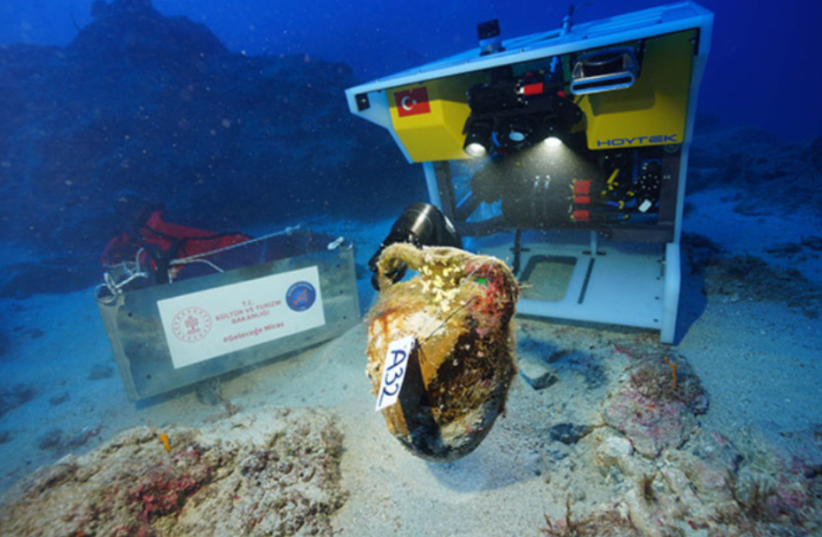
Underwater excavations near Kaş, Antalya, on Turkey’s southwestern coast, have yielded fascinating insights into ancient Mediterranean seafaring and trade. A team led by Associate Professor Dr. Hakan Öniz from Akdeniz University has been exploring a shipwreck dating back 1,100 years, during the Abbasid rule in the 9th-10th centuries. The discoveries highlight the crucial role of olives for sailors and have unearthed a rare sealed amphora, sparking excitement among archaeologists.
The excavation, part of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism’s “Legacy for the Future Project,” utilized advanced underwater robots to meticulously explore the wreck.
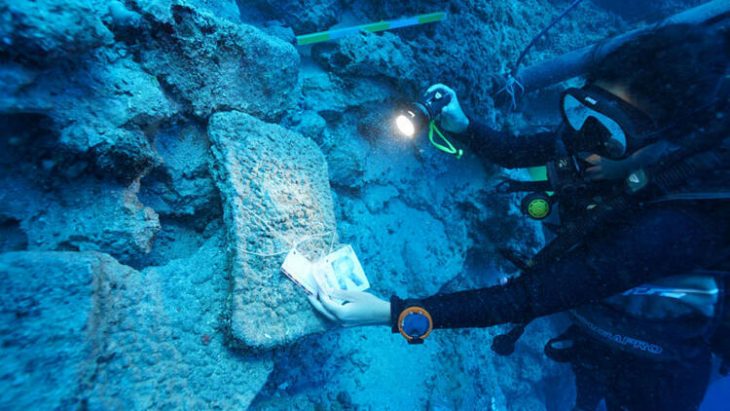
The shipwreck, located at a depth of 45-50 meters near Besmi Island, was found to be carrying a cargo of olive oil. According to historical accounts and the typology of amphorae discovered, the ship had set sail from the Gaza coast of Palestine before succumbing to a storm off the coast of Kaş. Dr. Öniz noted that while such amphorae are known in literature, this marks the first time they have been encountered in amphorae in Turkey.
Dr. Öniz explained that olives were an “indispensable food of sailors in the Mediterranean” for approximately 5,000 years, dating back to the Bronze Age. Their non-perishable nature made them ideal for long sea voyages. Submerged in seawater within amphorae, olives would become edible within a week and could last for months without spoiling, making them an essential provision alongside other staples like wheat and even live animals carried on board.
