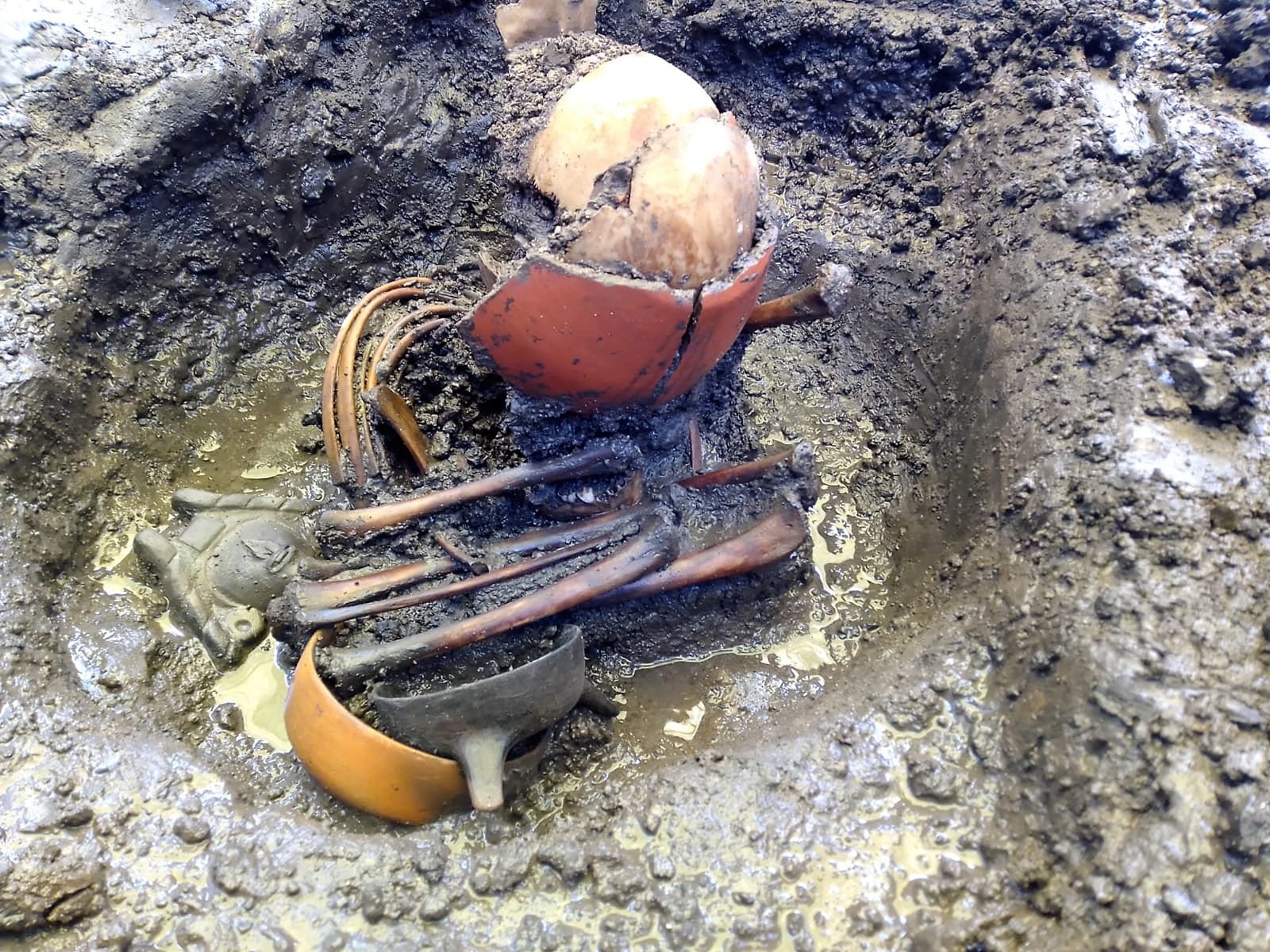
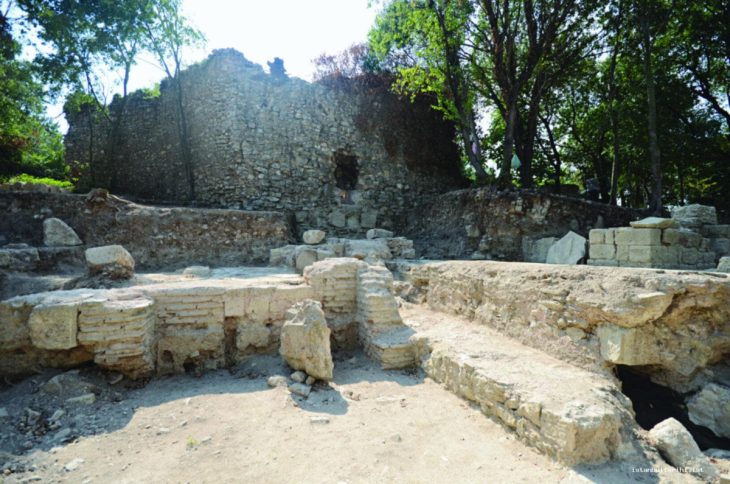
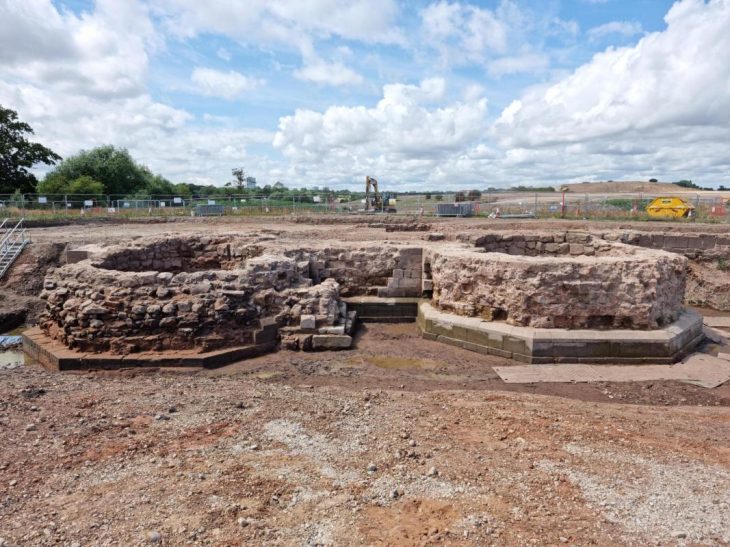
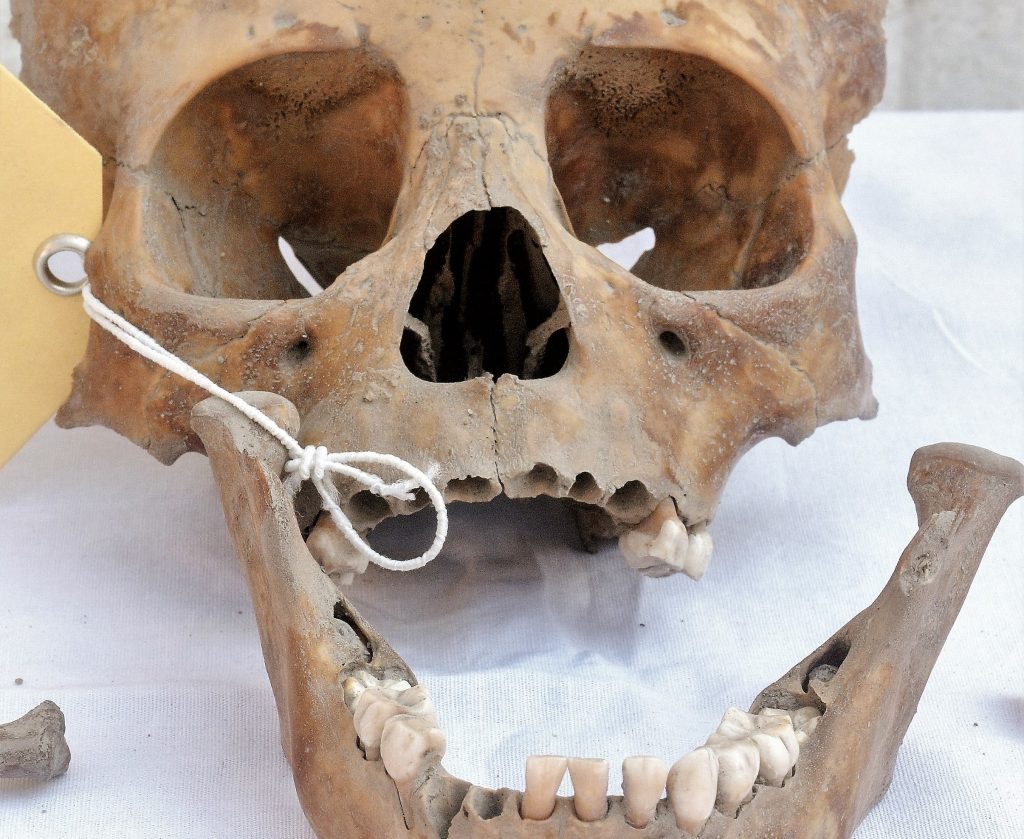
During an archaeological rescue effort in Mexico City’s historic central district of La Lagunilla, the remains of an Aztec house and the