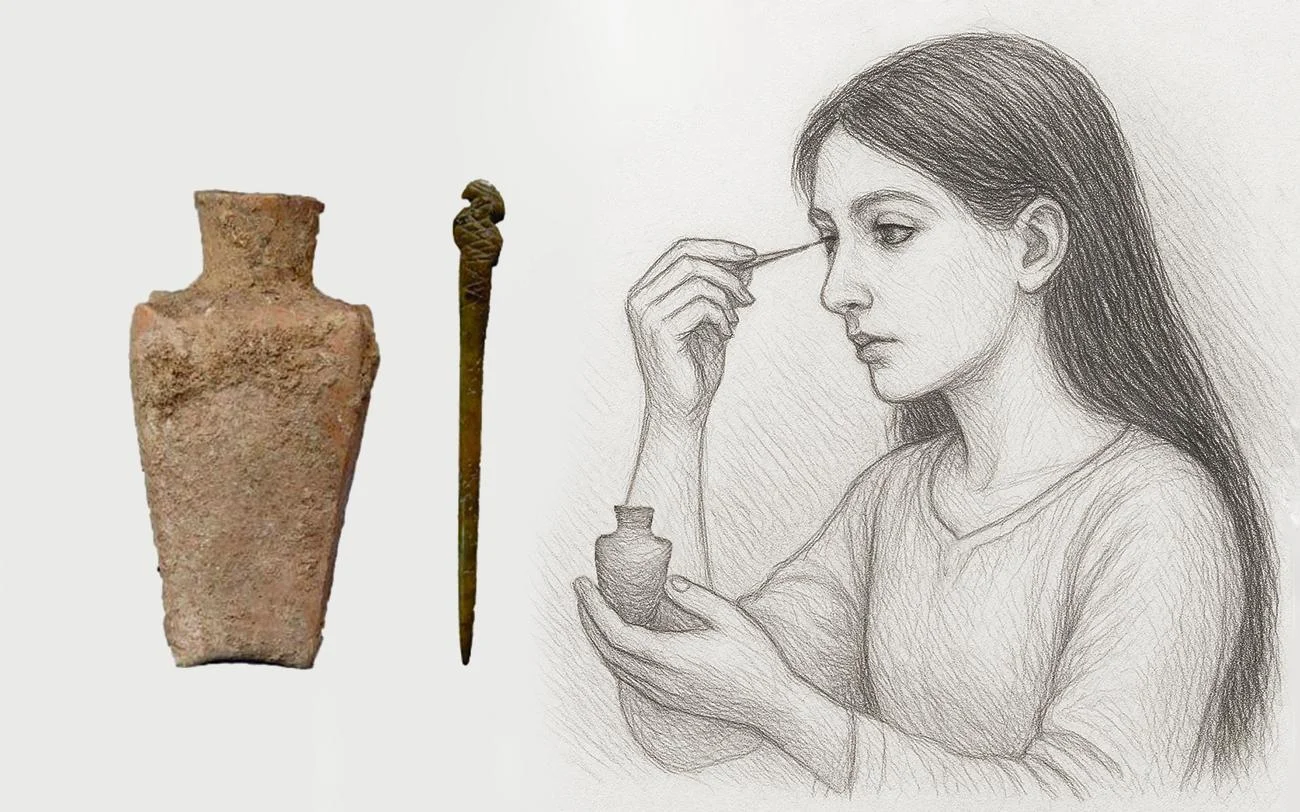Ancient black eyeliner found in Iron Age graves reveals a previously unknown cosmetic recipe using graphite and manganese oxide, predating modern formulations by millennia.