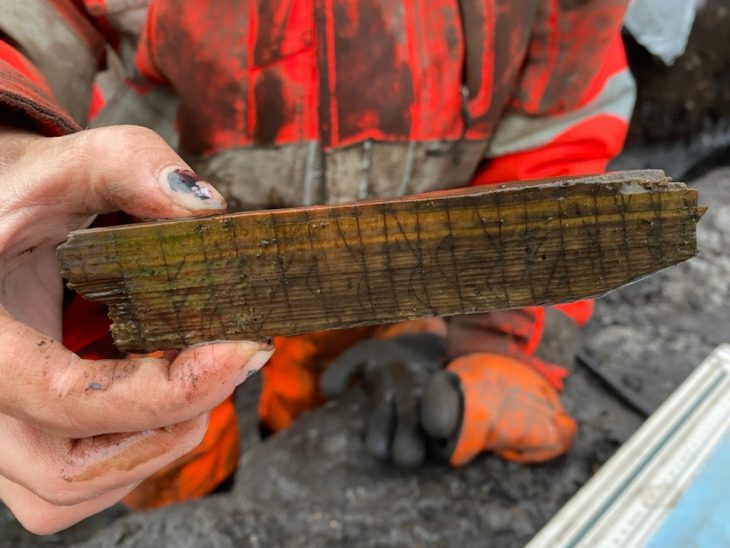
In a separate but related excavation at the same shipwreck site, the team also unearthed a remarkably well-preserved, sealed amphora. This discovery has generated considerable excitement as the contents of the sealed vessel remain unknown after a millennium underwater.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Following its careful retrieval from the seabed, the amphora underwent meticulous examination at Akdeniz University’s Underwater Archaeology Laboratory in Kemer. Experts painstakingly opened the seal, a process that took about an hour, and are now analyzing samples of the contents.
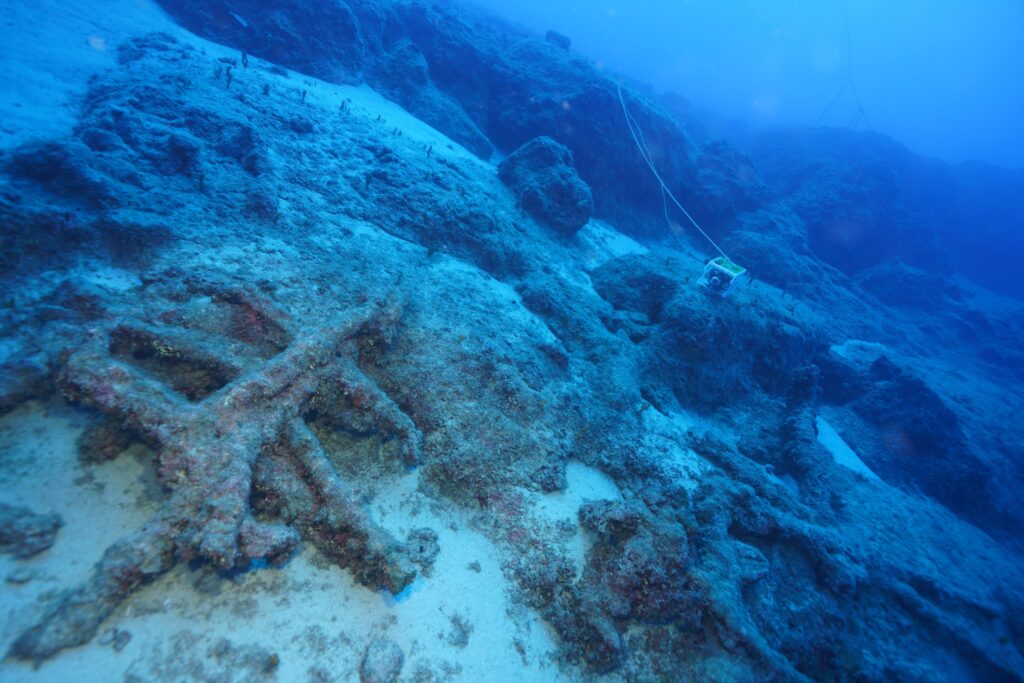

Dr. Öniz suggested that the trade ship likely visited multiple ports, carrying not only olive oil from Gaza, a key export of the time, but potentially also wine, possibly originating from the Tekirdağ Şarköy-Gaziköy region. He speculated that the wine might have been intended for immigrants, Christian pilgrims, or as gifts for visitors to Jerusalem, as local consumption in Palestine was unlikely.
The sealed nature of the amphora for over a thousand years makes this find particularly unique. Potential contents could range from olive pits, olive oil, or wine to even fish sauce or something entirely unexpected.
Professor Meltem Asiltürk Ersoy from Akdeniz University’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering emphasized the complexity of analyzing the contents after such a long period in the marine environment, noting that multiple analyses will be required to understand the transformations that may have occurred.
Restorer conservator Rabia Nur Akyüz detailed the careful process of handling the amphora, ensuring it remained continuously wet to preserve its fragile state.
As the excavation team continues their work, the findings are set to be displayed in the upcoming Mediterranean Underwater Archaeology Museum in Kemer, further enriching our understanding of ancient trade networks and culinary practices in the Mediterranean region. The discoveries not only highlight the significance of olives in maritime history but also open new avenues for research into the daily lives of sailors and traders in antiquity.
The analysis of the sealed amphora’s contents is eagerly awaited, promising further revelations about the cargo and trade practices of the era.
Cover Image Credit: Department of Cultural Heritage Conservation and Restoration at Akdeniz University