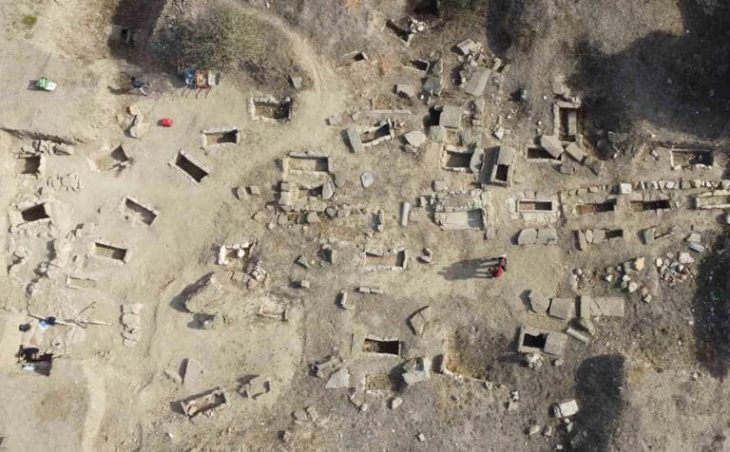
Archaeologists have unveiled a 5,000-year-old fortress hidden deep within the forests of Neamț County, Romania. This remarkable find, made possible through advanced LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology, sheds light on a significant period in human history, marking the transition from the Neolithic to the Bronze Age.
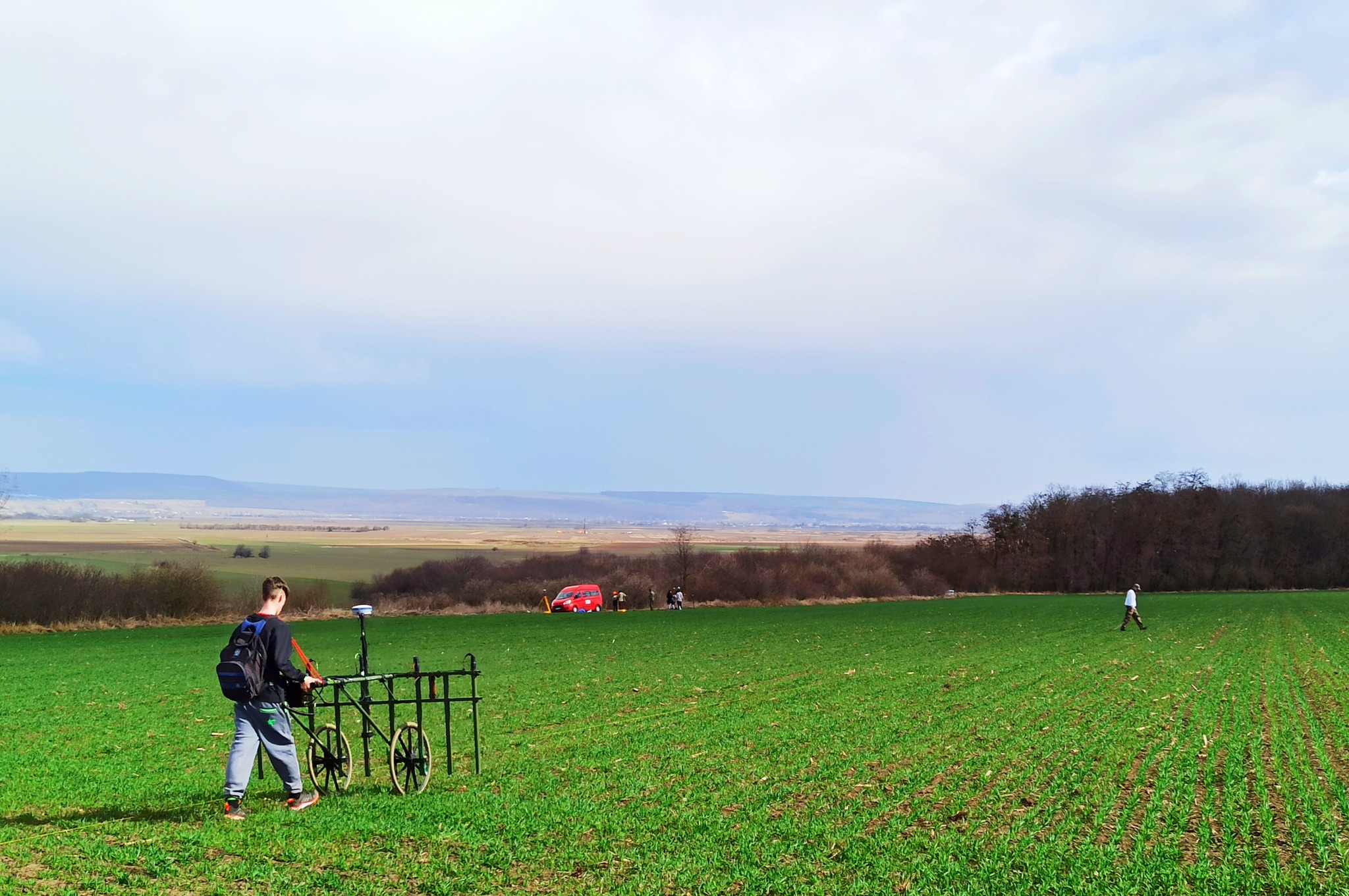
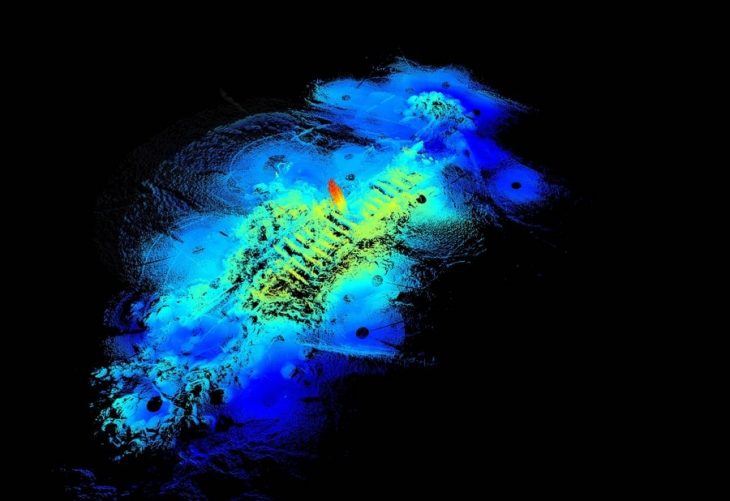
The fortress, obscured by centuries of dense vegetation, was mapped with precision using drones equipped with LiDAR, which emits laser pulses to create high-resolution terrain models.
