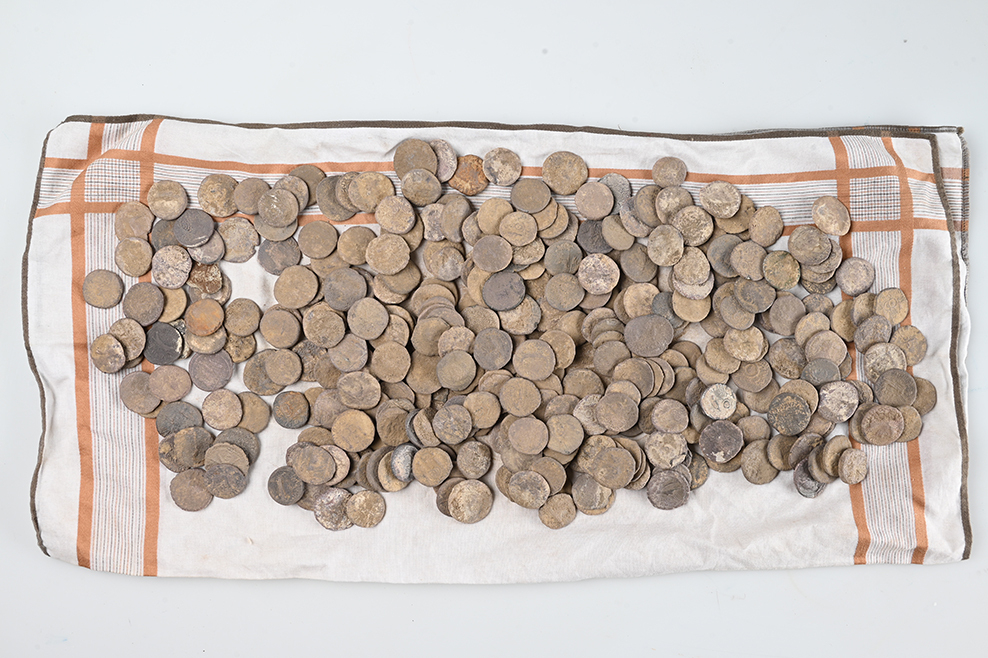
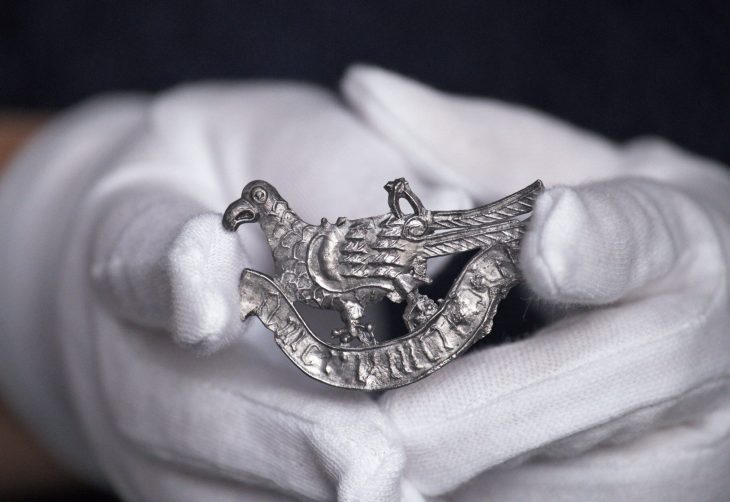
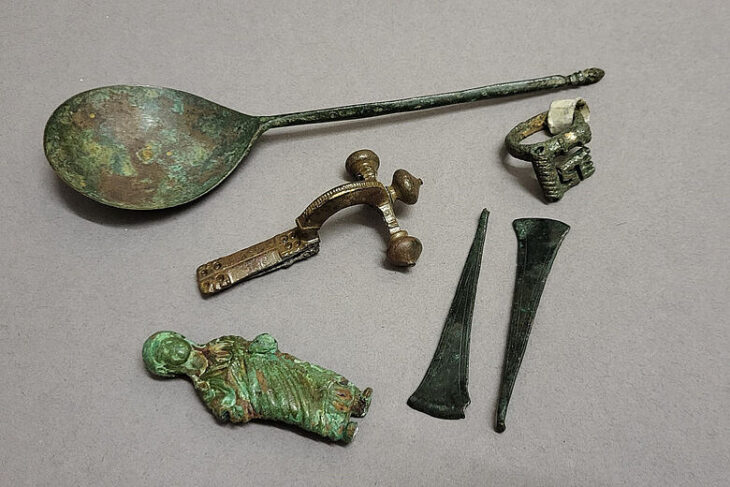
A remarkable archaeological discovery has come to light near Borsum, a village in the district of Hildesheim in Lower Saxony. Authorities have confirmed the recovery of a Roman silver hoard consisting of approximately 450 silver coins, several silver ingots, a gold ring, and a gold coin, making it one of the largest Roman treasure finds in northern Germany.
