Despite representing one of the most valuable portable cultural assets of Montenegro, the Pljevlja Diatreta is not accessible to visitors. The Local Museum in Pljevlja lacks the necessary special security measures and additional physical protection conditions to exhibit this world treasure.
This artifact, of inestimable value, is rarely even seen by the employees of that institution, which was founded by the Municipality of Pljevlja.
The Director of the Local Museum, Dejana Drobnjak, says that the current space in the Cultural Center in Pljevlja is not adequate to permanently display this valuable exhibit.
She says that it would only be possible with the Local Museum having its own building where the physical and technical protection arrangements could be implemented.
“For the display of exhibits of particular importance, such as the Pljeval diatretum, which represents the pinnacle of the glassmaking art of ancient Rome, special safety pedestals and additional physical protection conditions should be provided,” said Director Drobnjak.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Director Drobnjak also stated that the museum’s security and technical protection will be done out in accordance with the laws and regulations governing this area until the end of the year.
She says that diatretum is currently stored under special conditions.
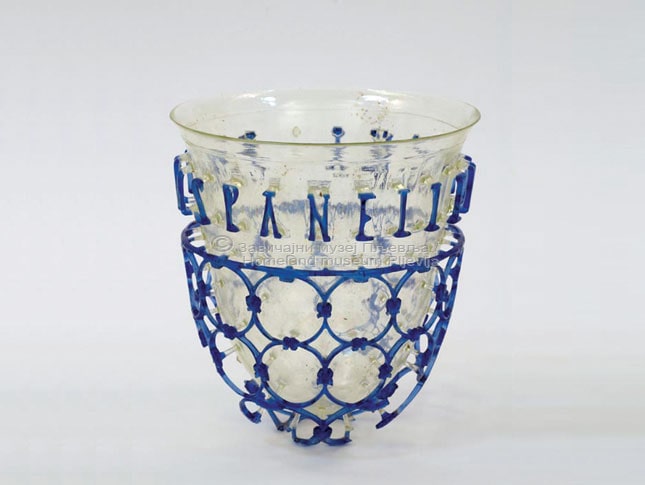

The cage cup or Diatretum
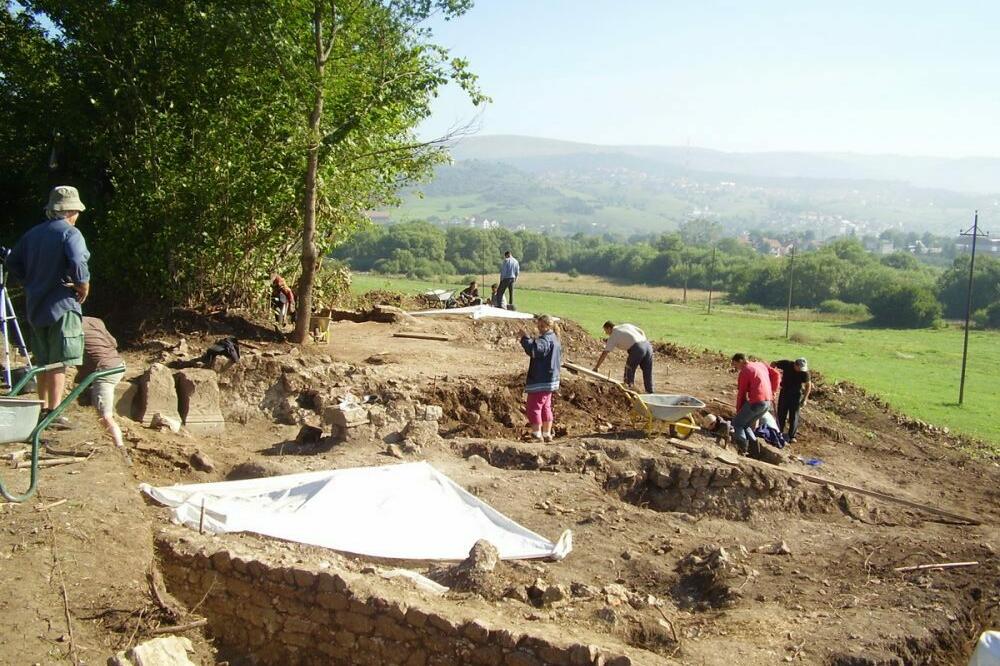
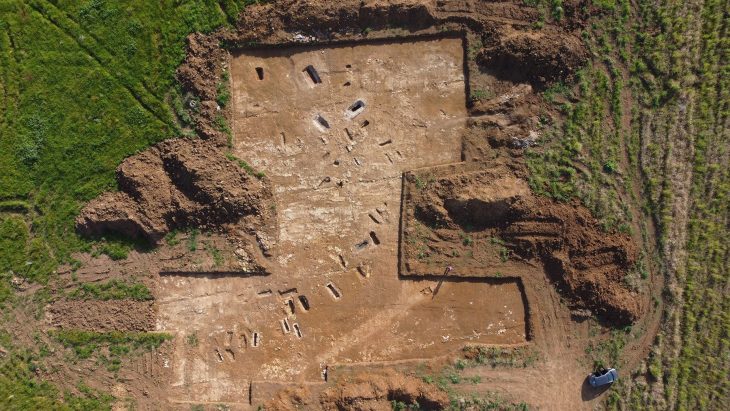
The Pljevlja cage cup (also called vas diatretum, plural diatreta, or reticulated cup) was found in 1975 at Komini/Komine near the city of Pljevlja in Montenegro. A cage cup is a type of luxury late Roman glass vessel. The cup is also a very rare example of a complete Roman cage cup or diatretum.