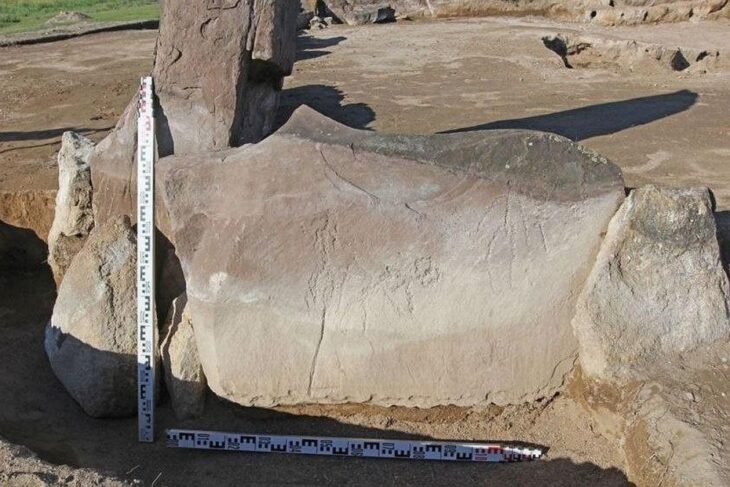
Archaeologist Vasile Diaconu, who led the study, emphasized the importance of this technology, stating, “Only by using modern technologies will we be able to better understand the complexities of archaeological sites.” The LiDAR scans revealed intricate details of the fortification, including large ditches and earthen mounds designed to enhance its defensive capabilities.
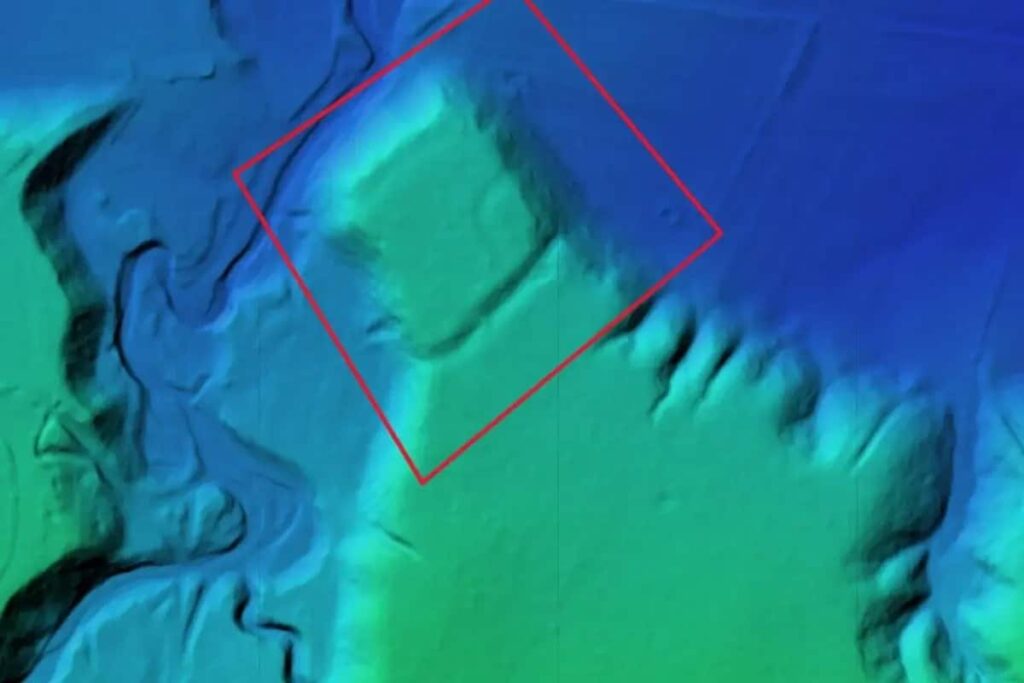

Strategically located in a high area, the fortress offered excellent visibility of the surrounding landscape, allowing its inhabitants to detect potential threats. The extensive ditches, some stretching several hundred meters, indicate the considerable human effort involved in its construction. Diaconu noted that these findings highlight the sophisticated planning and execution of ancient fortifications.
This project was not only a technological triumph but also a personal collaboration between Diaconu and his former student, Vlad Dulgheriu, the owner of Geocad Services, which facilitated the use of LiDAR technology. Diaconu expressed pride in Dulgheriu’s achievements, stating, “I’m honestly glad my former student has built his own road beautifully.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The discovery underscores the transformative role of modern technology in archaeology, enabling researchers to explore and document ancient sites that would otherwise remain hidden. As LiDAR continues to evolve, it promises to unveil more secrets of our past, offering new insights into ancient civilizations.