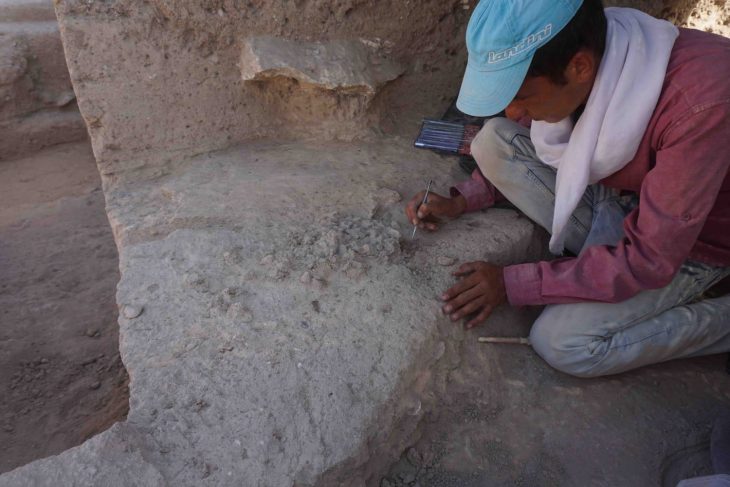
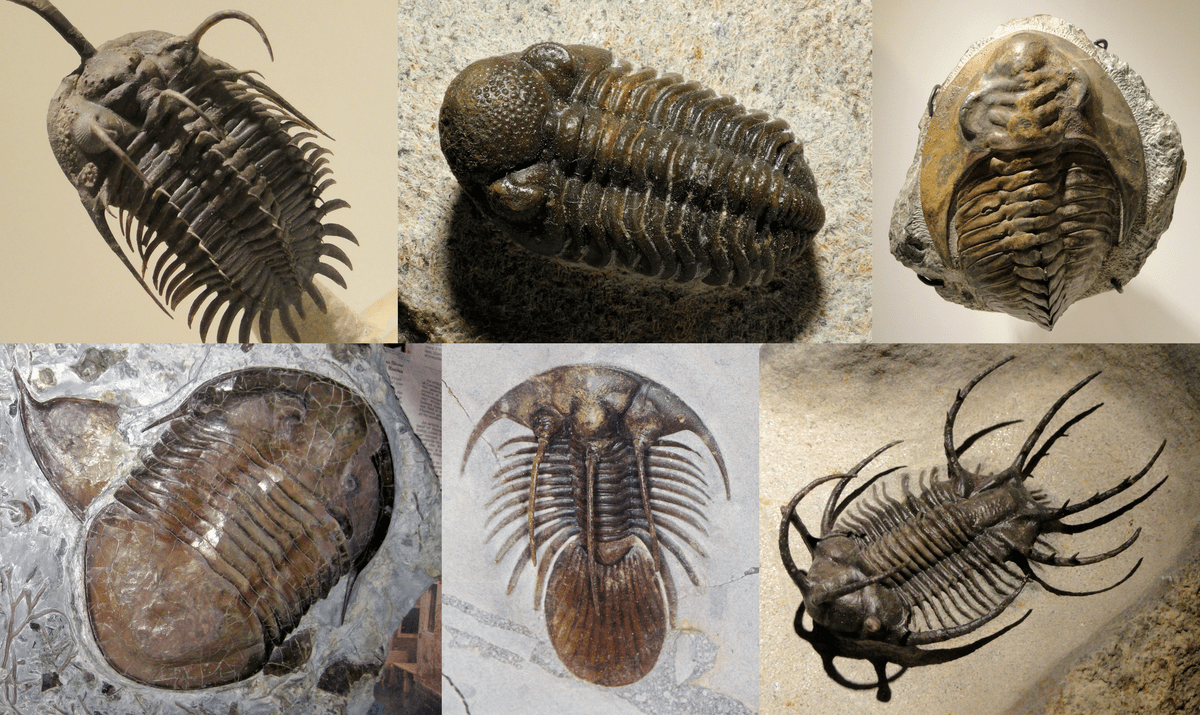
The humble trilobites may be extinct, but even as fossils, they can teach us much about our planet’s history. Indeed, ancient arthropods from nearly half a billion years ago, including ten newly discovered species, may be key to understanding Thailand’s place on the former supercontinent Gondwana.
