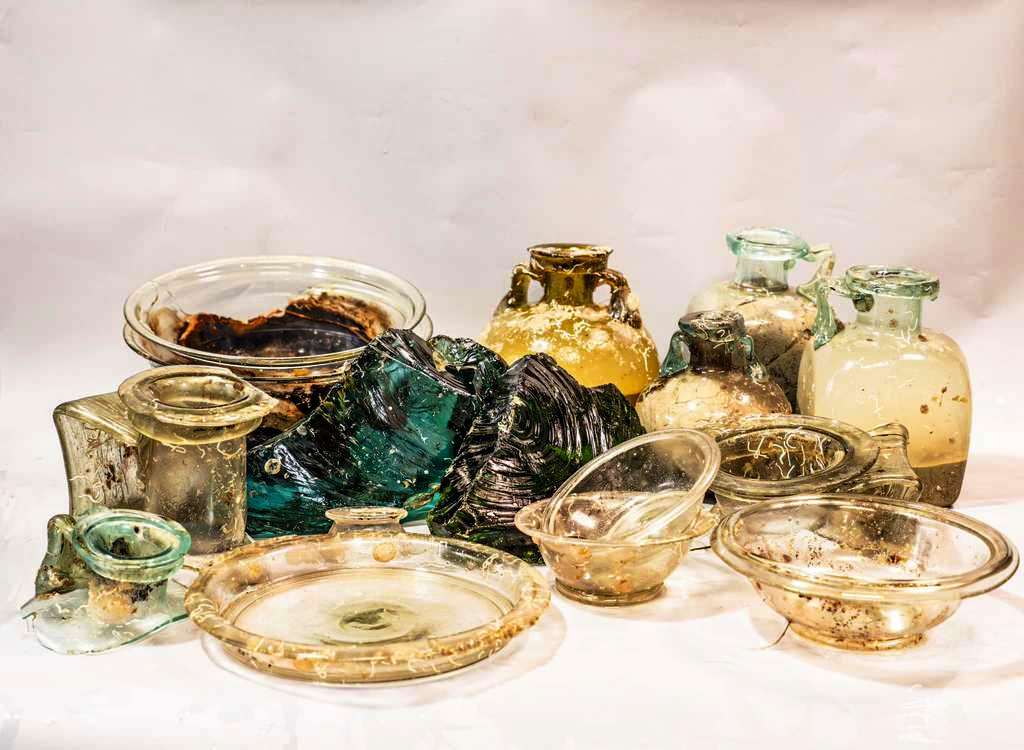
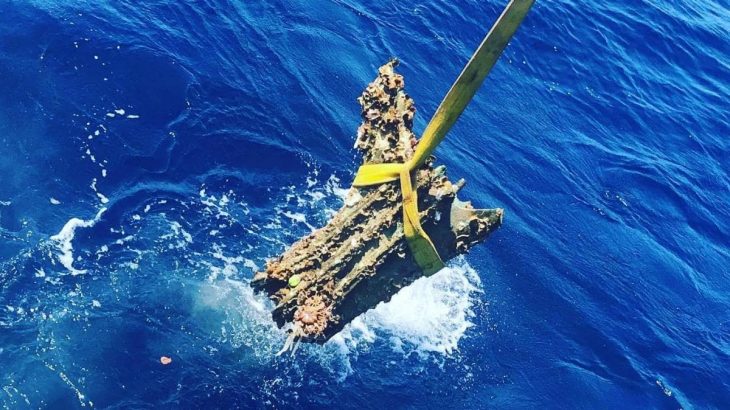
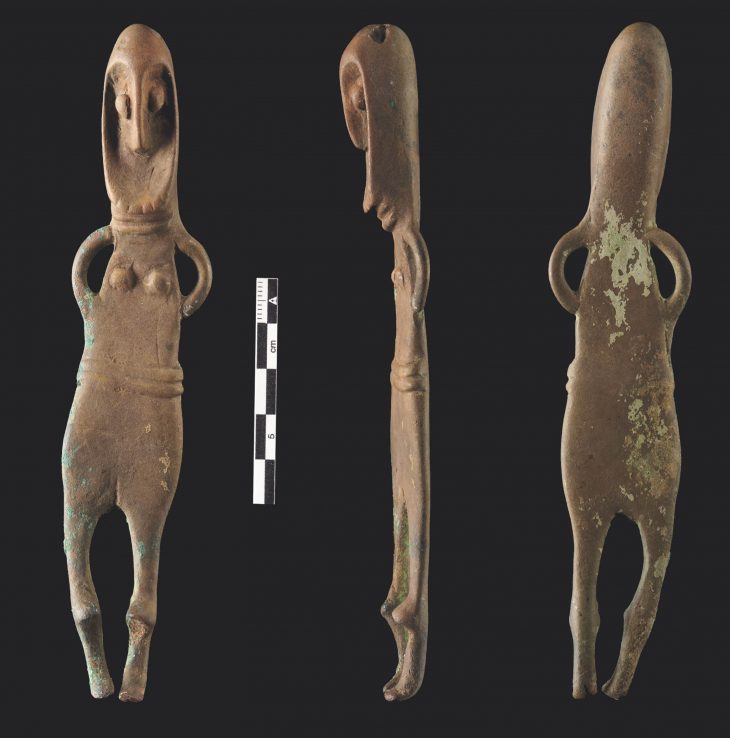
The Italian-French mission recovered a selection of glassware and raw glass blocks from the Roman shipwreck located at a depth of about 350 meters in the sea strip between Capo Corso (Corsica-France) and Capraia Island (Italy).