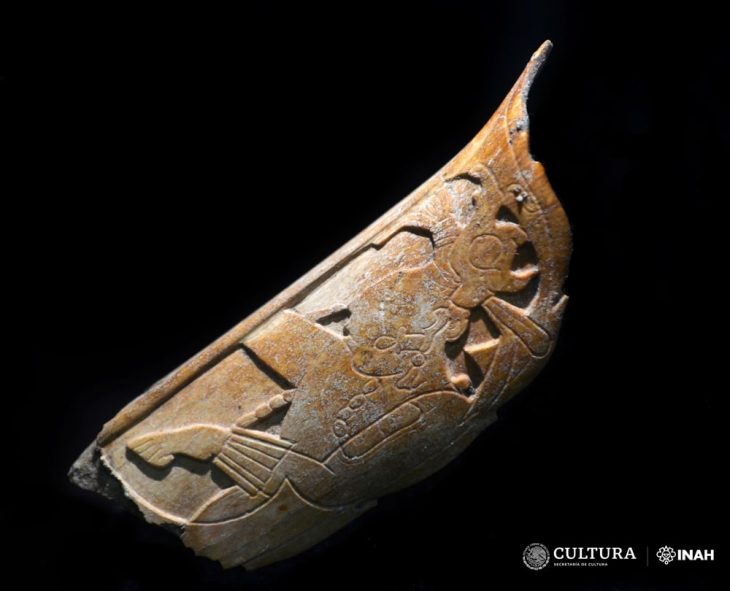
In a groundbreaking archaeological discovery, researchers have uncovered a never-before-seen kohl recipe dating back to the 7th–9th centuries BCE in northwestern Iran. The eye make-up, found in the Kani Koter cemetery on the edge of the former Assyrian Empire, features an innovative formula that completely diverges from traditional lead-based cosmetics of the Ancient Near East.
Led by Dr. Silvia Amicone from the University of Tübingen, the international research team found that the black eye powder was made from natural graphite and manganese oxide, without any traces