Trilobites are extinct sea creatures with half-moon-shaped heads that breathed through their legs. A 100-page monograph in the British journal offers great detail about the new species, including one named in honor of Thai Royal Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn.
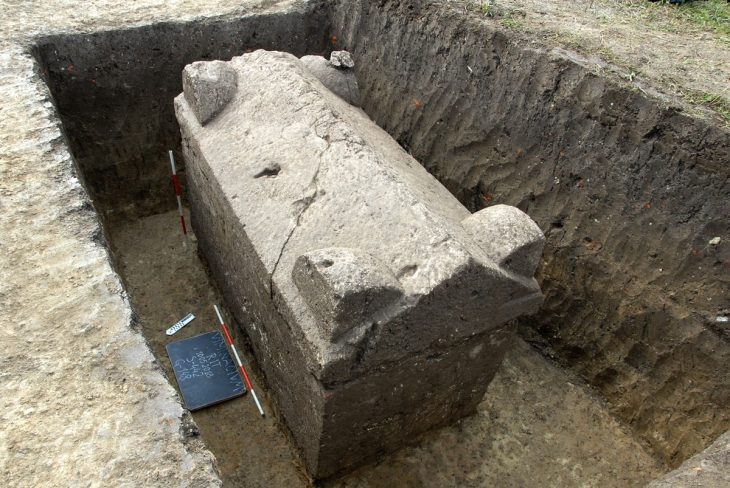
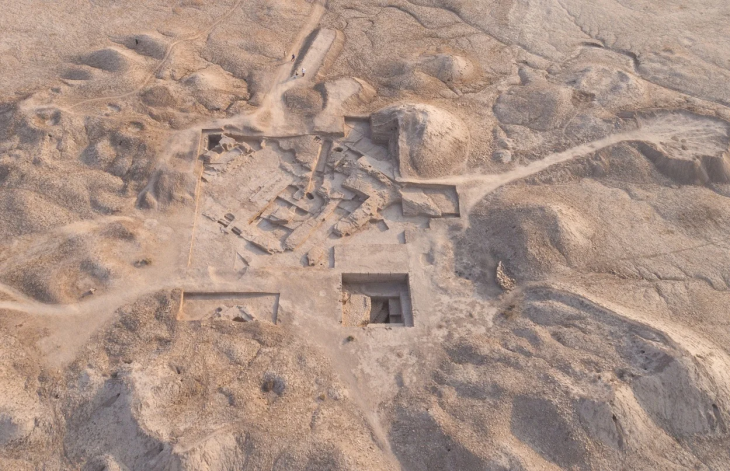
The trilobite fossils were trapped between layers of petrified ash in sandstone, the product of old volcanic eruptions that settled on the sea floor and formed a green layer called a tuff. Unlike some other kinds of rocks or sediment, tuffs contain crystals of zircon — a mineral that formed during an eruption and are, as the name of the rock layer containing them suggests, tough.
Zircon is chemically stable as well as heat and weather resistant. It is hard as steel and persists when minerals in other kinds of rocks erode. Inside these resilient zircon crystals, individual atoms of uranium gradually decay and transform into atoms of lead.
“We can use radio isotope techniques to date when the zircon formed and thus find the age of the eruption, as well as the fossil,” said Nigel Hughes, monograph co-author and UC Riverside geology professor.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
It is rare to find tuffs from this particular period of time, the late Cambrian period, between 497 and 485 million years ago. “Not many places around the world have this. It is one of the worst dated intervals of time in Earth’s history,” Hughes said.
