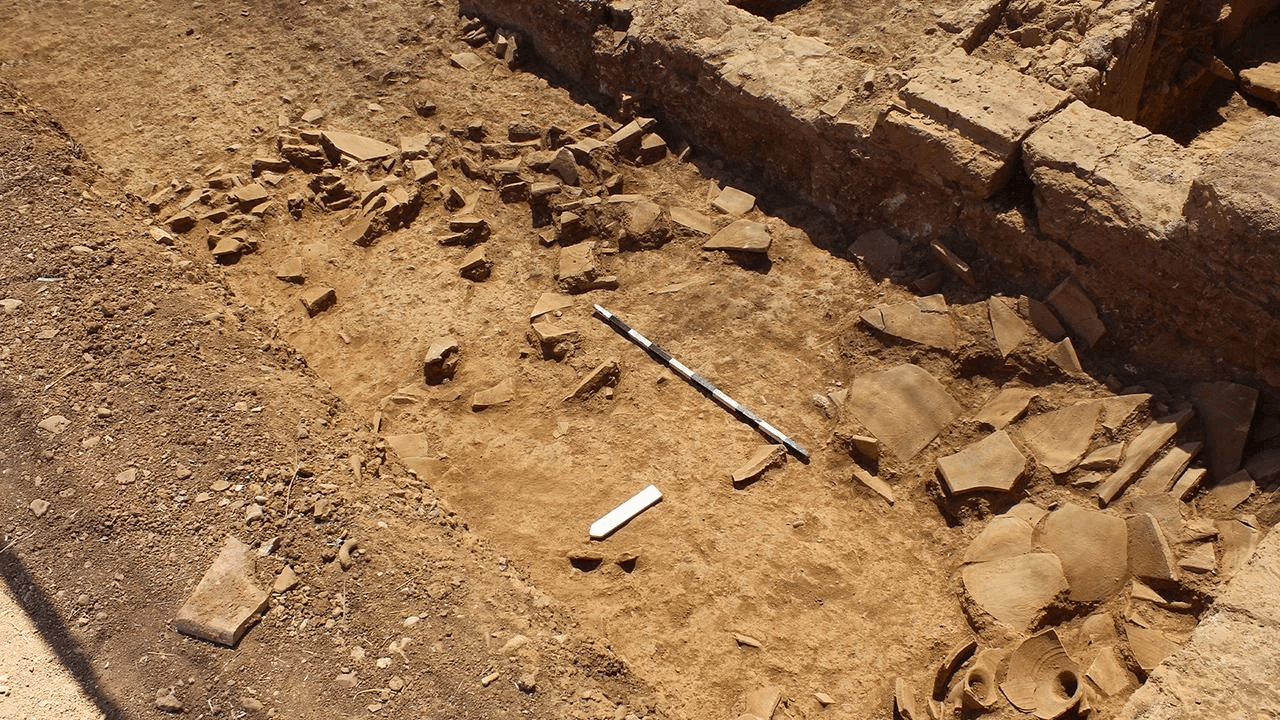
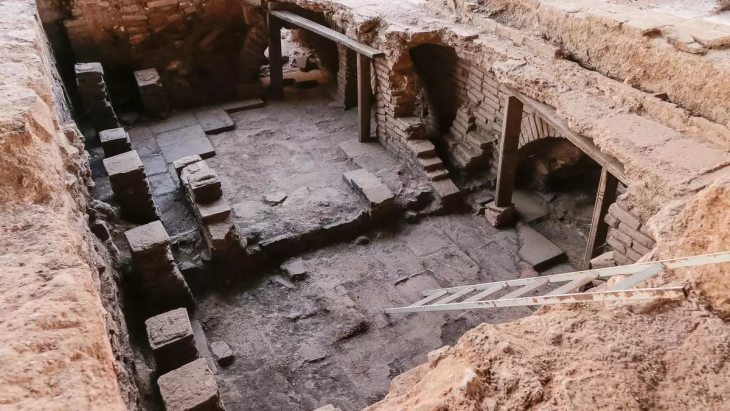
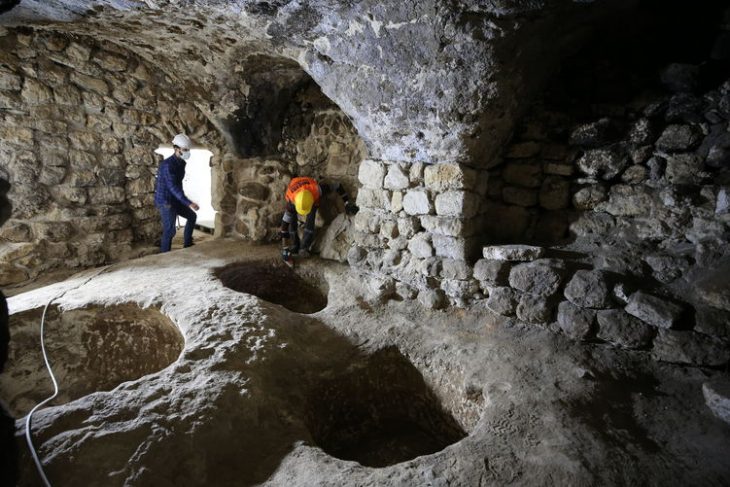
A team led by Scott Gallimore of Wilfrid Laurier University and Martin Wells of Austin College discovered a 1,600-year-old Roman-era wine shop in the ancient city of Sikyon in southern Greece, which was destroyed by a sudden event, possibly an earthquake or building collapse.