of lead or organic materials—an unusual combination that suggests a shimmering metallic aesthetic likely favored by the local elite.
“Instead of using lead, as was common across Mesopotamia and Egypt, this community developed a distinctive recipe using locally sourced minerals,” explained Dr. Amicone.
Published in the latest edition of Archaeometry, the study adds a new chapter to the understanding of Iron Age beauty practices, personal adornment, and the material culture of ancient Iranian societies living at the periphery of the powerful Assyrian Empire.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
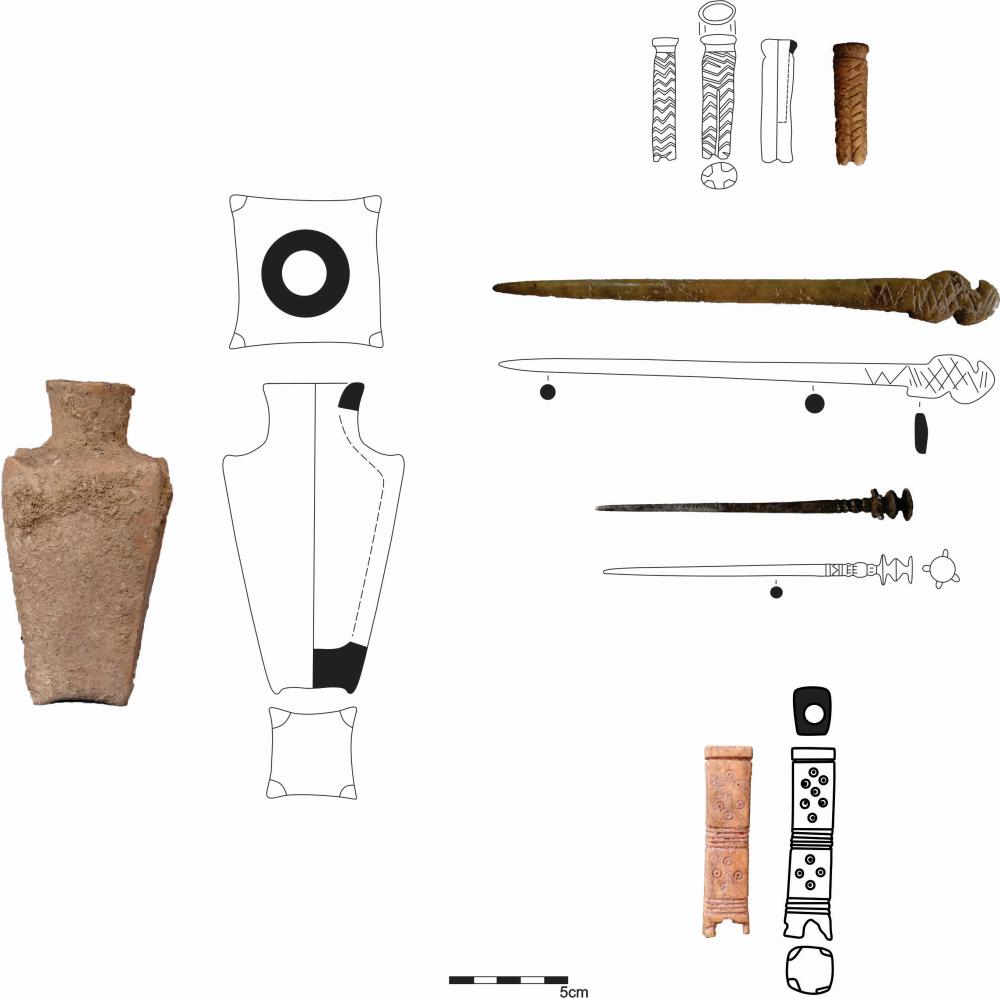

Elite Innovation in the Iron Age
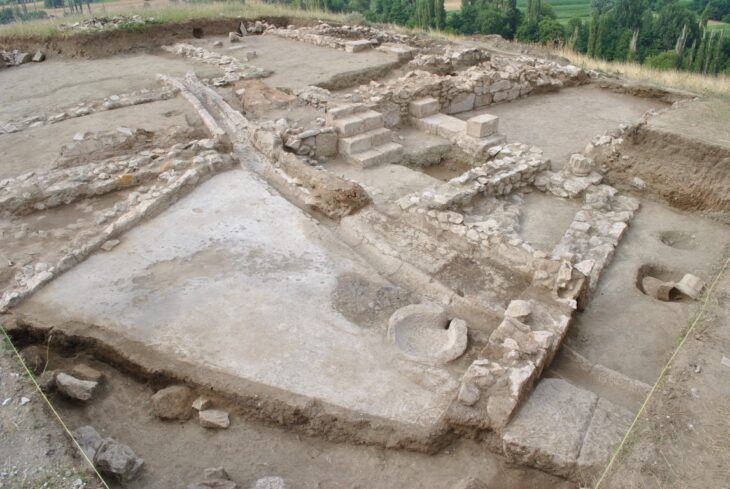
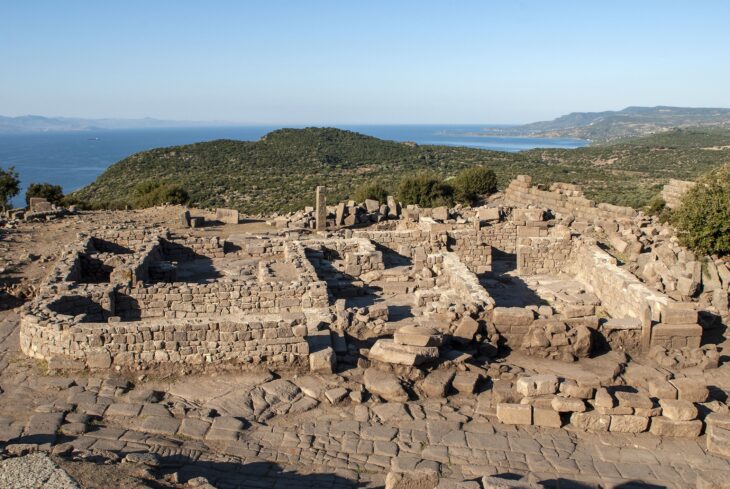
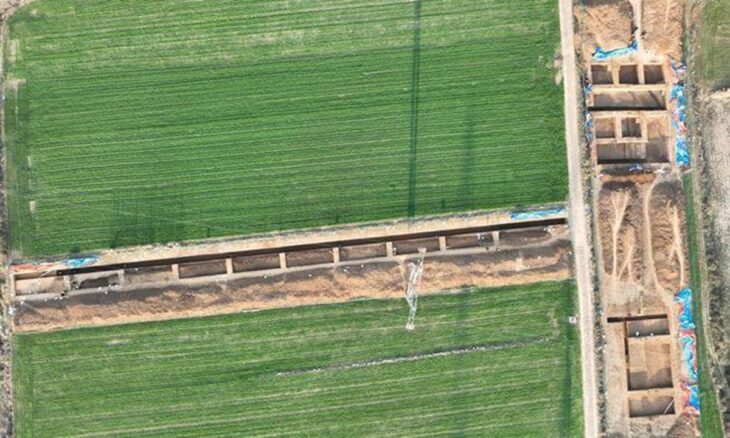
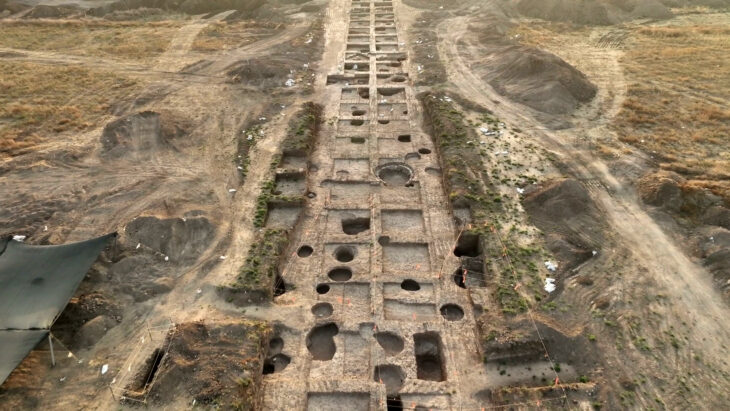
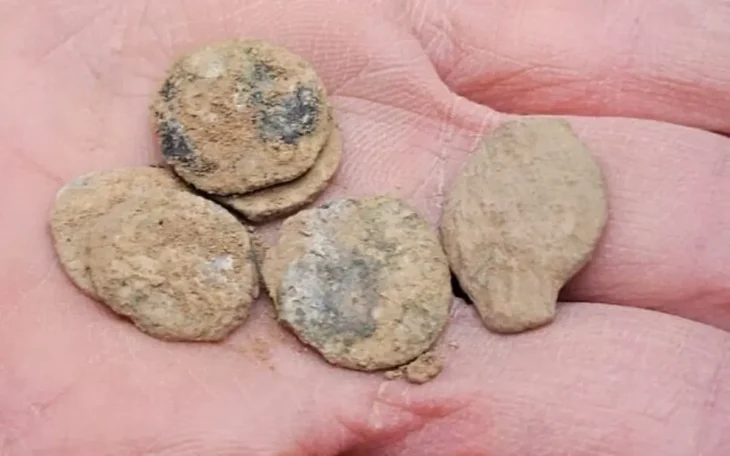
The Kani Koter burial site, nestled in the Zagros Mountains, contains graves from the Iron Age III period, many of which belong to high-status individuals. Alongside typical grave goods like mirrors and grooming tools, researchers found a ceramic vessel containing a black cosmetic powder. Its composition shocked scientists.
