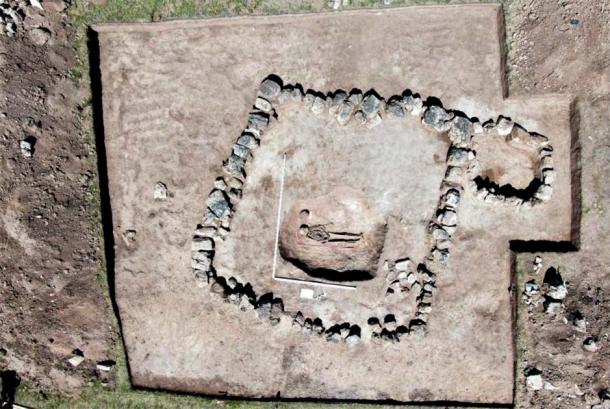
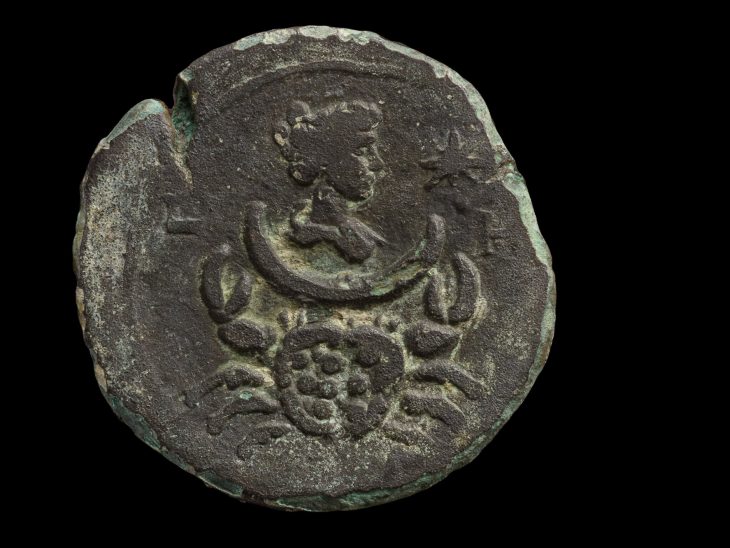
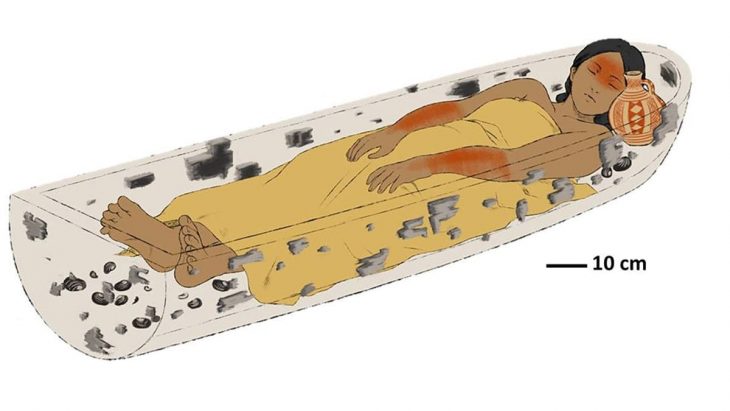
Russian archaeologists uncovered the grave of a Late Bronze Age man buried wearing a “charioteer’s belt”, a flat bronze plate with two curved hooks at the end reminiscent of a yoke used to harness draft animals, during a rescue archaeology excavation at the railway expansion site in the Askizsky region of Khakassia, in Southern Siberia.
This tool is thought to have been used by charioteers to cinch their reins to their waists, freeing up their hands for battle. This type of artifact has also been found in Chinese and Mongolian graves.
The tomb is dated to between the 11th and the 8th century B.C., a time when the Lugav culture was dominant in the area. Archaeologists and historians didn’t believe chariots were being used in this part of Asia that long ago.
Aleksey Timoshchenko, an archaeologist at the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnography of the Russian Academy of Sciences, told Live Science in an email that the object was found in its original placement at the waist of the person in the undisturbed grave.
