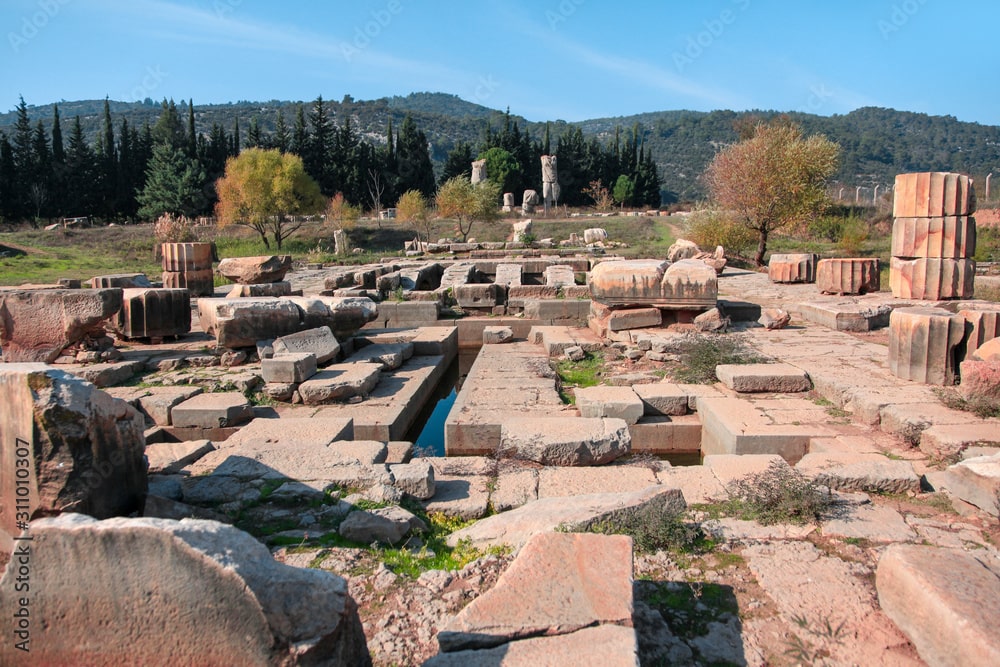
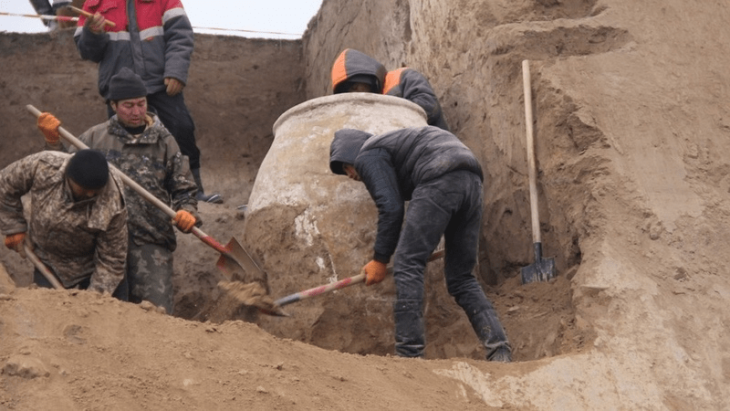
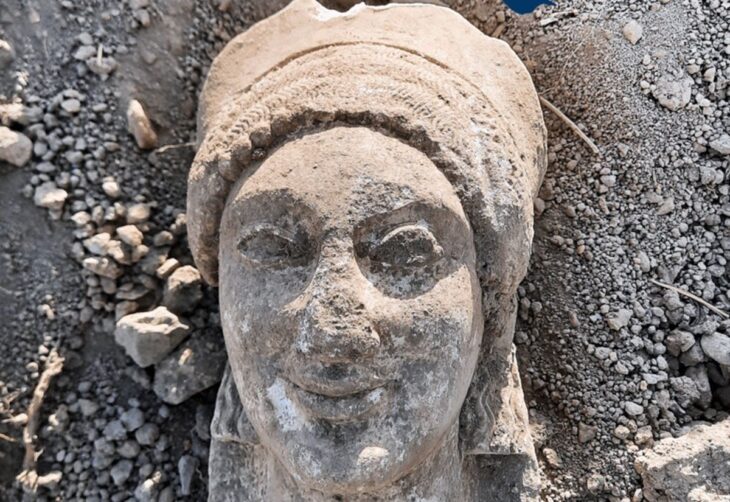
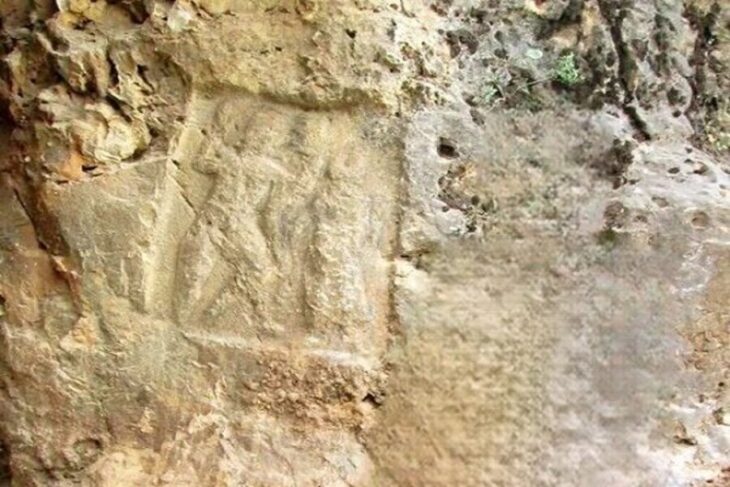
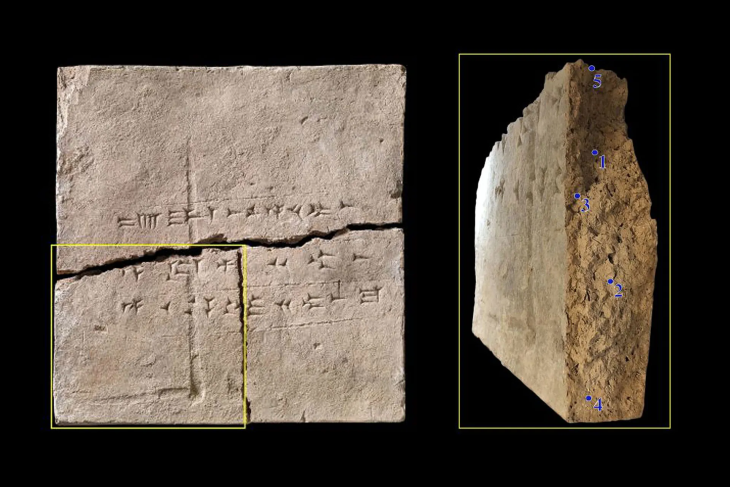
Game boards and forked cross motifs dating to the fifth and seventh centuries AD were discovered at the ancient Greek temple of Claros, on the southwest coast of Izmir, one of the most important pagan sanctuaries of Ionia.
The new findings show that Claros, which was thought to have been abandoned after the spread of Christianity, actually functioned for many years.
According to archaeologists, Claros was one of the three prophecy centers, along with Delphi and Didyma, in modern-day Greece.
It is thought that Claros was built in the name of Apollo, the god of Colophon, at the beginning of the 7th or 6th century BC. It was in the territory of Colophon, one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League, which was twelve kilometers to the north. The Homeric Hymns, which date from the sixth and seventh centuries BC, are the earliest literary references to this holy site. However, proto-geometric pottery found there indicates that it was occupied as early as the ninth century. A sacred cave near the Temple of Apollo, which was important in both the Hellenistic and Roman eras, indicates the presence of a Cybele cult here in the early periods. Every fifth year, in honor of Apollo, the Claria games were held at Claros.