The treasure, estimated to be around 2,000 years old and dating back to the early Roman Imperial period, was initially found in 2017 by an illegal metal detectorist. The finder only recently reported the hoard to the Hildesheim police and local heritage authorities, prompting a formal investigation and archaeological study.
From Illegal Discovery to Official Excavation
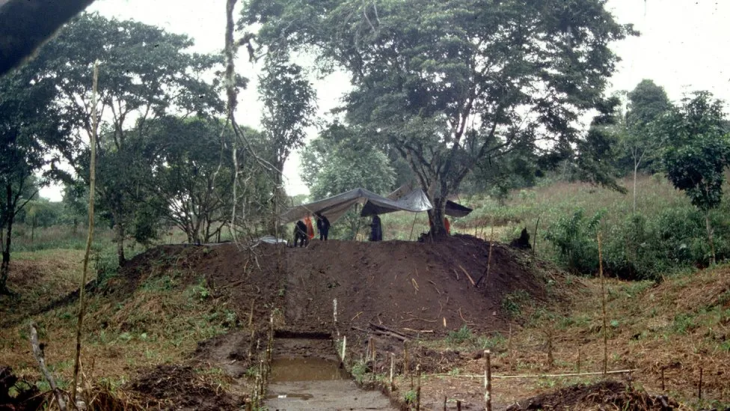
According to the Lower Saxony State Office for the Preservation of Monuments (Niedersächsisches Landesamt für Denkmalpflege, NLD), an initial inspection of the find site took place in April 2025 with the participation of the original finder. A comprehensive archaeological excavation followed last week, conducted by the NLD, the Lower Monument Protection Authority of the Hildesheim district, and the City Archaeology of Hildesheim.
The excavation aimed to locate the original digging site from 2017 and to recover any remaining objects still buried in the ground. Despite the destruction of the find’s original context due to the unauthorized excavation, archaeologists hoped to gain new insights into the circumstances of the hoard’s deposition nearly two millennia ago.
Their efforts proved successful: additional coins were uncovered, and the treasure has now been completely excavated and secured for conservation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
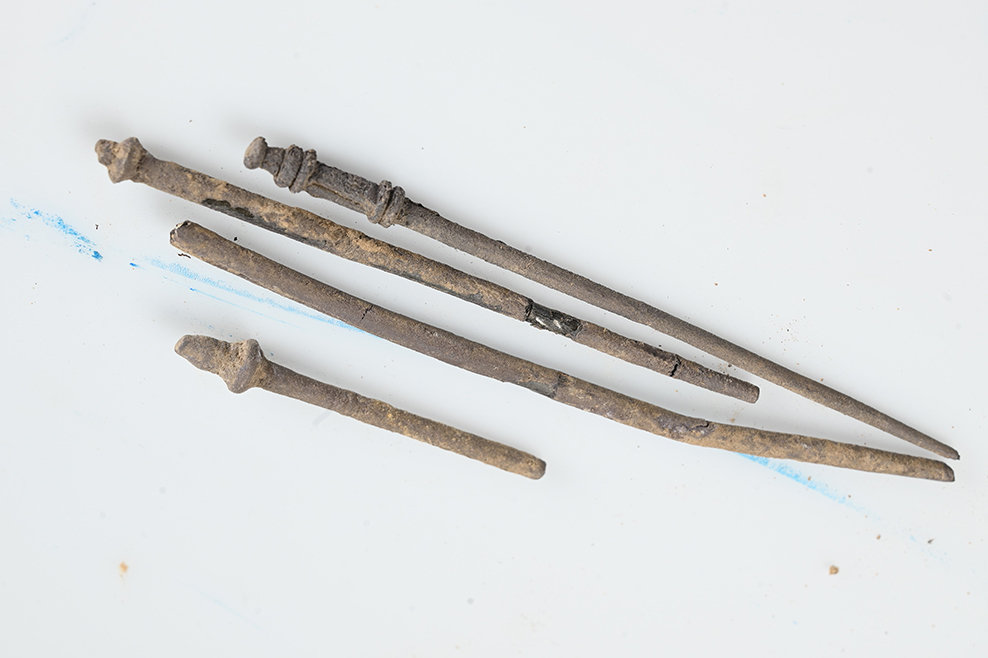

Scientific Analysis and Restoration Underway
The restoration and scientific examination of the Borsum silver hoard are now being carried out at the NLD. Experts believe that the coins date to the early Roman Imperial era, a period characterized by complex interactions between Romans and Germanic tribes across northern Europe.
