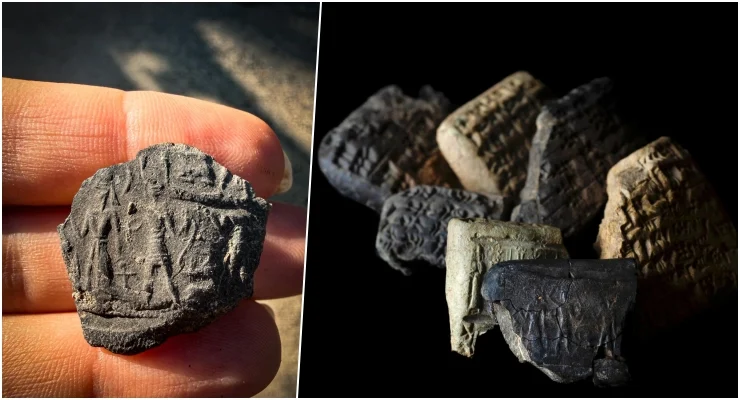
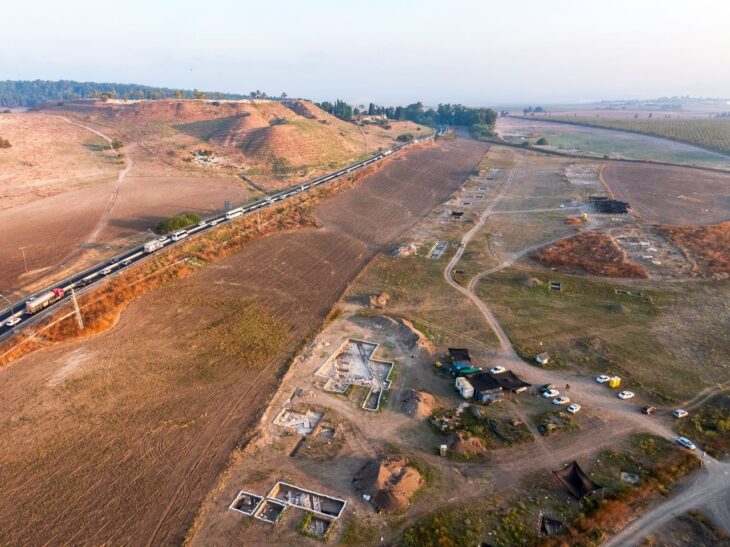
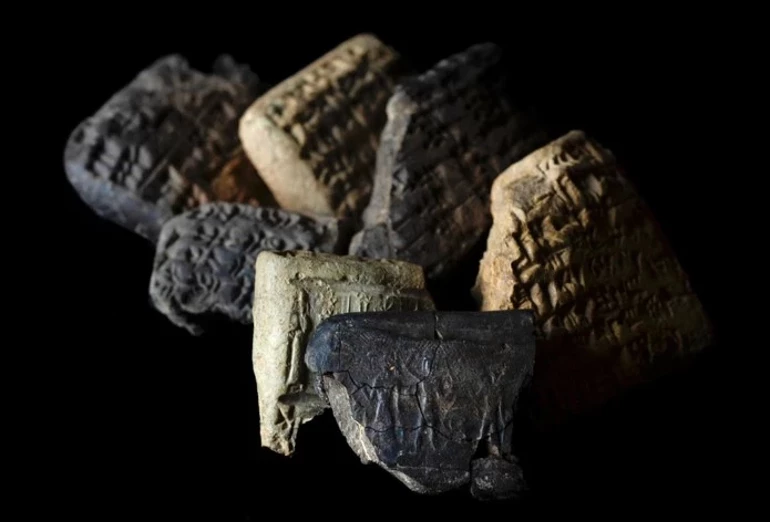
In the ancient heart of southern Türkiye, history has once again spoken through the clay. Archaeologists excavating the site of Aççana Höyük, known in antiquity as Alalakh, have unearthed a stunning discovery: 3,500-year-old cuneiform tablets written in Akkadian and seal impressions belonging to an unknown Hittite prince. Found within the charred remains of an administrative complex, these artifacts bridge two great civilizations — the Mitanni Kingdom and the Hittite Kingdom — revealing new insights into the political, economic, and spiritual world of the Late Bronze Age.
The discovery, carried out within the framework of the “Heritage for the Future” Project, was led by Prof. Dr. Murat Akar from Hatay Mustafa Kemal University’s Department of Archaeology. The findings shed fresh light on the political, administrative, and artistic life of the Late Bronze Age, roughly around 1500–1400 BCE.