“This is the first time we’ve seen kohl made entirely from graphite and manganese oxide,” said co-author Dr. Shelir Amelirad of Heidelberg University. “This points to creative material use and regional innovation—a truly unique signature in the archaeological record.”
Advanced analytical methods confirmed the absence of both lead and organic compounds. While organic components may have decomposed over time, the current findings suggest a deliberate and sophisticated formulation, reflecting a high level of technological and cultural adaptation.
Local Resources, Global Insights
The use of locally sourced minerals such as graphite and manganese oxide points to a sophisticated understanding of natural materials and their applications in personal adornment. These findings suggest that communities on the Assyrian Empire’s eastern frontier were not merely cultural recipients but active innovators in their own right.
“This discovery gives us deeper insights into how people on the periphery of major empires expressed identity and status,” said Amicone. “It adds to our understanding of Iron Age technology, cosmetics, and cultural exchange between Assyria and early Iranian societies.”
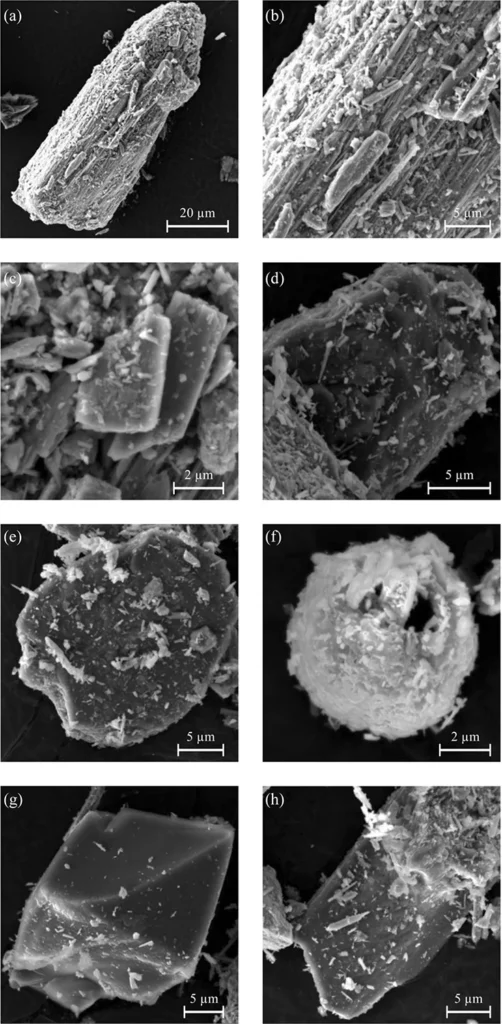

Cultural Significance of Ancient Iranian Cosmetics
These findings contribute to growing evidence that Iron Age communities in Iran were not simply cultural satellites of Assyria, but active innovators with unique aesthetic practices. The choice of minerals—graphite for smooth application and shine, and manganese oxide for deep pigmentation—demonstrates both cosmetic intention and regional resourcefulness.
“Such discoveries allow us to reconstruct not just how people looked, but how they thought about appearance, identity, and status,” said Dr. Amicone.
A Glimpse Into Ancient Beauty Rituals
The president of the University of Tübingen, Professor Dr. h.c. (Dōshisha) Karla Pollmann, emphasized the broader importance of such discoveries:
“Through modern science, we gain access to long-lost worlds—understanding how people lived, expressed themselves, and built their cultures.”
This 3,000-year-old eyeliner opens a new window into the daily life and personal expression of Iron Age elites. It also enriches our understanding of ancient chemical knowledge and cosmetic innovation far ahead of its time.
Silvia Amicone, Baptiste Solard, Shelir Amelirad, Eghbal Azizi, Lara Maritan, Maxime Rageot, Christoph Berthold, Karen Radner: Eye makeup in Northwestern Iran at the time of the Assyrian Empire: a new kohl recipe based on manganese and graphite from Kani Koter (Iron Age III). Archaeometry.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/arcm.13097