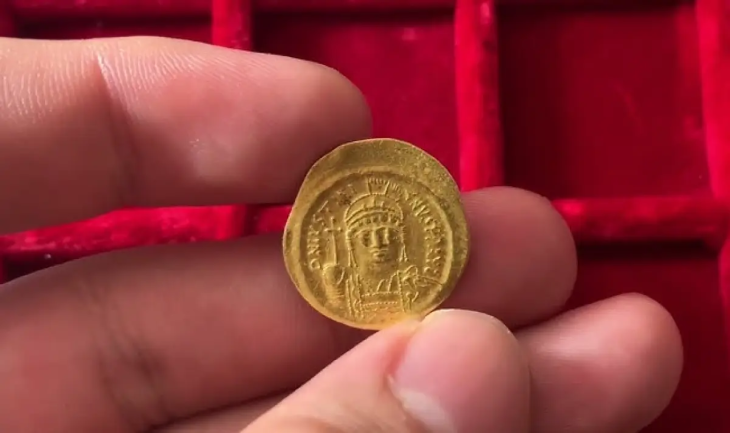
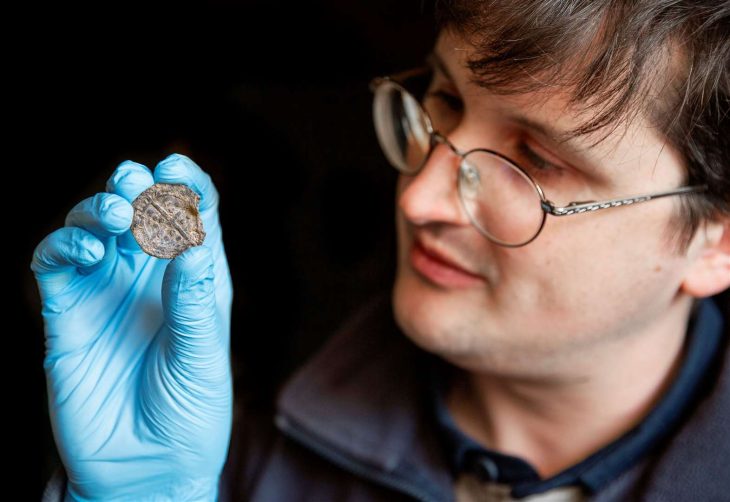
The discovery includes shattered vessels and a collection of 60 coins scattered on the floor, providing insight into the ancient establishment’s final moments.
The wine shop, situated in the ancient city of Sikyon (Sicyon) on the northern coast of the Peloponnese in southern Greece, operated during the period when the Roman Empire held sway over the region.
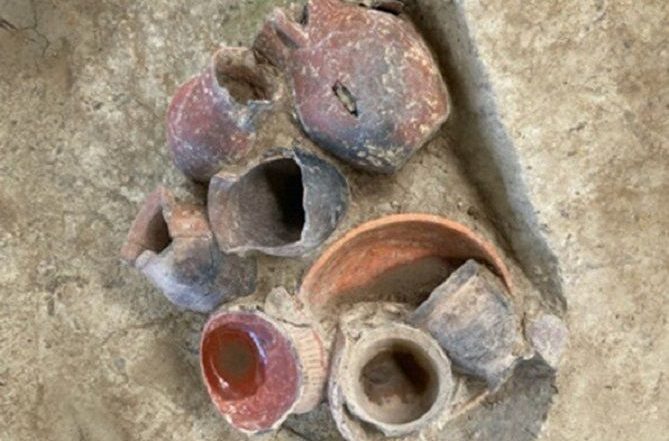
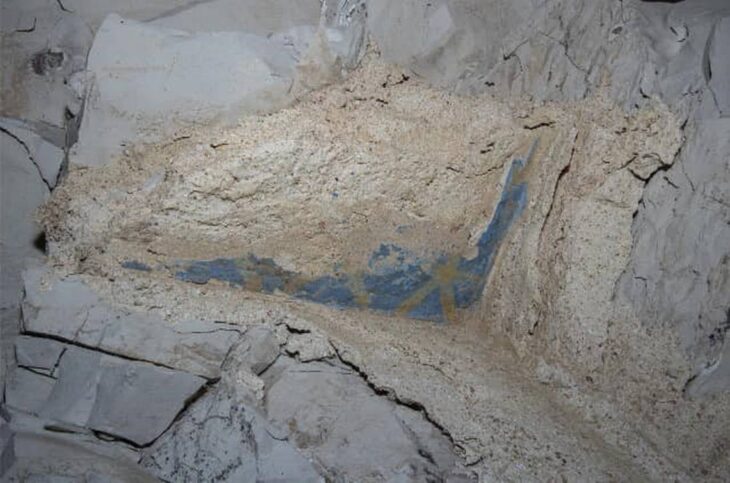
As experts investigated the wine shop, they discovered not only coins but also marble tabletops and various vessels made of bronze, glass, and ceramic, according to Live Science.
