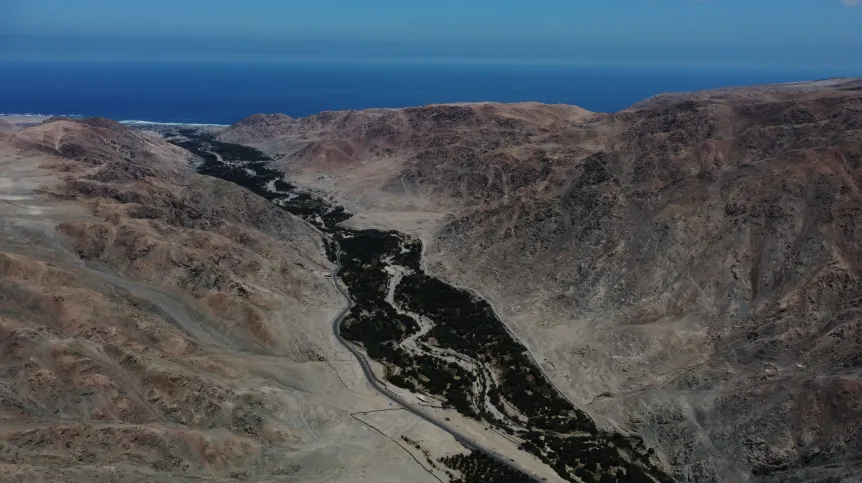
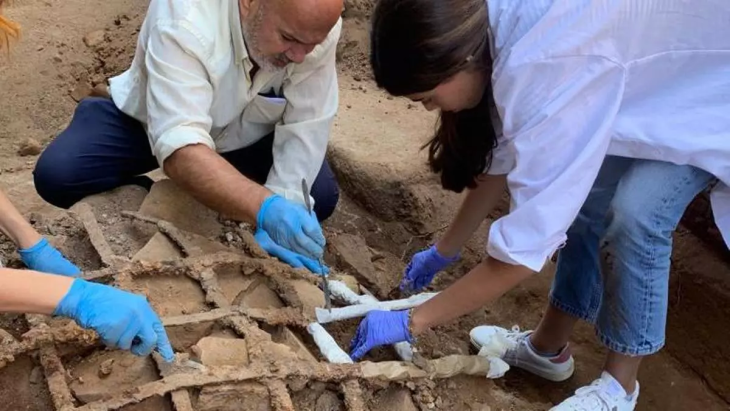
Archaeologists from the University of Wrocław have uncovered a 1,000-year-old mass grave at the El Curaca site in southern Peru, revealing the brutal deaths of mostly women and children during a violent raid. The victims show clear signs of trauma inflicted by star-shaped copper maces, shedding light on the violent conflicts that occurred in the region centuries ago.
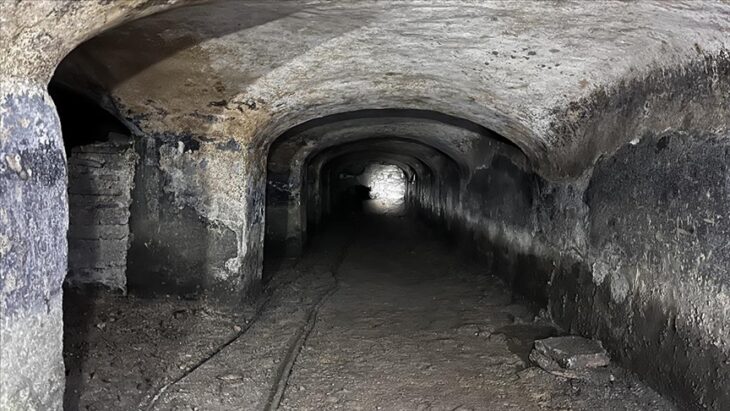
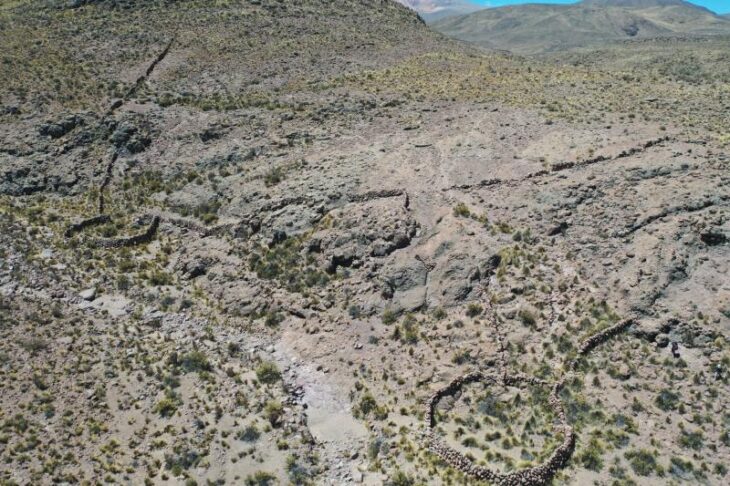
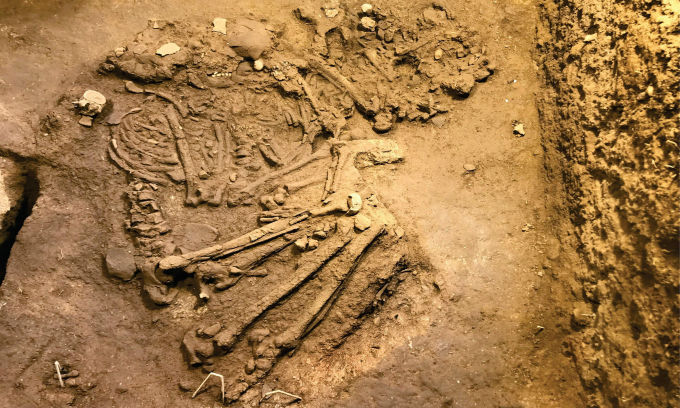
Located in the Atico River valley, El Curaca has been under systematic excavation since 2022. The burial site contains the remains of 24 individuals, carefully wrapped in shrouds and buried with grave goods, indicating that despite the violent circumstances, the community honored their dead with respect and ceremony.