burial place of four Aztec children from the Early Colonial period (1521-1620) were unearthed.
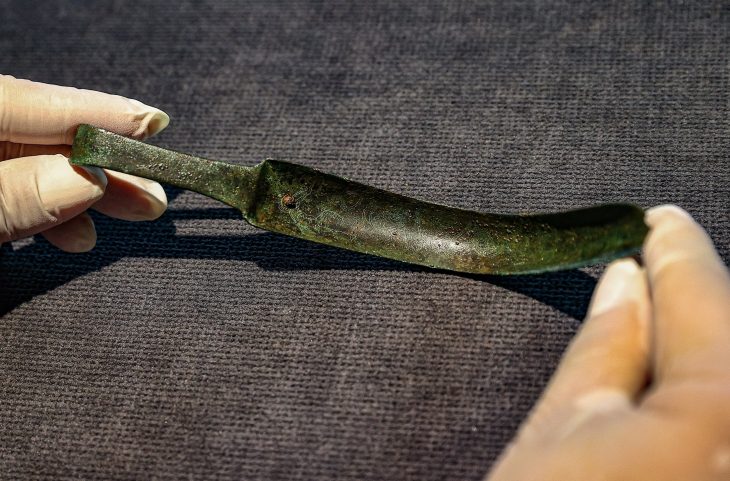
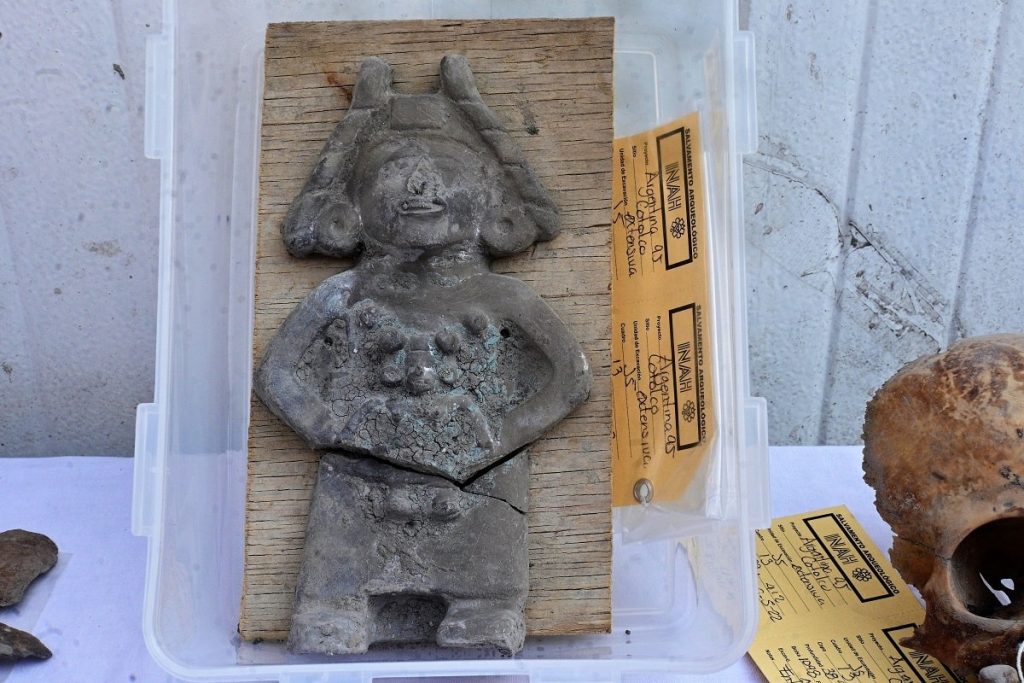
Excavations also uncovered pre-Hispanic objects largely intact centuries later, including clay vases, ceramic pots, and a