mulberry, and/or larch trees, which are 150–300 km away.

The fact that an elite member was buried at a border site that had been abandoned implies that the ancient Khitan fortifications were not just military strongholds but also sites with lasting cultural and symbolic significance that persisted long after the empire fell. Combining local elements with opulent pieces like gold and silver ornaments depicts a society in transition, shaped by the cultural influences of neighboring civilizations as well as its own nomadic traditions.
The results of their research were published in Archaeological Research in Asia.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ara.2024.100537
Cover ımage: The place of the discovery in the northeast of Mongolia. Photo: Amartuvshin Chunag et al.
















