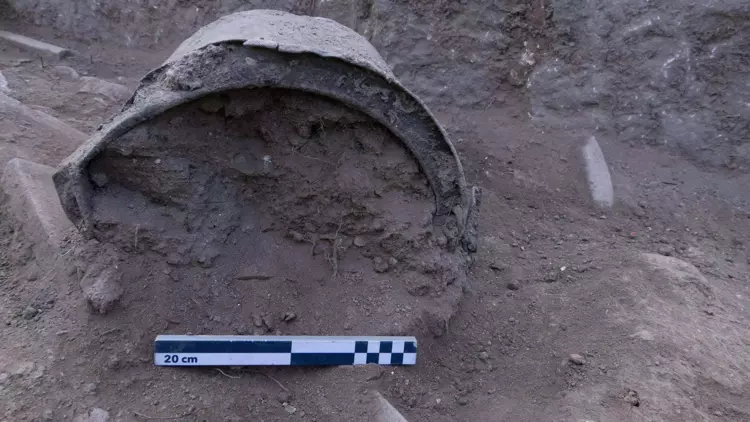
A remarkable archaeological discovery has been made in the ancient city of Pergamon (modern-day Bergama) in Turkey’s İzmir Province. Excavations at the UNESCO World Heritage-listed site revealed a 1,400-year-old bronze cauldron, found in a pool within the courtyard of the so-called “Mosaic House,” a significant Roman-era building complex.
The cauldron was unearthed in its original, undisturbed position and remains exceptionally well-preserved. After undergoing restoration and cleaning, the artifact is expected to be showcased at the Bergama Museum in the coming days, offering an unprecedented glimpse into the daily life and advanced craftsmanship of the era.
A Unique Glimpse into Roman and Byzantine Daily Life
The discovery was made near the Red Basilica (Kızıl Avlu), in an area referred to as the “Mosaic House” due to its richly decorated floors. According to Prof. Dr. Yusuf Sezgin, Head of Excavations and Chair of the Archaeology Department at Manisa Celal Bayar University, the building complex likely belonged to an influential Roman official or an important Christian cleric during the Byzantine period.
“The pool where the cauldron was found was not meant for swimming. It was likely used to collect rain or spring water for domestic purposes,” Prof. Dr. Sezgin explained. “The entire structure appears to have been abandoned in the 7th century AD, possibly due to Arab raids. Since then, it remained untouched, allowing us to discover this cauldron exactly where it was last used.”
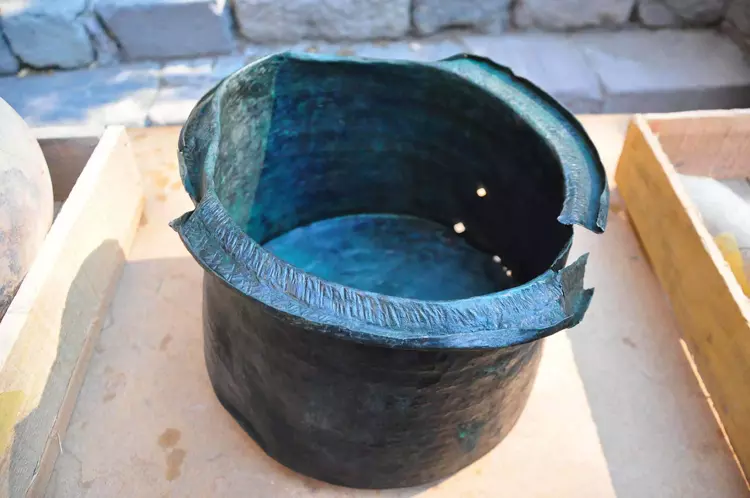

Bronze Craftsmanship Nearly Identical to Modern Techniques
Bronze was considered a valuable and expensive material in antiquity, typically reserved for special uses. Unlike the more common ceramic vessels of the time, this bronze cauldron is a rare find.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“What’s fascinating is the manufacturing technique,” Prof. Dr. Sezgin noted. “It was crafted using a hammering method, a technique still practiced today in places like Diyarbakır and Şanlıurfa. This find proves that traditional Anatolian bronze craftsmanship has remained nearly unchanged for over a millennium.”
The cauldron may have been used to transport water from the pool to a nearby kitchen structure, supporting theories about domestic life and resource usage during the late Roman and early Byzantine periods.
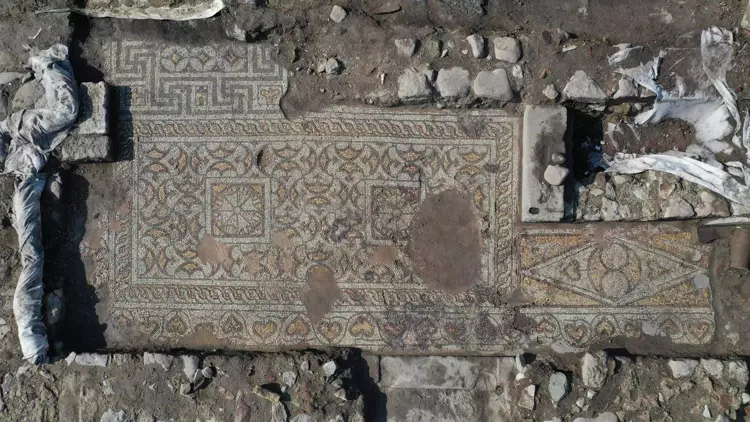

Scientific and Cultural Significance
Archaeologists emphasize the historical value of discovering the cauldron in situ. “The fact that it was found exactly in its original position, untouched for centuries, gives us direct insight into the cultural practices, technological capabilities, and daily routines of that era,” said Prof. Dr. Sezgin.
This find is part of broader excavations carried out under Turkey’s “Heritage for the Future” Project initiated by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism. The project aims to preserve and uncover the multi-layered cultural legacy of Pergamon, which includes remains from prehistoric, Hellenistic, Roman, Byzantine, Seljuk, and Ottoman periods.
Cover Image Credit: DHA