Archaeologists in central Kazakhstan have unearthed an exceptionally well-preserved tomb of a Saka warrior, revealing a pristine 2,500-year-old bronze sword still clutched in its owner’s hand. The discovery, made at the Karabiye burial site in the Aktogay district of the Karaganda region, has been hailed as one of the most significant archaeological finds from the early Iron Age in recent decades.
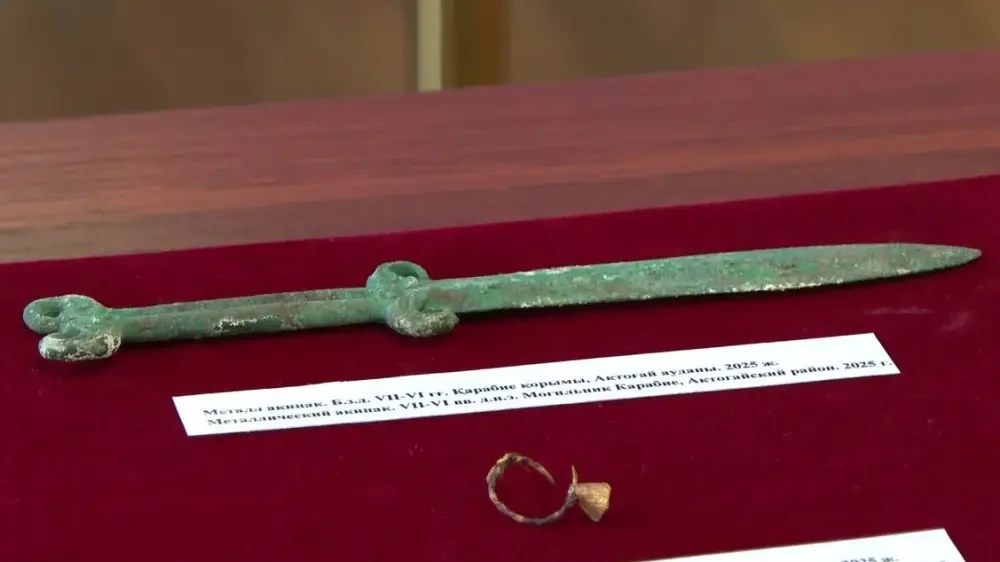
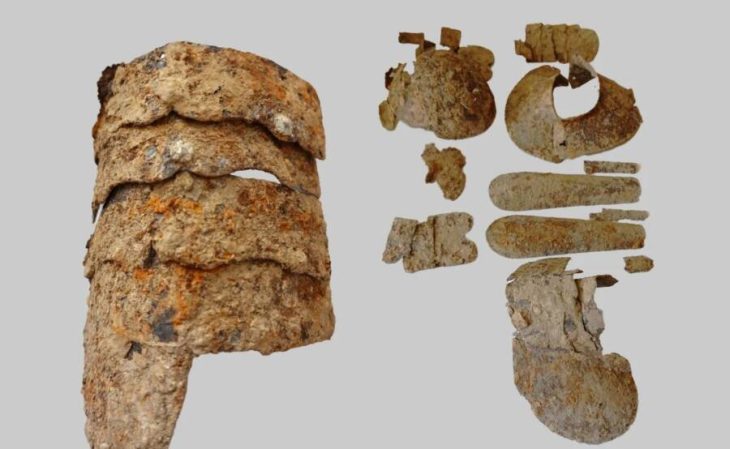
The excavation, carried out by a team from the Karaganda Regional History Museum, uncovered an untouched burial mound—known as Kurgan No. 1—dating to the 7th–6th centuries BC. Such undisturbed graves are extremely rare among Saka sites, many of which were looted long ago. Beneath layers of stone slabs lay the remains of a warrior positioned carefully according to ancient funerary traditions, his right hand still gripping a bronze akinak—a short sword emblematic of the Saka elite.
“After removing the covering slabs, we saw a skeleton in correct anatomical order. In his right hand was an akinak. We haven’t had such findings in many years,” said Dauren Zhussupov, head of the Archaeology Department at the regional museum.
The bronze weapon, about 30 centimeters long, is double-edged and intricately decorated with figures of steppe birds of prey and argali horns—symbols deeply associated with power and the free spirit of the nomads. Archaeologist Arman Beissenov described the sword as “a masterpiece of ancient metallurgy” and noted that no similar example has yet been found elsewhere in Kazakhstan.

A Window Into Saka Craftsmanship
The sword’s exceptional quality reveals the advanced metallurgical and artistic skills of the Saka, a confederation of nomadic tribes who dominated the Central Asian steppes from roughly the 8th to 3rd centuries BC. Known to the ancient Persians as Saka and to the Greeks as Scythians, these horseback warriors forged a sophisticated culture defined by mobility, animal symbolism, and elite artistry in gold and bronze.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Their weapons and ornaments were not only tools of war but also symbols of status and spirituality. The birds of prey etched into the akinak’s hilt may have represented divine guardianship or the sharp vision of warriors scanning the open plains. Similar motifs appear on the legendary “Golden Man” burial unearthed in Kazakhstan’s Issyk kurgan, suggesting a shared visual language of power across the Saka world.
Signs of a Warrior Elite
In addition to the sword, the Karabiye tomb contained five metal arrowheads and a gold earring, believed to have once adorned the warrior or served as an offering to accompany him into the afterlife. The presence of precious metal ornaments indicates that the man held a high social rank—perhaps a chieftain or a noble fighter.
The Saka were famed for their mounted archers, whose speed and precision transformed steppe warfare. Classical authors such as Herodotus described them as fierce yet disciplined, capable of defeating much larger armies through hit-and-run tactics. Their skill with the bow and their elaborate burial customs inspired later steppe cultures, including the early Turkic tribes.

Preserving the Past
The Karaganda team plans to conduct metallographic, radiocarbon, and anthropological analyses to determine the warrior’s age, origins, and the specific composition of the bronze alloy. The results, expected next winter, may shed new light on trade routes and technological exchanges in the early Iron Age.
The find underscores Kazakhstan’s growing importance as a center of archaeological discovery in Eurasia. Recent decades have seen the recovery of multiple Saka “Golden Men,” richly adorned with gold regalia, each rewriting part of the region’s early history. Yet, unlike many royal tombs, this latest discovery stands out for its untouched state—an unbroken link to a civilization that vanished over two millennia ago.
As Beissenov summarized, “This burial allows us to look directly into the world of the Saka. Every detail—from the weapon to the ornamentation—tells the story of people who lived, fought, and dreamed across the great steppes of Kazakhstan.”
Cover Image Credit: Karaganda Regional History Museum