“Every skull showed signs of severe trauma, likely caused by star-shaped copper mace heads or stone clubs,” said Professor Józef Szykulski, head of the excavation project and honorary professor at Universidad Católica de Santa María in Arequipa.
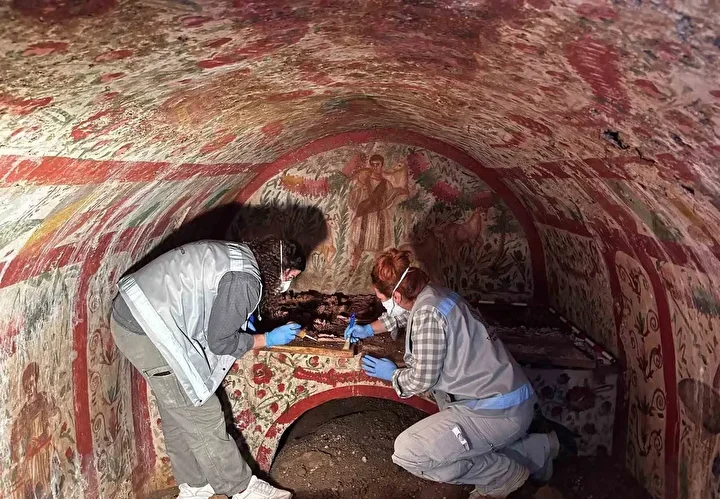
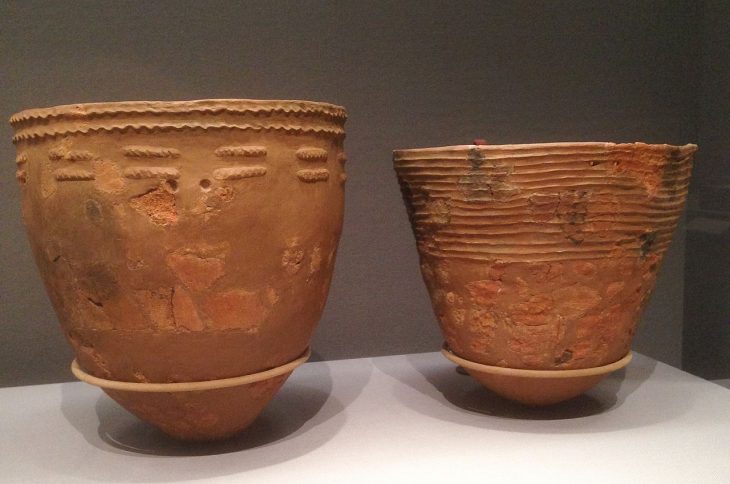
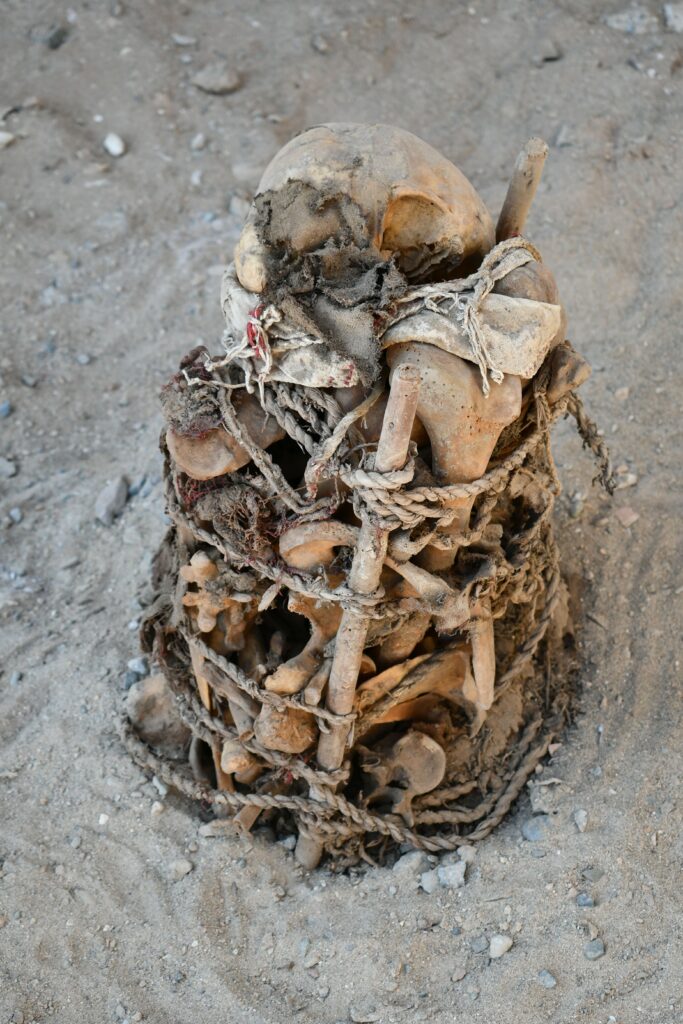
Despite the violent nature of their deaths, the victims were respectfully buried, wrapped in textile shrouds and surrounded by grave offerings including tools, ornaments, and pottery linked to the Chuquibamba (Aruni) culture, native to the Majes River basin south of Atico. The burial structures were even reinforced with stone walls, suggesting their community managed to repel the attackers and honored their dead with care.
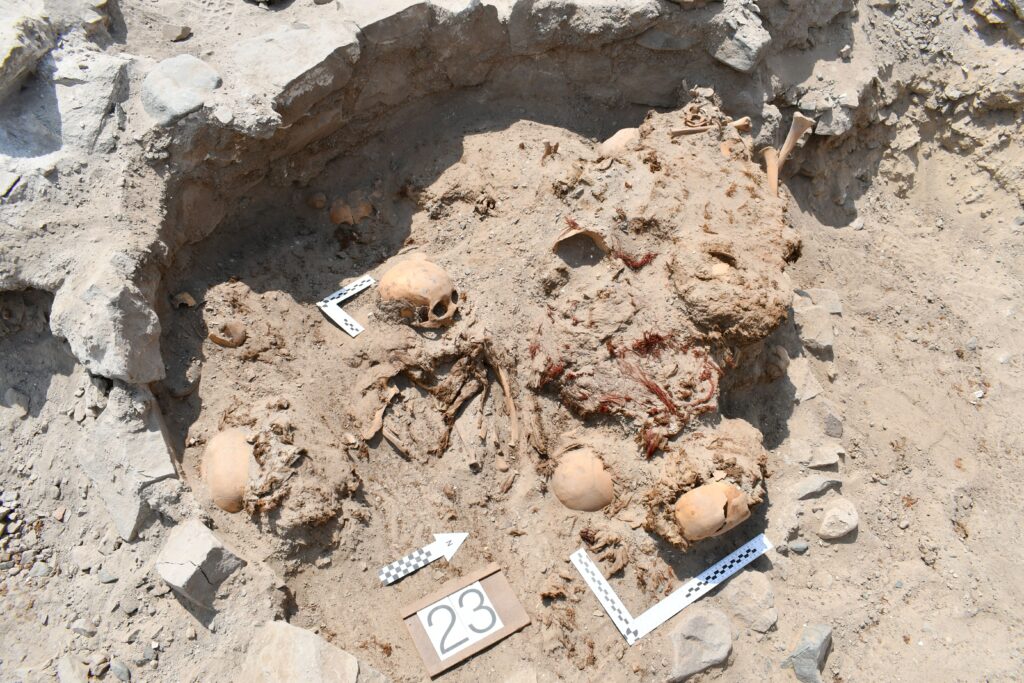

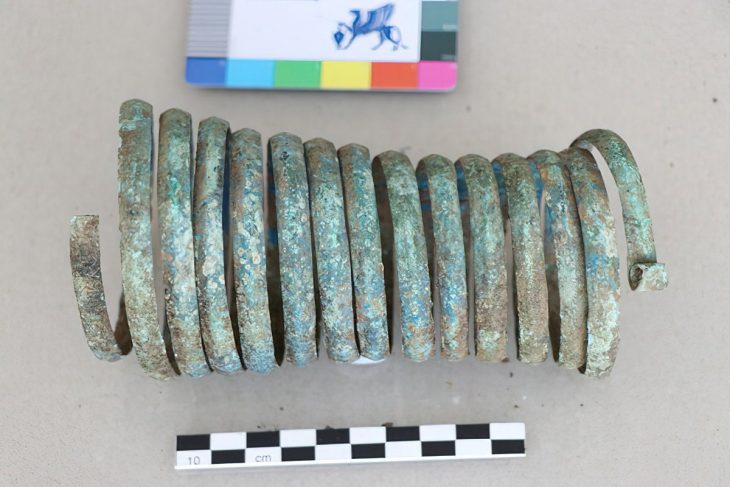
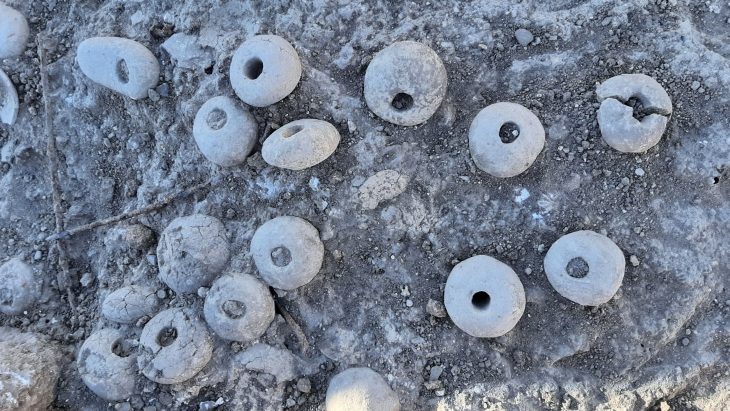
In addition to this dramatic mass grave, archaeologists also found a round stone-lined burial pit containing the remains of 29 women and children, buried over a span of 40 to 50 years. Radiocarbon