The U.S. and Iraqi archaeologists have unearthed ancient rock carvings believed to be more than 2,700 years old in Iraq’s northern city of Mosul.
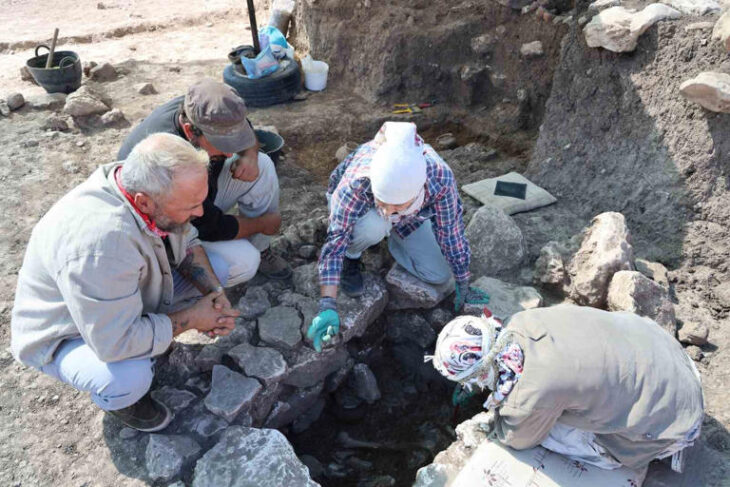
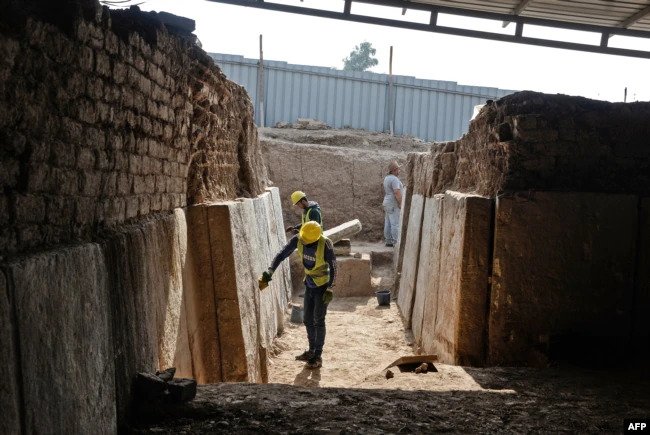
The marble slabs were discovered while restoring the Mashki Gate, an ancient monument partially destroyed by Islamic State militants (IS, formerly Isis) when they took over the city in 2016.
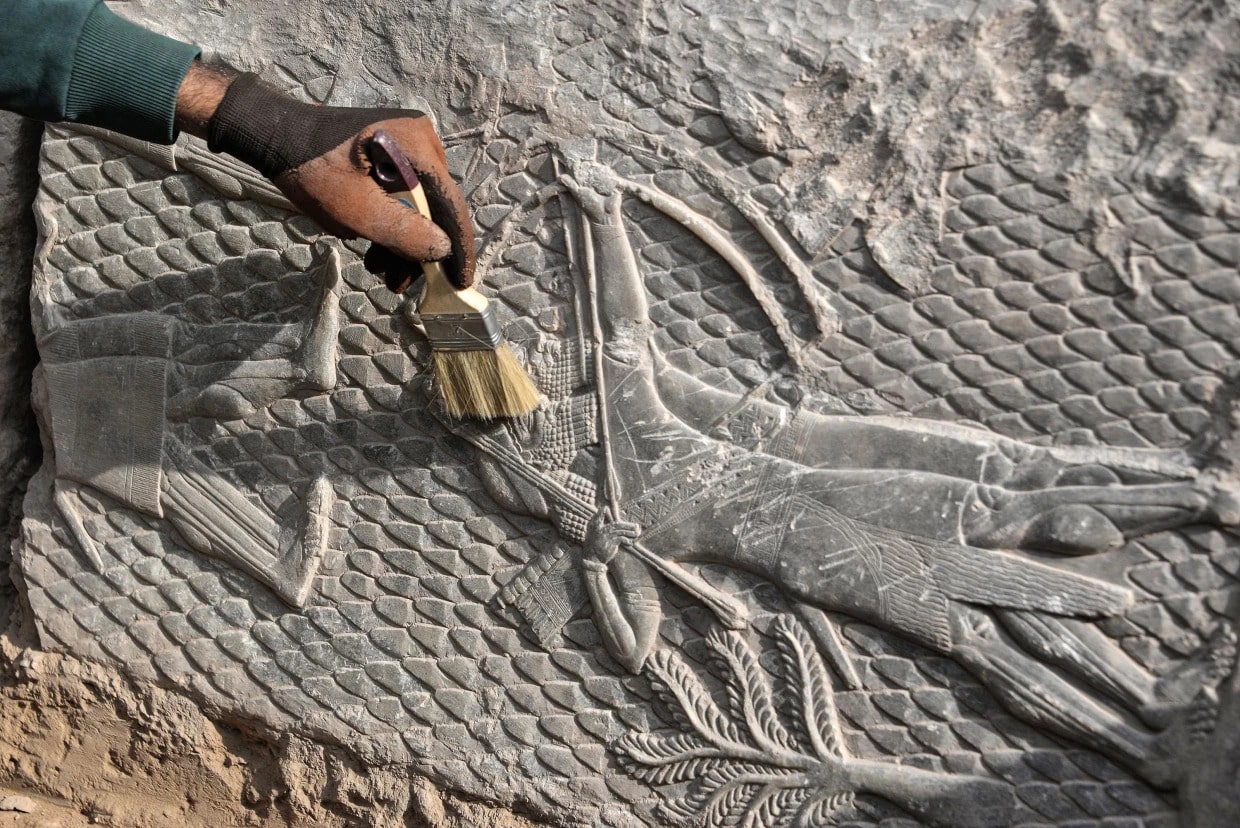
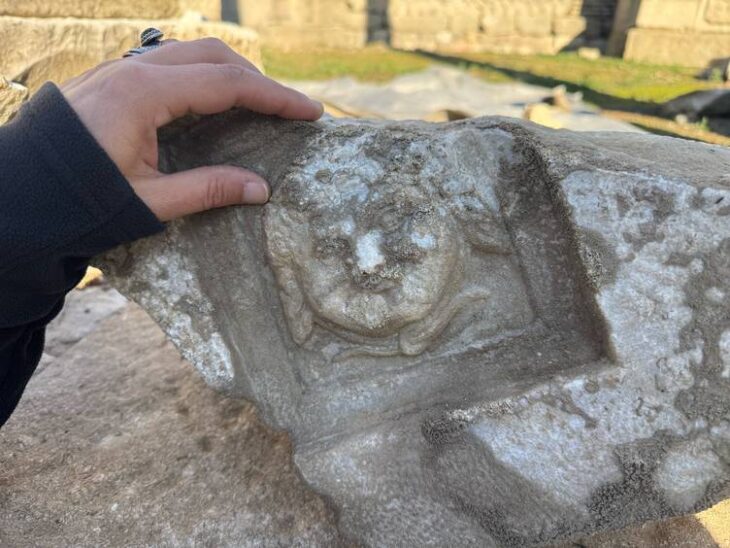
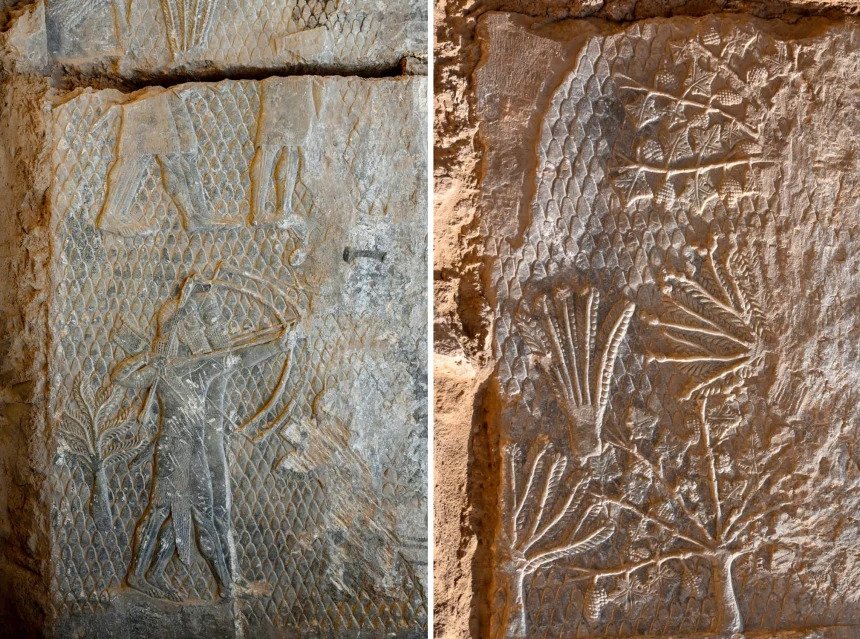
The relief carvings depict scenes of war from the reign of Assyrian kings in the ancient city of Nineveh, according to a statement issued by the Iraqi State Board of Antiquities and Heritage on Wednesday.
According to the Director General of the Department of Investigation and Excavation, Ali Shalgham said: “the cuneiform engravings were discovered that they belong to the time of King Sennacherib, who led his people between 750 and 681 BC.”

The discovery consists of eight marble (alabaster) slabs, which bear carvings featuring Assyrian soldiers, one of whom is intent on shooting an arrow, as well as palm trees, grapes, pomegranates, and figs that were located inside King Sennacherib’s palace.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Sennacherib was responsible for enlarging Nineveh, the imperial capital and largest city of the Assyrians, which was situated on a significant intersection between the Iranian plateau and the Mediterranean. He also built a magnificent palace.
Fadel Mohammed Khodr, head of the Iraqi archaeological team working to restore the site, said the carvings were likely taken from Sennacherib’s palace and used as construction material for the gate.
“We believe that these carvings were moved from the palace of Sennacherib and reused by the grandson of the king to renovate the gate of Mashki and to enlarge the guard room,” Khodr said.

The Mashki Gate was one of the largest in Nineveh, and was an icon of the city’s size and power. The gate was reconstructed in the 1970s but was destroyed with a bulldozer by IS militants in 2016.
Mr. Khodr said that when the marble slabs were positioned at the gate, they were partly buried. The sections underground were preserved and bear the carvings seen today; whatever was above ground was wiped smooth over the centuries.
ALIPH, the Swiss-based International Alliance for the Protection of Heritage in Conflict Areas, said the Mashki Gate had been an “exceptional building.” ALIPH is supporting the reconstruction of the Mashki Gate by a team of archaeologists from Iraq’s Mosul University alongside U.S. experts from the University of Pennsylvania.