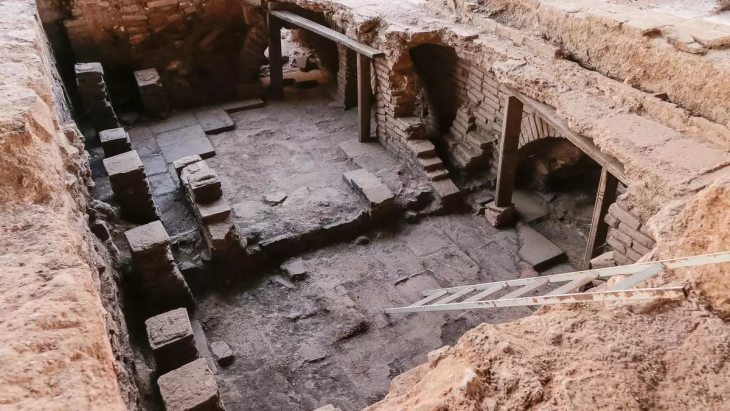
A Burnt Archive Revealing the Bureaucratic Heart of Alalakh
The discovery was announced by Minister of Culture and Tourism Mehmet Nuri Ersoy, who stated that it was made during excavations carried out as part of the “Heritage for the Future” (Geleceğe Miras) project.
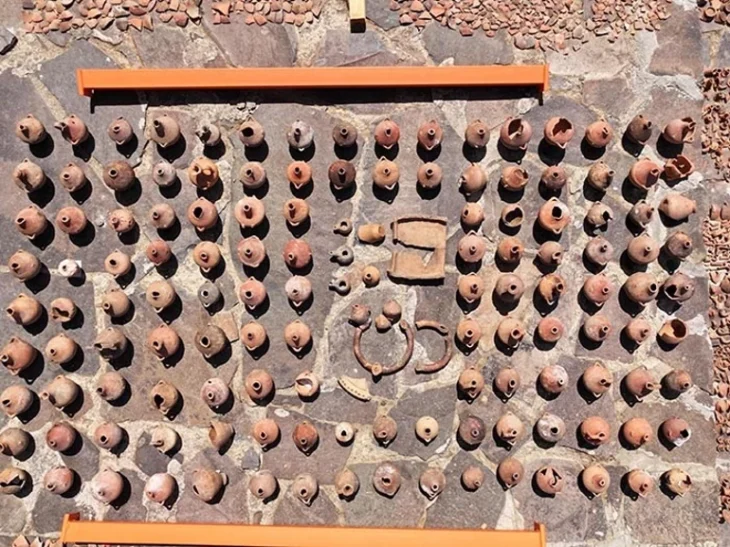
The tablets were found within a thick layer of burnt material, indicating that the city might have been destroyed by a major fire event. Despite the devastation, the tablets remained well-preserved, allowing researchers to decode details about the administration and trade of the Idrimi Dynasty, a local kingdom operating under the influence of the Mitanni Empire, one of the superpowers of the Late Bronze Age.
These tablets record furniture orders, personnel lists, and detailed distributions of food and raw materials — suggesting the existence of a well-structured bureaucracy operating under the authority of the Mitanni Kingdom. The documents, written in the Akkadian language, indicate the presence of a complex regional governance system and offer valuable insight into economic management and intercity trade during the Mitanni period.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

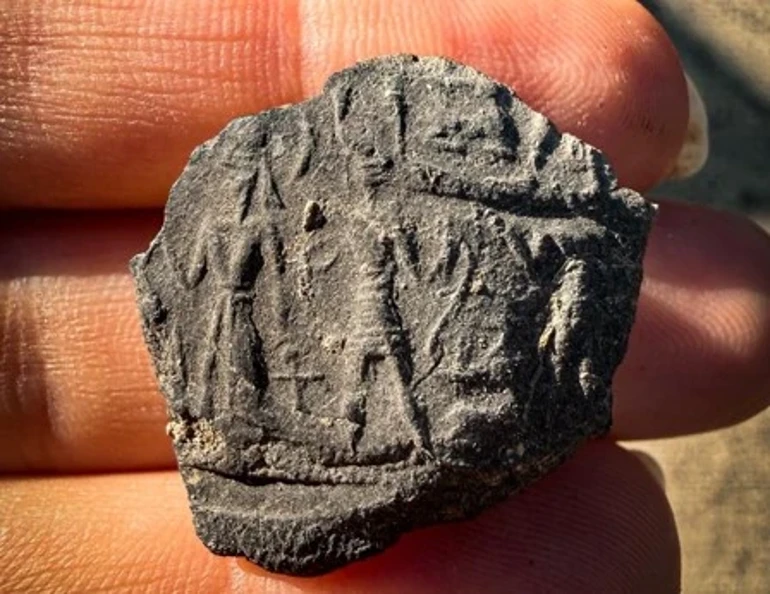
An Unknown Hittite Prince
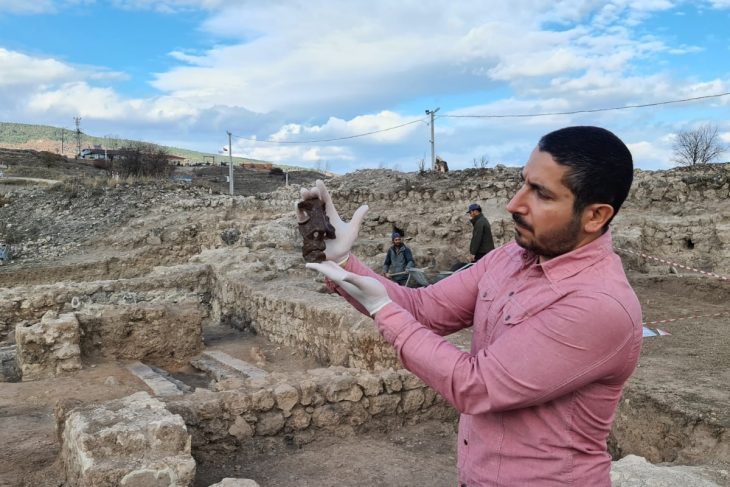
Perhaps even more striking than the archive itself is the discovery made in the upper, Hittite layers of the site: a series of seal impressions belonging to an unknown Hittite prince. These seals, which were part of the administrative system, provide valuable information about the governance and bureaucratic practices of the period.