The cargo, which consists primarily of worked pieces and raw blocks of glass in a range of sizes and colors that are ready to be blown into commercial tableware, is only the second known case to date in the Mediterranean.
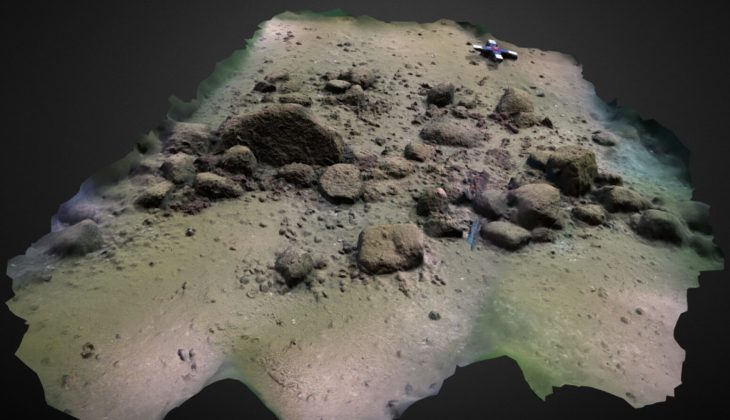
This one ship left thousands of glass fragments and tons of raw blocks on the sea floor. The wreck’s contents indicate that it last sailed in the late first or early second centuries A.D.
The bilateral mission was coordinated for the Italian part by the National Superintendency for Underwater Cultural Heritage (Ministry of Culture) directed by Superintendent Barbara Davidde and for the French part by the Département des Recherches Archéologiques subaquatiques et sous-marine-Drassm (Ministry of Culture), under the direction of the archaeologist Franca Cibecchini, responsible for Corsica. Inrap is also collaborating on the study mission of the wreck, with the archaeologist specialist of ancient glass Souen Fontaine (Responsable du Pôle Subaquatique-Inrap). For the first time, archaeological research has been associated with the marine biological observation of the fauna of these particular deep ecosystems thanks to the direct participation of the ecologist Nadine Le Bris (Sorbonne Université-Museum National d’Histoire Naturelle).

In 2012, the wreck was discovered 350 meters (1150 feet) deep. The wreck was initially thought to be in French territorial waters, and the underwater archaeology department of France’s Culture Ministry conducted some preliminary surveys in 2013 and 2015. Diplomatic negotiations on where to draw the border shifted the discovery site into Italian territorial waters in 2016, and the two countries agreed to collaborate on a wreck study. The joint mission’s first campaign took place in the first week of this month.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The French Culture Ministry has made available its flagship research vessel, the Alfred Merlin, equipped with its two ROVs Arthur and Hilarion to carry out research in the deep sea. Arthur, is a new ROV prototype designed and created with and for Drassm by Professor Vincent Creuze (University of Montpellier-LIRM), who actively participated in the mission. This robot, one of the smallest and lightest in its category, can reach 2500 meters and allows not only to shoot high-definition video but also to ventilate or vacuum the sediment and recover objects. The Rov Hilarion, piloted by the archaeologist Denis Degez (Drassm) produces high-definition videos up to a depth of 500 m.
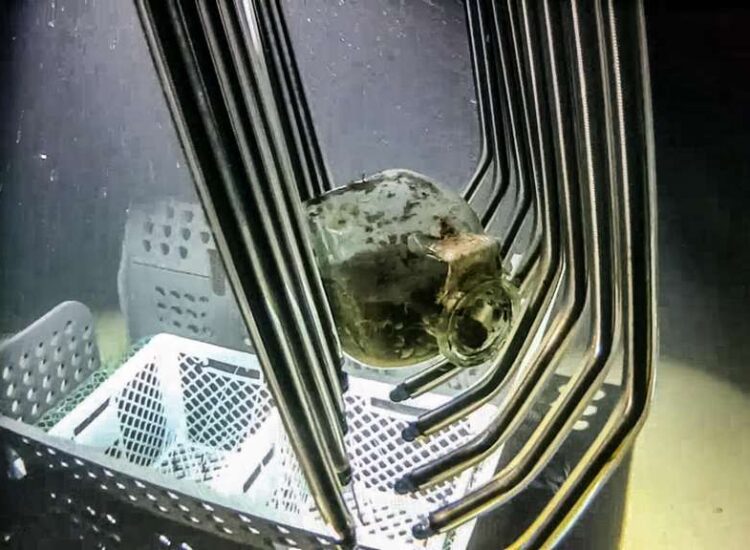
Arthur recovered a variety of glass pieces, including bottles, plates, cups, bowls, a small unguentarium (cosmetic vessel), and several raw blocks. Two large bronze basins and a few amphorae were brought to the surface in addition to the glassware.
At the moment the wreck is dated between the end of the 1st century and the beginning of the 2nd century AD but an in-depth study of the materials will be able to provide further details on the chronology of the shipwreck and more information on the route traveled by the ship on its last journey. At an initial analysis of the load, given the type of visible amphorae (“carrot” amphorae, oriental amphorae including probable Beirut-type amphorae and some Gauloise 4 amphorae) and the quantity of glass vessels and blocks of raw glass, the archaeologists believe that the ship must have come from a port in the Middle East, perhaps from Lebanon or Syria, and that it was headed for the French Provençal coast.