The Pljevlja cage cup originates from the 4th century AD. It has a clear body and blue cage, and the inscription VIVAS PAN[H]ELLENI BONA M[emoria] (“Live, Panhellenius, in good [memory]”) is found around the rim. It is in the Heritage Museum Pljevlja.
The height of the diatretum is 14.9 cm, the diameter of the opening is 13.3 cm and the base is 3.7 cm. It was made in one of the famous Cologne workshops.
It is characteristic of the stage of the late Roman Empire and is a reflection of the peak of the development of glassmaking skills in antiquity, when the decoration rises from the surface and encompasses the entire vessel, like a mesh basket.
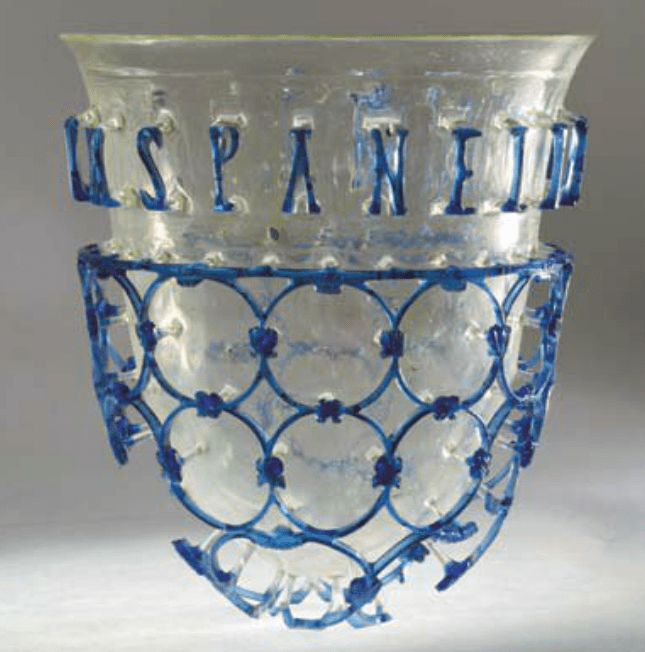

Diatretum was used on festive occasions. She was like the queen of the evening at the table of a powerful lord or the emperor himself, made to show beauty, to testify to opulence. Apart from its primary, practical purpose, this expensive goblet was also a reflection of belonging to a certain class. Its aesthetic dimension is also very important because it reflects the lifestyle, taste, and fashion of an era. And then, after many feasts at which it was presented, the diatretum was buried together with its owner.
About fifty cups or, more often, fragments have survived, and there are only a few in near-complete condition. Pljevlja diatretum is one of these unique near-complete cups. Most have a cage with circular geometrical patterns, often with an “inscription”, or phrase in letters above the reticulated area as well. Some have a flange, or zone of projecting open-cut molding, above the lower patterns and below the lettering.
Pljevlja cage cup has never been restored and has its original, nearly two-millennium-old paint.
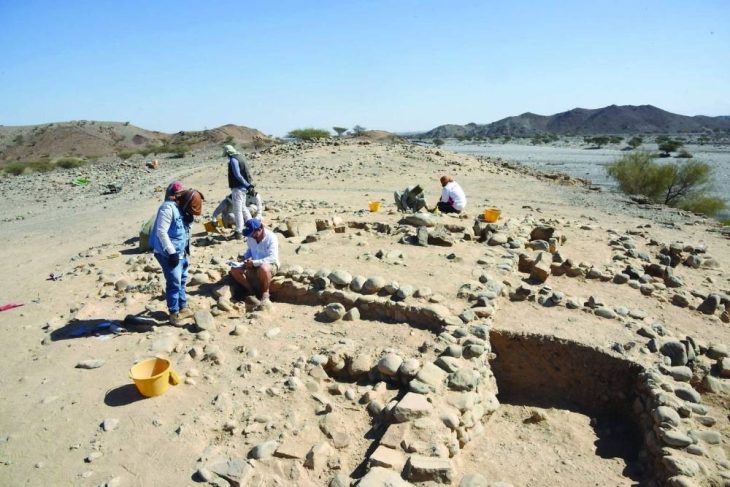
Cover Photo: The site where diatreta was found in 1975. Photo: Goran Malidžan
The Vijesti news was translated using Google Translate.