The cylinder seals, once used to authenticate official documents, also feature elaborate scenes — including depictions of the Storm God battling winged creatures, a motif rich in Hittite and northern Syrian religious symbolism. Together, these findings highlight the complex interplay of administration, politics, and religion in the region during a time of transition between Mitanni and Hittite influence.
Bridging the Mitanni and Hittite Worlds
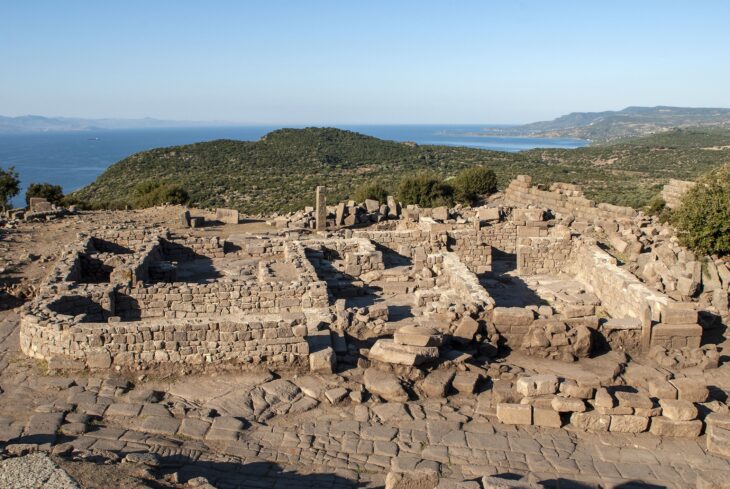
Aççana Höyük, identified with ancient Alalakh, was a vital cultural and political bridge connecting Anatolia, Mesopotamia, and the Levant. The coexistence of Mitanni and Hittite layers at the site illustrates the region’s strategic importance and its transformation through successive empires.
The newly found tablets and seals reveal how the region shifted from being under Mitanni influence to becoming part of the Hittite imperial system. The evidence suggests a gradual but tangible integration of administrative and artistic practices between these two great powers of the Late Bronze Age.

A Legacy for the Future
Minister of Culture and Tourism Mehmet Nuri Ersoy celebrated the discovery as “a gift from our ancestors to the future,” emphasizing its importance for both Turkish archaeology and world heritage. The finds will undergo conservation and digital documentation, with plans for future display at the Hatay Archaeology Museum.
As excavations continue, Aççana Höyük once again proves to be a key to understanding the complex political landscape of the Late Bronze Age — where forgotten kings, hidden archives, and now, an unknown Hittite prince emerge from the depths of history.