This device was actually designed to be attached to a charioteer’s belt. The charioteer could rest their hands while controlling the horses pulling the chariot by wrapping the reins around the belt. This was an item of convenience for a charioteer and its telltale appearance leaves no question as to the identity of the deceased person who was buried with it.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
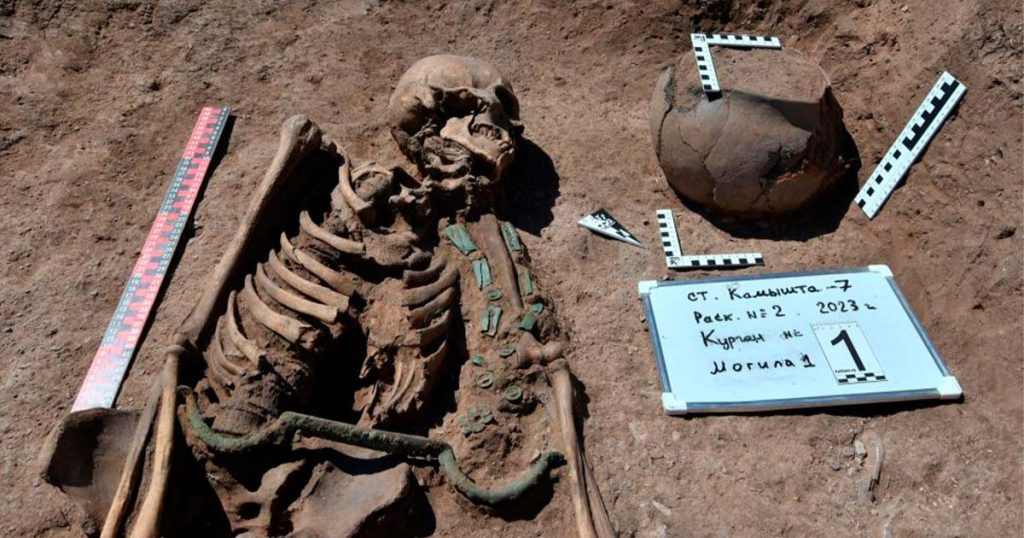

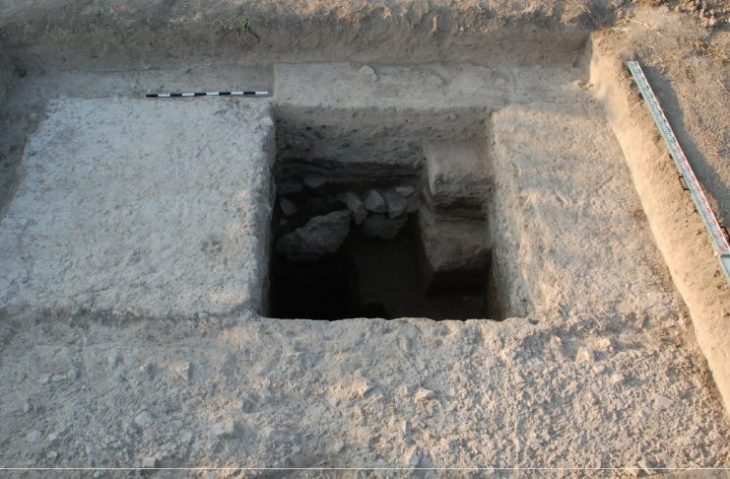
The charioteer’s tomb is a square masonry tomb with an earthen mound built on top of it. The deceased was buried with a bronze knife, bronze jewelry, including a necklace with rectangular pendants typical of Lugav culture, and a belt.
This type of artifact has previously been discovered at other archaeological sites in Russian territory. However, the object’s shape was so unusual that archaeologists initially had no idea what it was used for.
“For a long time in Russian archaeology, this was called a PNN — an ‘item of unknown purpose,’” Novosibirsk State University archaeologist and Institute of Archaeology and Ethnology consultant Oleg Mitko told Live Science.
In recent years, archaeologists working in Mongolia and China have unearthed the tombs of multiple Bronze Age charioteers, along with their buried horses and chariots. The metal rods were there inside the tombs as well, making it clear that they were an accessory used by chariot drivers in ancient times.
The site under excavation contains material remains of a cemetery as well as a settlement from this period, and the Lugav barrows in the cemetery can be grouped into three stages — the transition to the Lugav culture, the Lugav middle stage, and the late stage, when characteristics from the next culture (Tagar) appear mingled with the Lugav features. The charioteer’s tomb is from the middle stage.
Cover Photo: IAET SB RAS