stone figure of a woman holding a child, the institute said in a statement this week.
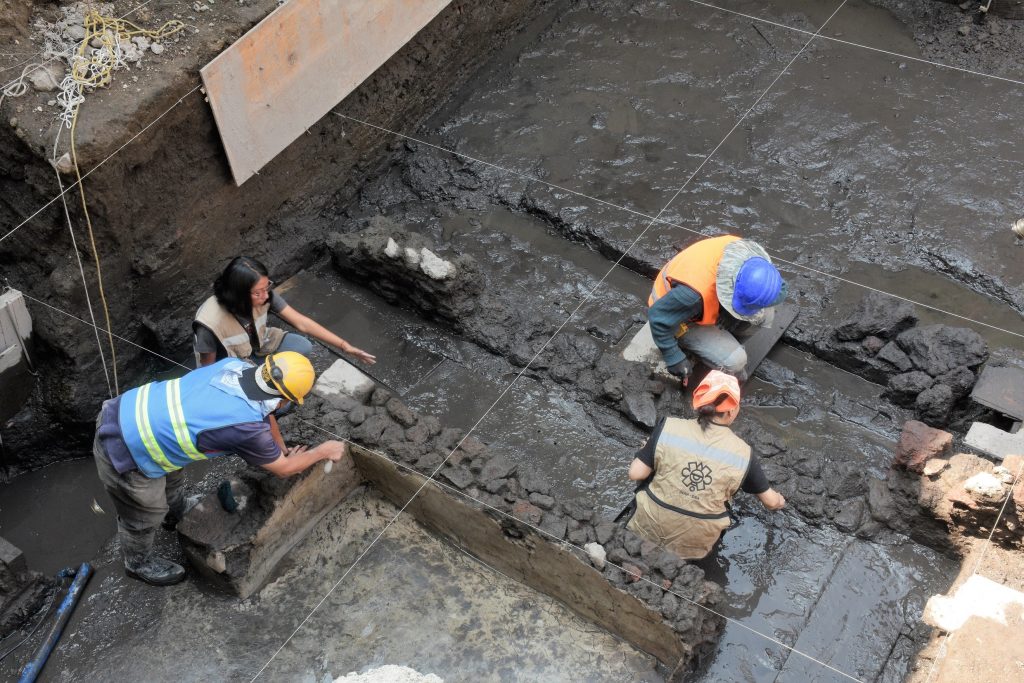
After August 1521, a pivotal month in Mexican History, one of the first actions taken by the Spaniards was to create a new layout on top of the ruins of Tenochtitlan. Through this new layout, they expelled the indigenous people to the periphery, thus placing themselves at the socio-political core of the emerging viceroyalty city. However, from their homes and away from these foreign gazes, the Aztecs kept multiple acts of resistance that resurface today through archaeology.