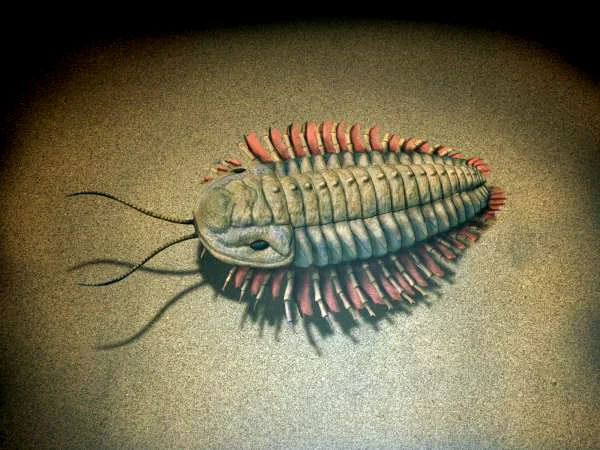

“The tuffs will allow us to not only determine the age of the fossils we found in Thailand, but to better understand parts of the world like China, Australia, and even North America where similar fossils have been found in rocks that cannot be dated,” said Shelly Wernette, former Hughes lab geologist now at Texas State University, and first author of the monograph.
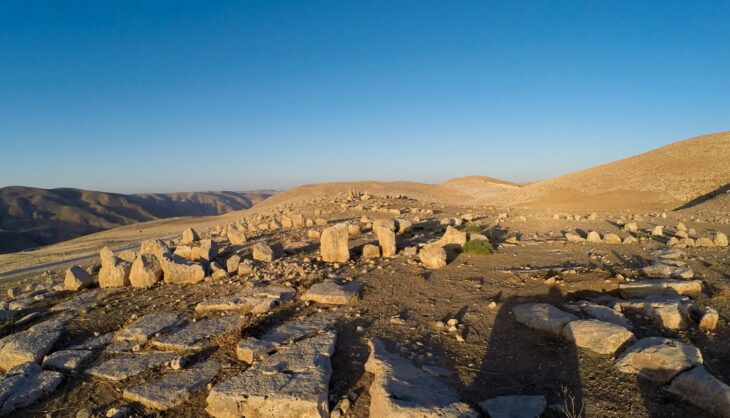
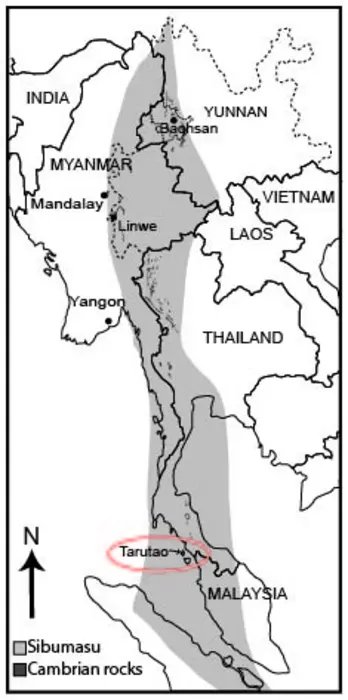
The fossils were uncovered on the coast of an island called Ko Tarutao. It is about 40 minutes southwest from the mainland via high-speed boat and is part of a UNESCO geopark site that has encouraged international teams of scientists to work in this area.
For Wernette, the most interesting discovery was 12 types of trilobites that have been seen in other parts of the world, but never in Thailand before. “We can now connect Thailand to parts of Australia, a really exciting discovery.”
During the trilobites’ lifetime, this region was on the outer margins of Gondwanaland, an ancient supercontinent that included Africa, India, Australia, South America, and Antarctica.
“Because continents shift over time, part of our job has been to work out where this region of Thailand was in relation to the rest of Gondwanaland,” Hughes said. “It’s a moving, shape shifting, 3D jigsaw puzzle we’re trying to put together. This discovery will help us do that.”
For example, take the species named for Royal Princess Sirindhorn. The species was named in tribute to the princess for her steadfast dedication to developing the sciences in Thailand. “I also thought this species had a regal quality. It has a broad headdress and clean sweeping lines,” Wernette said.
If researchers can get a date from the tuffs containing her namesake species, Tsinania sirindhornae, and determine when they lived, they will be able to say that closely related species of Tsinania found in northern and southern China are roughly the same age.
Ultimately, the researchers feel that the pictures of the ancient world hidden in the fossils they found contain invaluable information for the present day.
“What we have here is a chronicle of evolutionary change accompanied by extinctions. The Earth has written this record for us, and we’re fortunate to have it,” Hughes said. “The more we learn from it the better prepared we are for the challenges we’re engineering on the planet for ourselves today.”
Cover image: Wikipedia