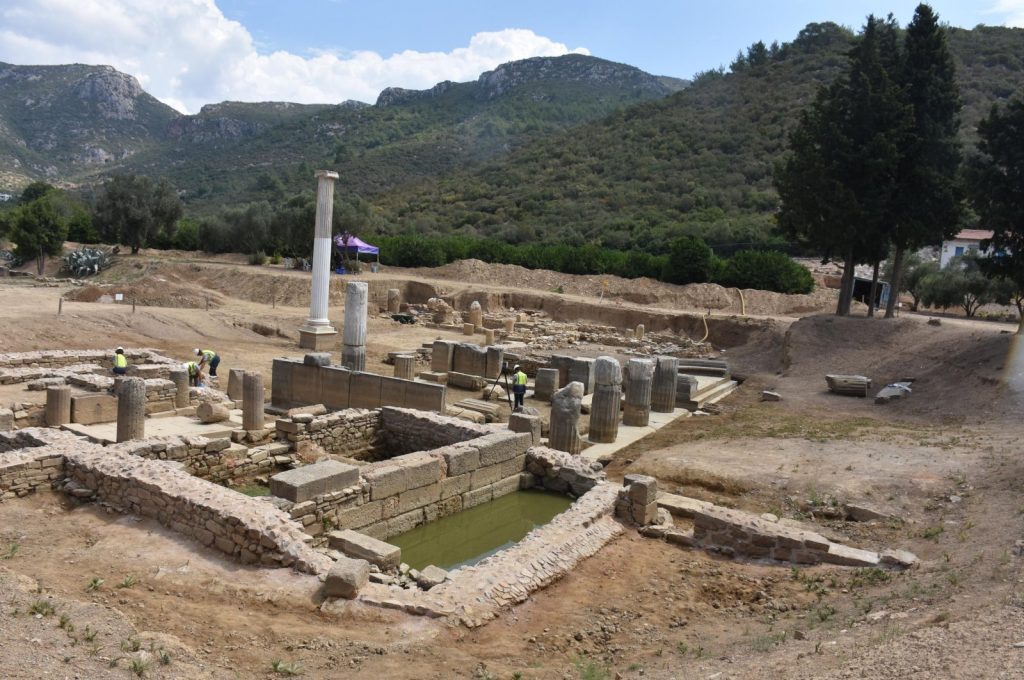

Although it was previously thought that Claros served as a prophecy center until the spread of Christianity in the fourth century, new evidence suggests that it did not lose prominence until the seventh century.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
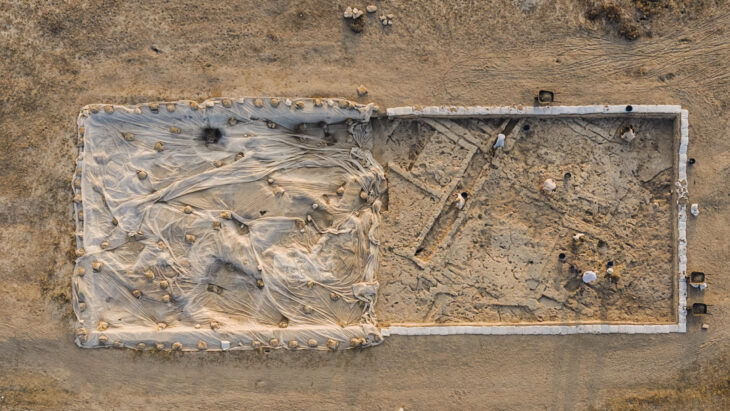
In the new period excavations in Claros, which dates back to the 13th century B.C., traces belonging to the fifth to the seventh century B.C. have been found. Nine stone game boards and forked cross motifs engraved under a Doric head of the Hellenistic Temple of Apollo, as well as ceramic finds, have been discovered as a result of archaeological research.
These discoveries support the claim that the sanctuary, which was thought to have been abandoned or emptied by the Roman Empire since 380 A.D. when Christianity was accepted as the official religion as it symbolized the pagan faith, was actually inhabited or visited for a longer period of time.

Stating that important decisions such as wars and city establishment in ancient times were made after the approval in the prophecy center, Onur Zunal of Ege University Faculty of Letters, who serves as a consultant to the excavations in Claros, said: “Claros is one of the most important sites of the ancient period. Our recent work here showed us that the sanctuary continued to be used even after the declaration of Christianity as the official religion of Claros in 380 A.D. We discovered that it did not lose its charm in the fourth century and continued to be used until the seventh century A.D., taking into account the current findings.”
Emphasizing that the “sacred space” function of Claros continued despite the conversion to Christianity, Zunal said: “There are still people who visit this place. There are many people who believe in the energy of Claros. We have also witnessed that people who believe in Apollo come here at certain times and perform certain rituals. Therefore, in fact, it would even be wrong to say that the city was abandoned in the seventh century A.D. Even in the 2020s, people who believe in Claros somehow come here and do their own rituals.”
Zunal also stated that articles on the studies that advanced the sanctuary’s history by about 300 years had been published in national and international journals.