Juan Carlos Campos Varela, the chief archaeologist of the project, run by the Mexican Government Ministry of Culture through the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH), said that, from a historical point of view, this area was part of Cotolco neighborhood, and belonged to Atzacoalco partiality, one of the four great territorial divisions of Mexico-Tenochtitlan.

The Aztecs were a civilization that had rituals of human sacrifice. However, the researchers explained that the cause of death of the children found was linked to the harsh living conditions endured by the indigenous people who were unable to escape from Tenochtitlan.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
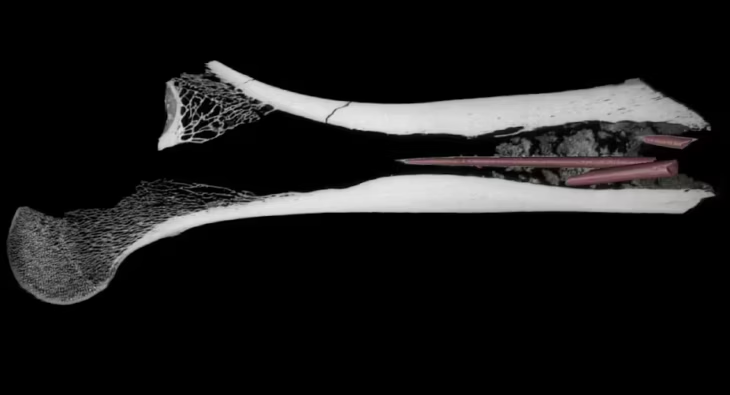
A clear indicator of this hypothesis is the skull of the oldest infant. Cribra orbitalia, a disease directly associated with anemia, infections, parasitosis and dietary imbalance, can be observed in the roofs of its ocular orbits. Thanks to the analysis of the size of its bones and dental bud, it can be inferred that the infant may have died between the ages of six and eight.
The hypothesis could be proved by verifying whether the smallest infant is an unborn child, perhaps spontaneously aborted due to some nutritional deficiency or maternal stress, and by also considering the results of previous archaeological salvages.
“Three years ago we excavated in front of the site we are now working on, and we found three adult burials and four infant burials, also from the Early Colonial period. Therefore, if we add those children with the ones we have today, the evidence indicates that, at least in this neighborhood of Cotolco, the ones who were dying the most were the infants”.
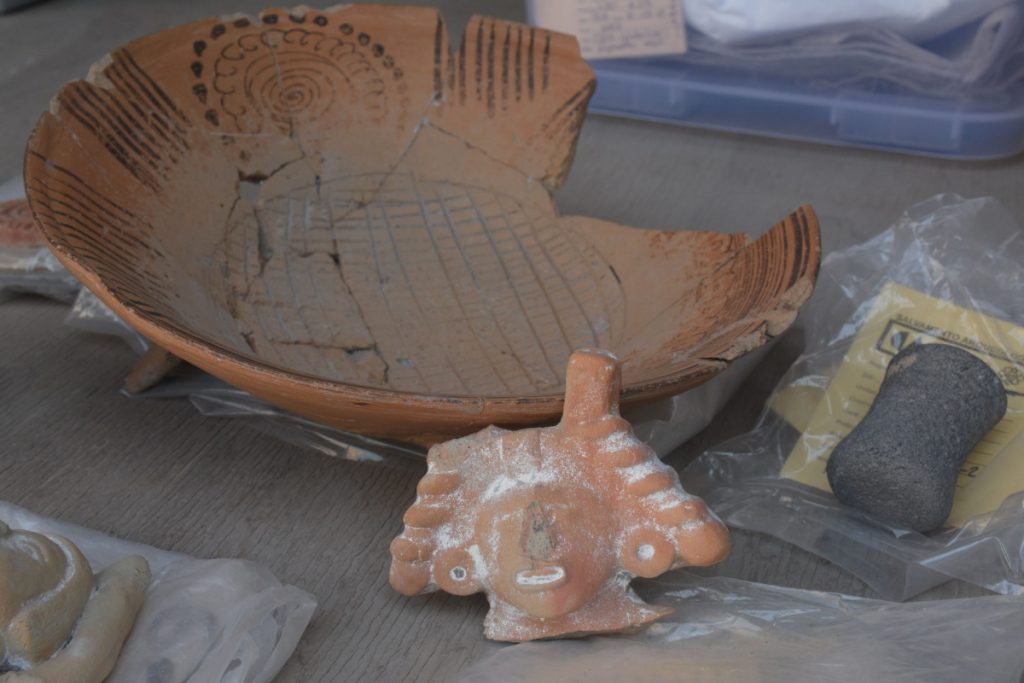

Although it is complicated to determine the sex of each of the four recently discovered remains -this will be research in the laboratory-, their mortuary offerings are of special interest. “Two of them had no offering and were only primary burials placed in early viceregal strata. The probable unborn child was accompanied by two tripod ceramic bowls and layed inside a globular pot –35 centimeters in diameter and 50 centimeters high– which tells us about the survival of a funerary practice that sought to return him to the maternal womb, represented by the pot.” Campos Varela notes.