dating places this collective grave in the 5th–6th centuries CE. Unlike the massacre victims, these individuals showed no signs of violent death. They were interred with intricately woven Nazca-style textiles, colorful thread spools, spindles, and ornamental pendants—some featuring human faces or entire figures carved from semi-precious stones.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The unusually high number of child burials at El Curaca has raised further questions. “In most pre-Columbian communities, child mortality was already high, but here the rate appears even more alarming,” noted Professor Szykulski. One theory suggests the culprit might be arsenic contamination from nearby copper and gold deposits. The toxic element, if introduced into local water sources, could have posed serious health risks. Ongoing lab analyses in Peru may soon confirm whether this environmental hazard played a role in the community’s tragic past.

The burial site and its grave goods are closely associated with the Chuquibamba (Aruni) culture, a little-known yet distinct pre-Columbian society that thrived in southern Peru between the 9th and 13th centuries CE. Centered in the Majes River basin, the Chuquibamba people developed a unique cultural identity, evident in their finely crafted ceramics, vibrant textiles, and stone-lined tombs. Though influenced by neighboring civilizations such as the Nasca, Wari, and Tiahuanaco, the Chuquibamba maintained their own artistic and architectural traditions. The discoveries at El Curaca expand the known reach of this culture toward the Pacific coast and shed light on their funerary practices, social structure, and violent encounters during a turbulent era in Andean history.
The El Curaca project is being carried out by the University of Wrocław in collaboration with Universidad Católica de Santa María, under the NCN’s OPUS21 grant.
Cover Image credit: General view of the El Curaca site in the Atico Valley. Credit: Prof. Józef Szykulski