However, determining the exact date and purpose of the hoard’s burial will require detailed study. Archaeologists hope to learn whether the treasure was hidden by Roman soldiers, traders, or local Germanic inhabitants, and what circumstances — possibly related to conflict, trade, or ritual — led to its deposition.
Once the analysis is complete, researchers will also be able to identify the origin of the coins and precious metals, shedding light on the economic and cultural connections between the Roman Empire and the regions beyond its frontiers.
Legal and Cultural Implications
The finder of the hoard has since attended a training course for responsible metal detecting, organized by the NLD. Although his original discovery in 2017 was illegal, the public prosecutor’s office in Hildesheim has dropped the case due to the statute of limitations.
In Lower Saxony, the use of metal detectors for archaeological purposes is strictly regulated. Detectorists must obtain a special permit to ensure that significant archaeological finds are properly documented and preserved for future research. Unauthorized excavations can lead to the loss of invaluable historical information, as happened in this case.
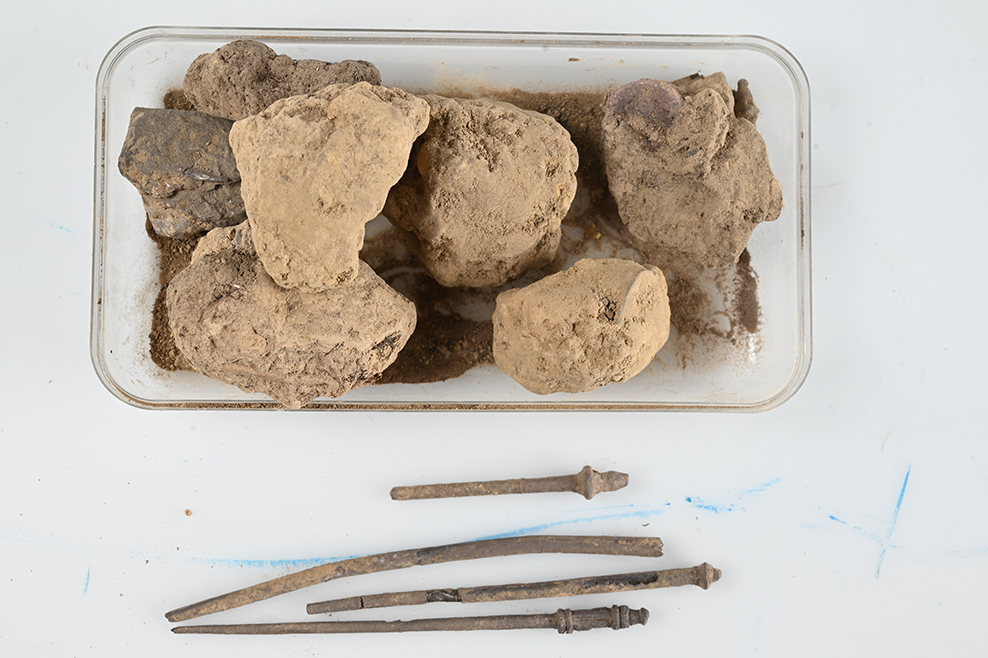

A Window into the Past
The Borsum silver hoard represents a significant archaeological discovery that may transform our understanding of Roman activity in northern Germany. As one of the largest Roman coin hoards ever found in Lower Saxony, it offers a rare glimpse into a turbulent period marked by trade, warfare, and cultural exchange between Romans and Germanic peoples.
Once the conservation and analysis are complete, the Hildesheim authorities plan to exhibit the treasure to the public, highlighting both its historical importance and the need for responsible archaeological practice.
Lower Saxony State Office for the Preservation of Monuments
Cover Image Credit: Bartels, PI Hildesheim, ZKD/FK Forensik