The best-preserved offering from the site is that of an infant between the ages of six and eight. This offering is composed of: five small vessels, two spinning frames and a blue-pigmented figurine. Due to its iconography, it is likely that the figurine represents a woman holding a girl on her lap, thus the bone remains could probably be female.
It is worth mentioning that another offering was found on the site, which housed a blue-pigmented vessel –30 centimeters in diameter and 35 centimeters high– and contained the bones of a bird. Although it lacks the attributes of Tlaloc, god of rain, its coloring could associate it with the aquatic world, and it seems to be still revered under the Pre-Columbian tradition.

Aztec dwelling
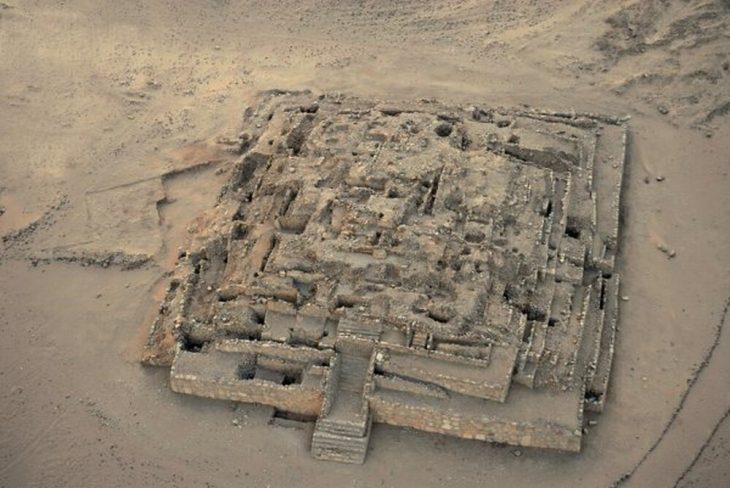
The Pre-Columbian Aztec dwelling found consisted of four rooms—probably the kitchen, due to the presence of a tlecuilli or fire pit—a corridor, and a small patio, possibly containing an altar.
Knowing these areas is very important for researchers because: allows lets them know the spaces of daily life at the end of the Late Postclassic period (1480-1521 C.E.). These spaces were located towards the limits of Atzacoalco and Cuepopan, and the borders of Tenochtitlan and Tlatelolco.
“It is interesting to find rammed earth with stuccoed sections, and as lime was not an immediate product in the Basin of Mexico, we can infer that before the arrival of the Spaniards, families that had access to certain foreign resources may have lived here. Some of them could have been families of priests or warriors, who had access to that kind of resources even though they were not part of the ruling elite,” Campos Varela concluded.
As part of the DSA project, more than 200 complete and semi-complete objects were recovered, including toys, whistles, plates, spouted vessels, coins, and medals, ranging from the 16th to the 19th centuries.
Cover Photo by Alejandra Núñez Mejía DSA-INAH