The archaeological site reveals a complex that housed the wine shop on its northern end. The larger complex featured a series of workshops equipped with kilns and installations designed for pressing grapes or olives.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
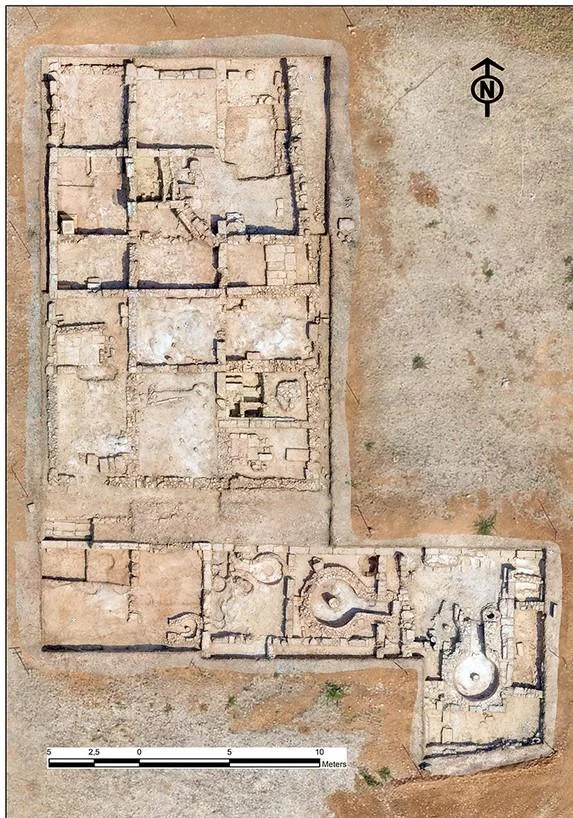

Despite the abundance of artifacts, the researchers, in an email interview with Live Science, expressed the challenge of pinpointing the specific types of wine sold at the establishment.
“Unfortunately, we don’t have any direct evidence of the types of wine that may have been sold. We have some evidence of grape pips (Vitis vinifera), but we aren’t able to say anything more specific than that right now,” Gallimore told Live Science in an email.
Aside from wine, the shop may have sold other products such as olive oil. According to Scott Gallimore, the majority of the coins discovered date back to the Constantius II era, which lasted from 337 to 361. The most recent coin in the collection was minted between 355 and 361.
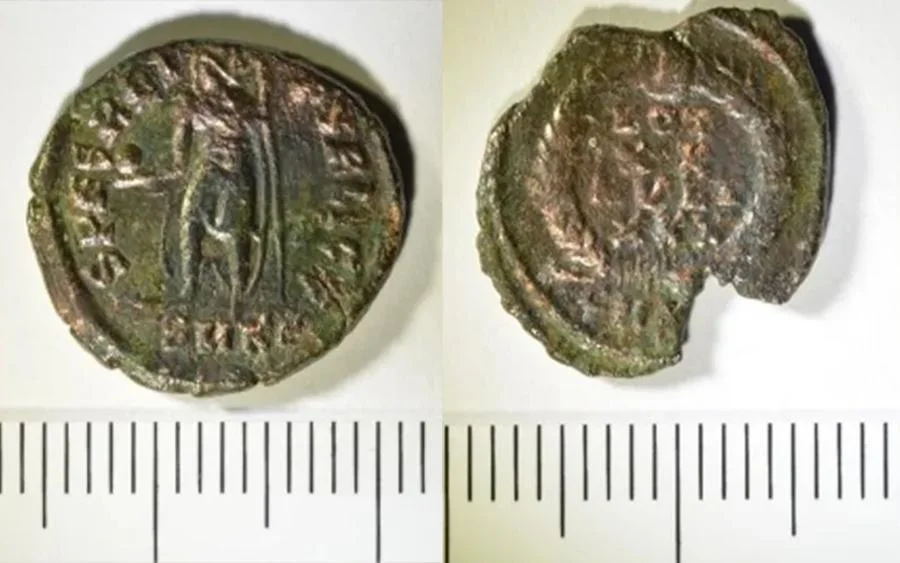

The scattered arrangement of these coins on the shop’s floor suggests that they were kept together, possibly in a ceramic container or some form of bag. The destructive event, which led to the abandonment of the wine shop, caused this container to fall and scatter the coins, leaving the establishment in ruins.
The destruction could have been caused by an earthquake or a possible roof collapse caused by environmental factors, such as excessive rainfall, said Gallimore.
The larger complex, including the shop, seems to have been deserted in the early fifth century, potentially around the time of the destructive event.
Cover Photo: The Roman-era wine shop in Greece. Credit: Scott Gallimore